-
Dalingshan Industrial Guangdong
Dominar el control de temperatura de la fermentación cervecera para lograr el éxito en la elaboración de cerveza
Dominando el control de temperatura de la fermentación en cervecerías
En el mundo de la elaboración de cerveza, lograr la cerveza perfecta depende de un control preciso de la temperatura. La fermentación es un proceso crucial para la calidad de la cerveza. La cerveza se puede elaborar en casa usando un fermentador cónico para una mejor fermentación. Ya sea que sea un cervecero experimentado o un cervecero casero apasionado, mantener la temperatura óptima es crucial para una calidad y un sabor consistentes en su cerveza o vino. Este artículo profundiza en las complejidades del control de la temperatura de fermentación, explorando varios métodos, desde controladores de temperatura digitales básicos hasta glicol avanzado. Un enfriador puede ayudar a mantener una temperatura de fermentación controlada para sus cervezas y ofrece información sobre cómo elegir el sistema adecuado para su configuración de elaboración. Con el equipo de control de temperatura adecuado, puede controlar con confianza su temperatura de fermentación y elevar su cerveza al siguiente nivel.
Índice
- ¿Por qué es tan importante el control de la temperatura de fermentación?
- Control básico de temperatura: uso de un controlador de temperatura digital
- Control avanzado de temperatura: el poder de los enfriadores de glicol
- Cómo elegir el controlador de temperatura adecuado para sus necesidades
- Comprensión de los controladores de temperatura de dos etapas
- Cámaras de fermentación: creando el ambiente ideal
- Monitoreo de la temperatura de fermentación: herramientas y técnicas
- Optimización del control de temperatura para diferentes estilos de cerveza
- Solución de problemas de temperatura de fermentación
- El futuro del control de la temperatura de fermentación
¿Por qué es tan importante el control de la temperatura en la cervecería de fermentación?
Temperatura de fermentación. La levadura juega un papel fundamental en la formación del carácter de la cerveza. La levadura, el microorganismo responsable de la fermentación, es muy sensible a las fluctuaciones de temperatura. Mantener la temperatura correcta durante todo el proceso de fermentación es esencial por varias razones:
- Perfil de sabor: La levadura produce diferentes compuestos aromáticos a distintas temperaturas. Algunas cepas de levadura producen ésteres frutales deseables a temperaturas más altas, mientras que otras crean sabores más limpios y vibrantes a temperaturas más bajas. Desviarse del rango óptimo de temperatura puede resultar en sabores desagradables, como ésteres indeseados, alcoholes fusel (con un sabor áspero y similar al del disolvente) o un exceso de compuestos de azufre.
- Tasa de fermentación: La actividad de la levadura se ve directamente influenciada por la temperatura, por lo que es esencial mantener una temperatura de fermentación controlada. Las temperaturas más altas aceleran la fermentación, mientras que las más bajas la ralentizan. Mantener una temperatura constante garantiza una fermentación predecible y controlada, evitando paradas o descontroles de fermentación.
- Atenuación: La atenuación se refiere al grado en que la levadura convierte los azúcares en alcohol y dióxido de carbono. La temperatura de fermentación afecta la atenuación, lo que influye en el contenido alcohólico final y el cuerpo de la cerveza.
- Salud de la levadura: Las temperaturas extremas pueden estresar o incluso matar la levadura, lo que provoca una fermentación incompleta o sabores indeseables.
Control básico de temperatura: uso de un controlador de temperatura digital
Para muchos cerveceros caseros, un controlador de temperatura digital ofrece una forma sencilla y eficaz de controlar la temperatura de fermentación. Estos dispositivos funcionan activando y desactivando cíclicamente un elemento calefactor o refrigerante para mantener una temperatura establecida. Si necesita regular con precisión la temperatura de fermentación de su cerveza, un controlador de temperatura digital ofrece una solución asequible y accesible.
Así es como suelen funcionar:
- Sonda de temperatura: Se coloca una sonda de temperatura dentro de la cámara de fermentación, lo cual es esencial para mantener la fermentación a la temperatura adecuada. La sonda monitorea la temperatura real.
- Unidad controladora: La sonda se conecta a una unidad controladora, que muestra la temperatura actual y le permite establecer la temperatura deseada.
- Elemento de calefacción/refrigeración: El controlador está conectado a un elemento calefactor (como una almohadilla térmica o un cinturón) y/o a un elemento de enfriamiento (como un refrigerador o congelador).
