-
Dalingshan Industrial Guangdong

6 advantages of packaged air-cooled chillers
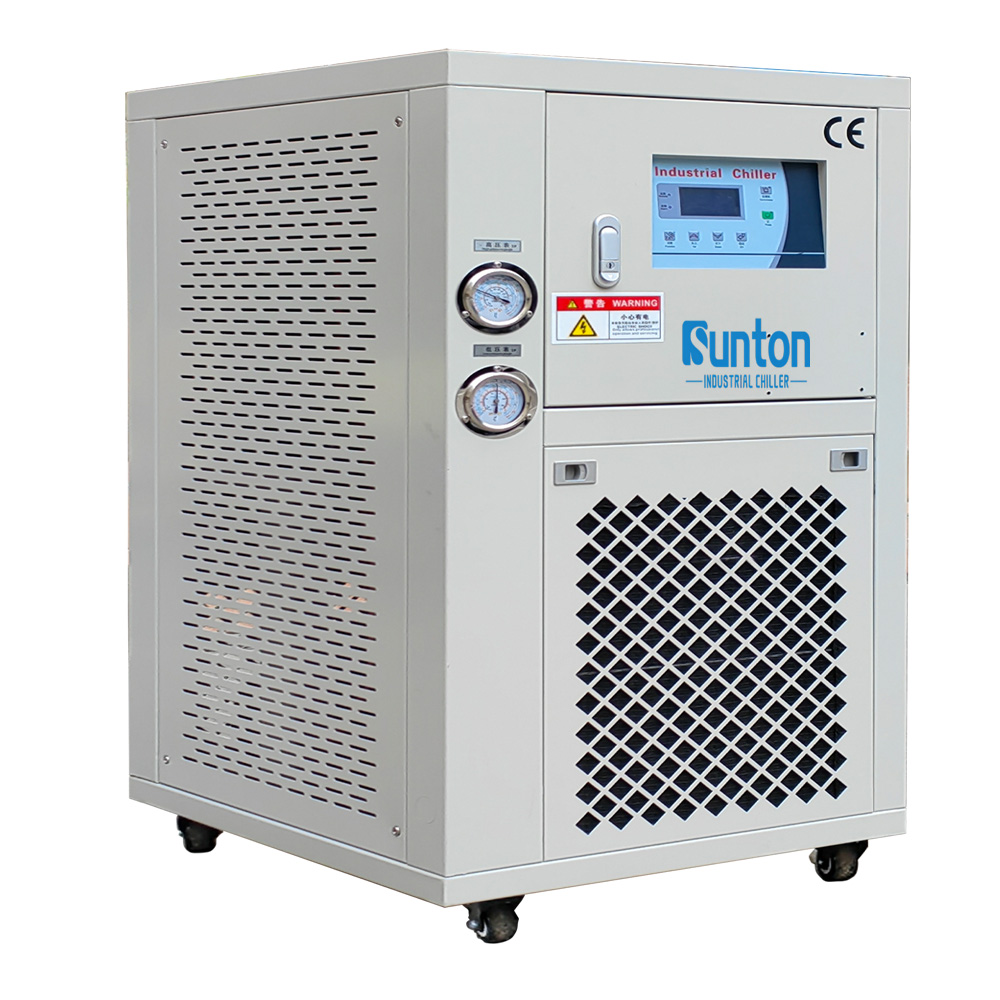
Packaged Air-Cooled Chiller: The Ultimate Cooling Solution for Industrial Applications
As an industrial water chiller manufacturing plant, we understand the critical role that efficient and reliable cooling systems play across a wide range of industries. This article delves into the world of packaged air-cooled chillers, exploring their numerous advantages, diverse applications, and why they are the preferred choice for businesses in the plastics and rubber, machining, food and beverage, chemical and pharmaceutical, electronics, laser, printing, medical, laboratories and research, and data center sectors. Whether you’re looking to optimize your production processes, reduce operating costs, or enhance product quality, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into how packaged air-cooled chillers can meet your specific needs.
Table of Contents
1. What is a Packaged Air-Cooled Chiller and How Does It Work?
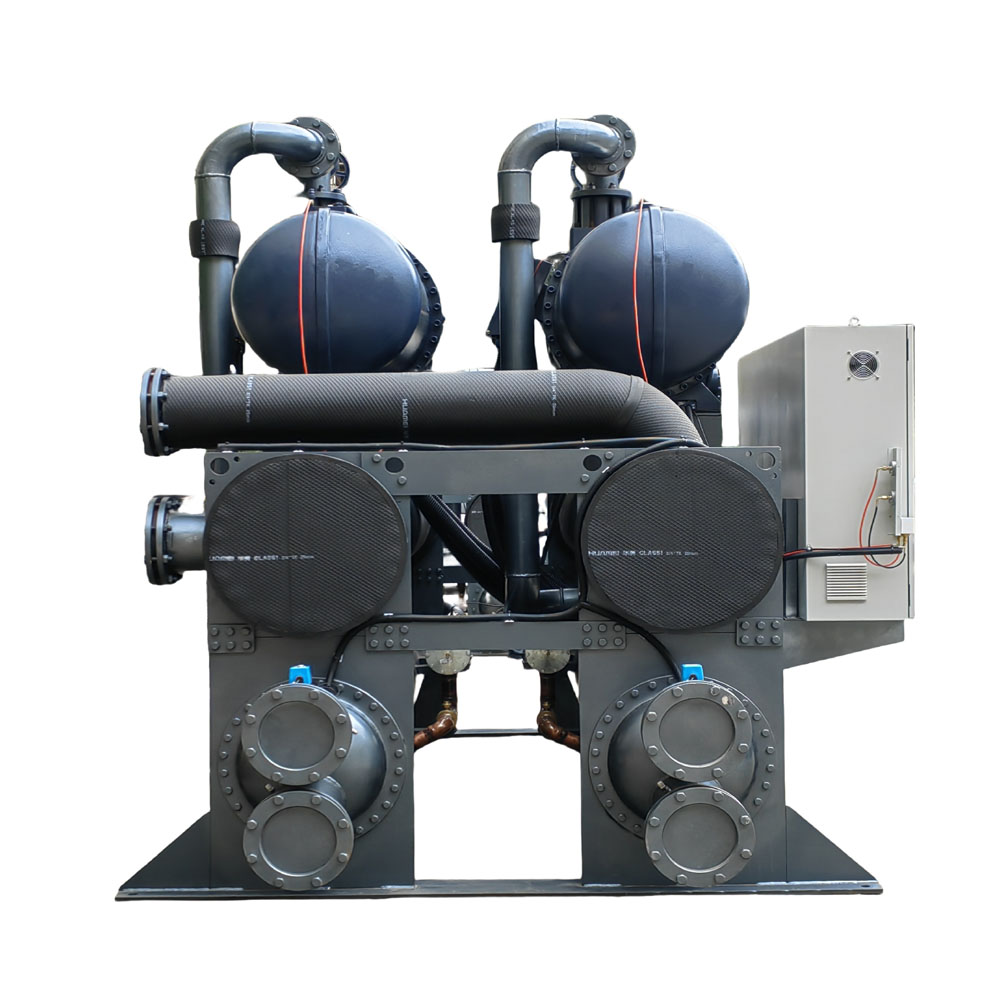