- Sistema de relé: El controlador utiliza un sistema de relé para encender o apagar el elemento de calefacción o refrigeración según la diferencia entre la temperatura real y la temperatura configurada.
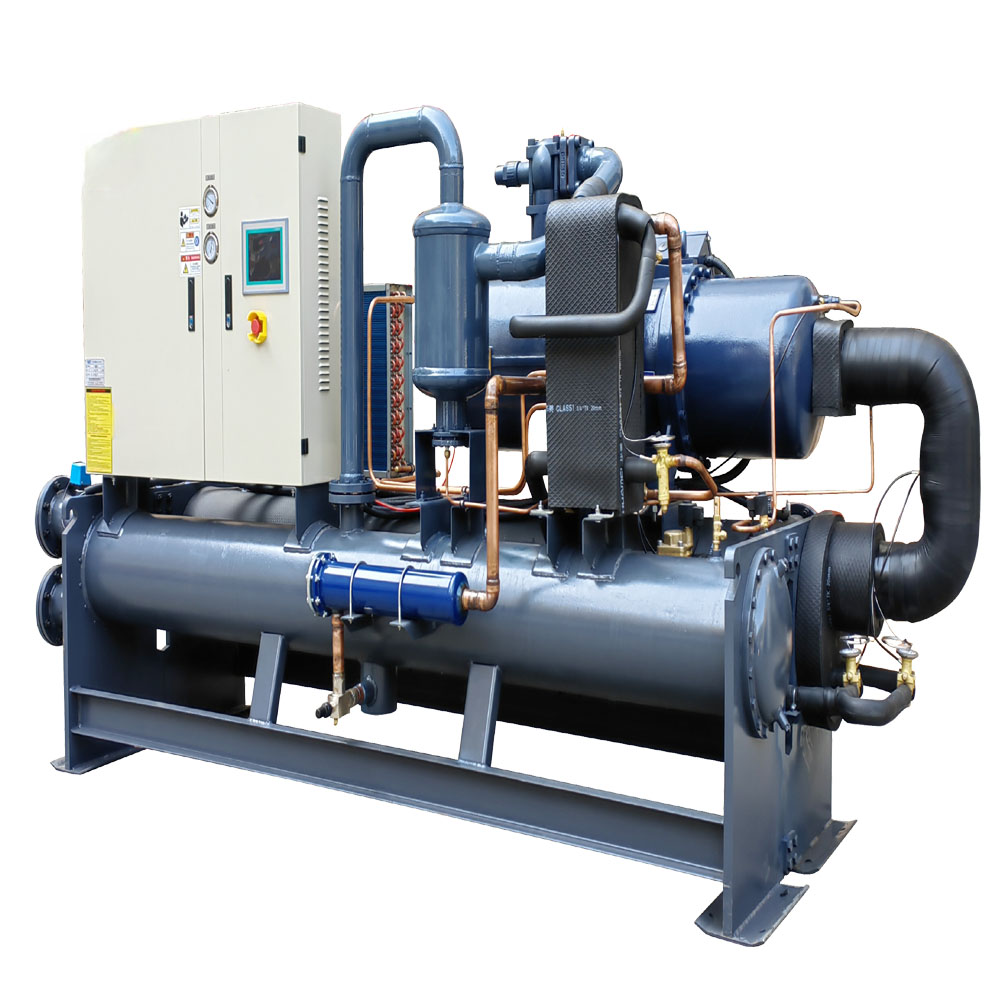
Los controladores de temperatura digitales proporcionan una mejora significativa respecto a los métodos manuales, permitiendo a los cerveceros caseros mantener una temperatura de fermentación más constante. Enfriador de agua de tornillo refrigerado por agua ofrece opciones para necesidades de refrigeración más robustas.
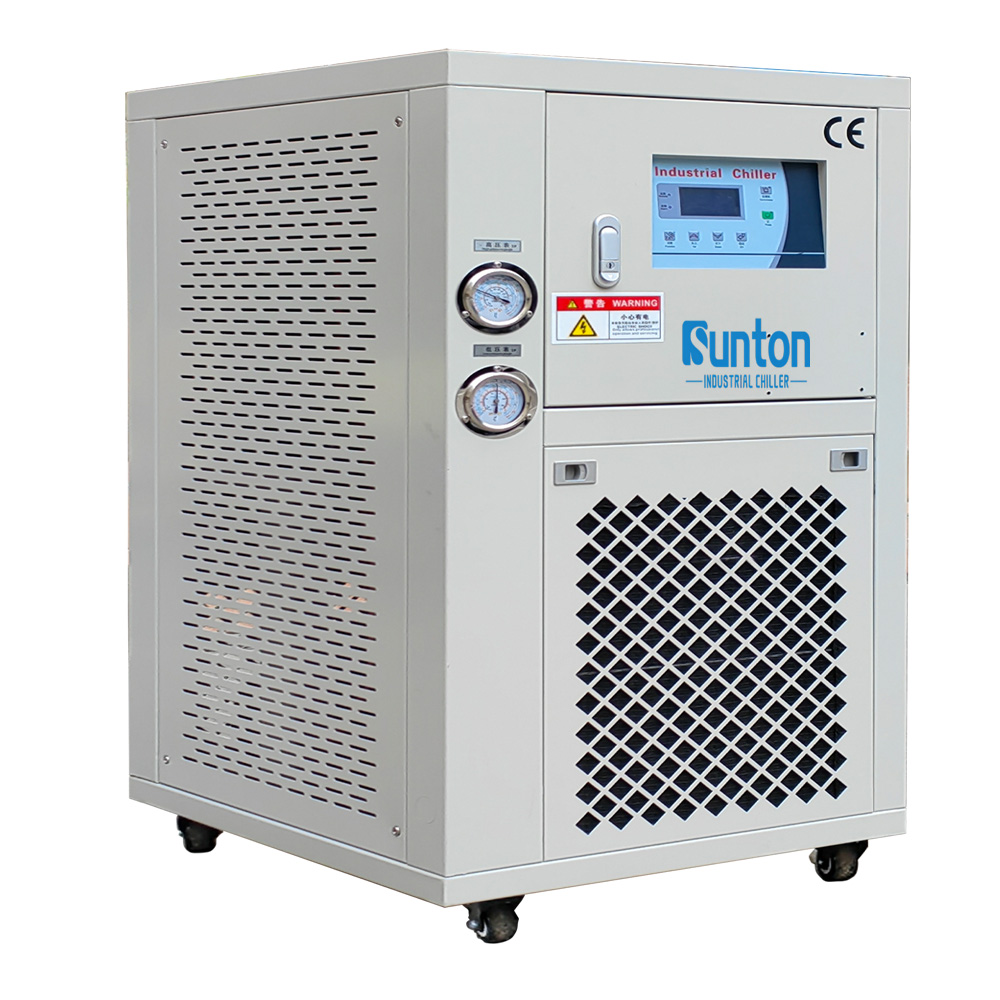
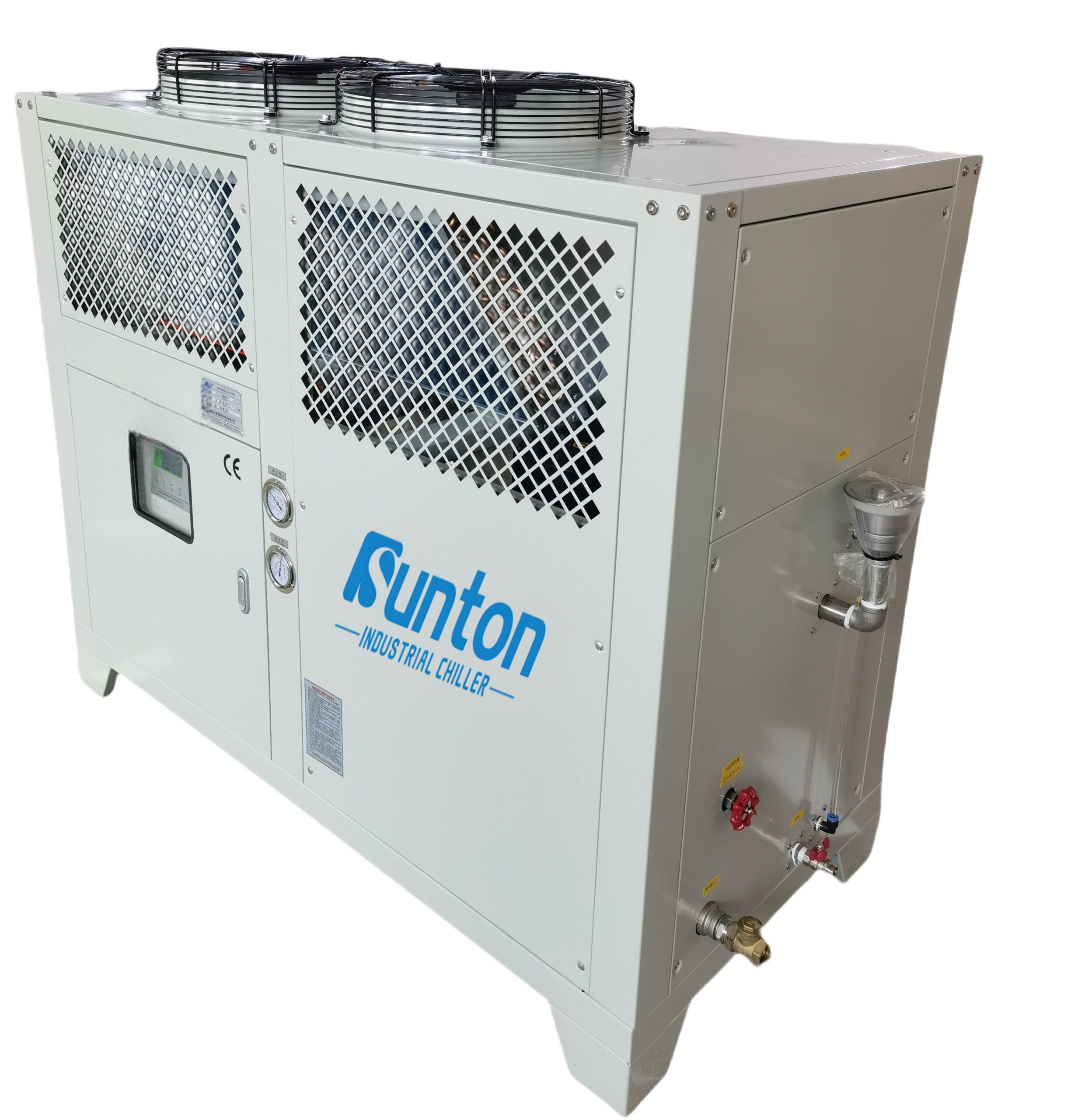
Control avanzado de temperatura: el poder de los enfriadores de glicol
Para cerveceros más avanzados, especialmente aquellos que operan a mayor escala o buscan el máximo control de temperatura, los enfriadores de glicol ofrecen una solución superior. Un enfriador de glicol es un sistema de refrigeración que utiliza una solución anticongelante de grado alimenticio, generalmente propilenglicol, para enfriar el fermentador. Consulte nuestros Enfriadoras de glicol para una variedad de opciones.
Esta es la razón por la que los enfriadores de glicol son los preferidos por muchos cerveceros caseros profesionales y serios:
- Control preciso de temperatura: Los enfriadores de glicol pueden mantener temperaturas muy precisas, a menudo con una precisión de fracciones de grado, lo que garantiza condiciones óptimas de fermentación. Esto es especialmente importante para estilos como las lagers, que requieren temperaturas de fermentación muy específicas y constantes.
- Enfriamiento rápido: Los enfriadores de glicol pueden enfriar rápidamente el mosto después de la ebullición o ajustar la temperatura de fermentación si es necesario.
- Flexibilidad: Se pueden utilizar para enfriar fermentadores a diferentes temperaturas simultáneamente, lo que los hace ideales para cervecerías con diversos programas de producción. El glicol puede enfriar la cerveza casi hasta el punto de congelación.
- Capacidad de calentamiento: Algunos enfriadores de glicol también se pueden utilizar para calentar, proporcionando un control completo de la temperatura durante todo el proceso de elaboración de la cerveza.
Cómo elegir el controlador de temperatura adecuado para sus necesidades
La elección entre un controlador de temperatura digital y un enfriador de glicol depende de varios factores:
- Escala de operación: Para la elaboración casera de cerveza en lotes pequeños, un controlador de temperatura digital puede ser suficiente. Para lotes más grandes o para operaciones comerciales, suele ser necesario un enfriador de glicol.
- Presupuesto: Los controladores de temperatura digitales son generalmente más asequibles que los enfriadores de glicol.
- Nivel de control: Si necesita un control de temperatura muy preciso, especialmente para estilos como las cervezas, un enfriador de glicol es la mejor opción.
- Espacio: Los enfriadores de glicol requieren más espacio que los controladores de temperatura digitales.
- Versatilidad: Si necesita enfriar varios fermentadores a diferentes temperaturas o requiere capacidades tanto de calentamiento como de enfriamiento, un enfriador de glicol ofrece mayor versatilidad. Para operaciones más grandes, considere un Enfriadoras centrales de tornillo refrigeradas por agua.
Comprensión de los controladores de temperatura de dos etapas
Un controlador de temperatura de dos etapas es un tipo de controlador digital de temperatura más avanzado que puede controlar simultáneamente un elemento calefactor y uno refrigerante. Esto permite una mayor precisión al mantener la temperatura deseada. Tanto para cerveceros caseros como profesionales, esta es una excelente manera de controlar la temperatura de su café.
Así es como funciona:
- Dos relés: Un controlador de dos etapas tiene dos relés, uno para el elemento de calentamiento y otro para el elemento de enfriamiento.
- Punto de ajuste y diferencial: Se establece la temperatura deseada (punto de consigna) y un diferencial. El diferencial es la variación de temperatura admisible por encima y por debajo del punto de consigna antes de que se active el elemento de calefacción o refrigeración.
- Cambio automático: El controlador cambia automáticamente entre los modos de calefacción y refrigeración según sea necesario para mantener la temperatura dentro del diferencial establecido.
Los controladores de temperatura de dos etapas son especialmente útiles para mantener temperaturas de fermentación estables en entornos con temperaturas ambiente fluctuantes. Para operaciones de mayor envergadura, recomendamos explorar nuestra Enfriador de agua Scroll refrigerado por agua.
Cámaras de fermentación: creando el ambiente ideal
Una cámara de fermentación es un recinto aislado que alberga el fermentador. Un fermentador cónico ayuda a mantener la fermentación limpia y proporciona un ambiente estable para la levadura. Las cámaras de fermentación pueden variar desde simples cajas aisladas hasta refrigeradores o congeladores modificados. Los cerveceros caseros suelen usar refrigeradores o congeladores modificados como cámaras de fermentación. Al usar un refrigerador o congelador, se necesita un controlador de temperatura para anular el termostato interno del aparato y mantener la temperatura de fermentación deseada.
Estos son los beneficios de utilizar una cámara de fermentación:
- Estabilidad de temperatura: Una cámara de fermentación bien aislada ayuda a proteger la bebida en fermentación de las fluctuaciones de la temperatura ambiente.
- Control de luz: Las cámaras de fermentación pueden bloquear la luz, lo que puede afectar negativamente el sabor de la cerveza.
- Control de la contaminación: Una cámara de fermentación sellada ayuda a prevenir la contaminación por microorganismos transportados por el aire.
- Control de olores: Si está fermentando en interiores, una cámara de fermentación puede ayudar a contener cualquier olor fuerte producido durante la fermentación.
Monitoreo de la temperatura de fermentación: herramientas y técnicas
El control preciso de la temperatura de fermentación es crucial para garantizar resultados óptimos. A continuación, se presentan algunas herramientas y técnicas comunes:
- Termómetro: Una forma sencilla y económica de leer la temperatura es con un termómetro. Existen varios tipos, como termómetros de tiras adhesivas, termómetros flotantes y termómetros digitales con sonda.
- Pantalla del controlador de temperatura: La mayoría de los controladores de temperatura digitales muestran la temperatura actual, lo que proporciona una forma conveniente de monitorear la fermentación.
- Registradores de datos: Para un monitoreo más avanzado, los registradores de datos pueden registrar lecturas de temperatura a intervalos regulares, lo que permite monitorear las fluctuaciones de temperatura a lo largo del tiempo. Algunas cafeteras avanzadas utilizan un panel de control para monitorear y controlar la temperatura.
Optimización del control de temperatura para diferentes estilos de cerveza
Los distintos estilos de cerveza tienen diferentes rangos óptimos de temperatura de fermentación. A continuación, se presentan algunas pautas generales:
- Cervezas: La mayoría de las cepas de levadura ale se desarrollan mejor entre 15 y 22 °C (60 y 72 °F). Algunas cepas, como las levaduras ale belgas, toleran temperaturas de fermentación más altas.
- Cervezas: Las cepas de levadura lager prefieren temperaturas más frías, normalmente entre 7 y 13 °C (45 y 55 °F).
- Estilos híbridos: Algunos estilos, como las cervezas comunes de California, se fermentan con levadura lager a temperaturas más cálidas.
Es esencial investigar la cepa de levadura específica que estás utilizando y seguir el rango de temperatura de fermentación recomendado para esa cepa.
Solución de problemas de temperatura de fermentación
Incluso con el mejor equipo, puede experimentar problemas de temperatura de fermentación. Aquí tiene algunos problemas comunes y soluciones en la fermentación casera:
- Fermentación estancada: Si la fermentación se detiene prematuramente, podría deberse a una temperatura demasiado baja. Intente calentar suavemente el fermentador a la temperatura adecuada.
- Fermentación descontrolada: Si la fermentación es demasiado intensa, podría deberse a una temperatura demasiado alta. Intente enfriar el fermentador al rango adecuado. Si tiene problemas para mantener una temperatura de fermentación estable, un enfriador de glicol podría ser útil.
- Sabores extraños: Los sabores extraños pueden deberse a diversos factores, como una temperatura de fermentación inadecuada. Si sospecha que la temperatura es la causa, revise sus métodos de control de temperatura y realice los ajustes necesarios.
El futuro del control de la temperatura de fermentación
El campo del control de la temperatura de fermentación está en constante evolución. A continuación, se presentan algunas tendencias a tener en cuenta:
- Controladores inteligentes: Espere ver controladores de temperatura más sofisticados con conectividad Wi-Fi, lo que permite el monitoreo y control remoto a través de teléfonos inteligentes u otros dispositivos.
- Integración con el software de elaboración de cerveza: Los sistemas de control de temperatura pueden integrarse cada vez más con el software de elaboración de cerveza, lo que permite ajustes automatizados de temperatura basados en parámetros de recetas y datos en tiempo real.
- Tecnologías de refrigeración avanzadas: Las innovaciones en tecnologías de enfriamiento, como el enfriamiento termoeléctrico, pueden ofrecer nuevas posibilidades para un control preciso y energéticamente eficiente de la temperatura de fermentación.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cuál es la temperatura ideal de fermentación para la mayoría de las cervezas?
La mayoría de las cepas de levadura ale funcionan mejor entre 15 y 22 °C (60 y 72 °F). Sin embargo, es fundamental consultar las recomendaciones específicas para la cepa de levadura que se esté utilizando.
¿Cómo puedo enfriar mi fermentador si se calienta demasiado?
Puedes intentar mover el fermentador a un lugar más fresco, colocarlo en un baño de agua o usar un elemento de enfriamiento como una botella de agua congelada o un enfriador de glicol.
¿Puedo utilizar un refrigerador normal para controlar la temperatura de fermentación?
¿Puedo utilizar un refrigerador normal para controlar la temperatura de fermentación? Sí, se puede utilizar un refrigerador normal como cámara de fermentación, pero necesitará un controlador de temperatura para anular el termostato interno del refrigerador y mantener la temperatura adecuada.
¿Cuáles son los beneficios de utilizar un controlador de temperatura de dos etapas?
Un controlador de temperatura de dos etapas puede controlar tanto un elemento de calefacción como uno de refrigeración, lo que permite un control de temperatura más preciso y un cambio automático entre los modos de calefacción y refrigeración.
¿Cómo funcionan los enfriadores de glicol?
Los enfriadores de glicol utilizan un sistema de refrigeración para enfriar una mezcla de agua y glicol, que luego circula a través de un intercambiador de calor o una camisa alrededor del fermentador para mantener la temperatura deseada.
¿Necesito un enfriador de glicol para elaborar cerveza casera?
Si bien no es estrictamente necesario para todos los cerveceros caseros, un enfriador de glicol ofrece ventajas significativas para quienes buscan un control preciso de la temperatura, especialmente para cervezas lager o lotes grandes.
Conclusión
- La temperatura es clave: Mantener la temperatura de fermentación correcta es esencial para producir cerveza de alta calidad.
- Elija las herramientas adecuadas: Seleccione un sistema de control de temperatura que se ajuste a sus necesidades y presupuesto, ya sea un simple controlador de temperatura digital o un enfriador de glicol avanzado. Si necesita un enfriador, explore nuestra Enfriador de tornillo refrigerado por aire opciones.
- Monitorear y ajustar: Controle periódicamente la temperatura de fermentación y realice los ajustes necesarios para mantenerla dentro del rango óptimo.
- Consideremos una cámara de fermentación: Una cámara de fermentación puede ayudar a estabilizar las temperaturas y proteger su bebida de factores externos.
- Experimenta y aprende: No tengas miedo de experimentar con diferentes temperaturas de fermentación para ver cómo afectan el sabor de tu cerveza.
Al dominar el control de la temperatura de fermentación, podrá llevar su elaboración al siguiente nivel, produciendo una cerveza consistente, sabrosa y de alta calidad que estará orgulloso de compartir. Para todas sus necesidades de refrigeración cervecera, considere a los expertos. ¡Contáctenos hoy mismo!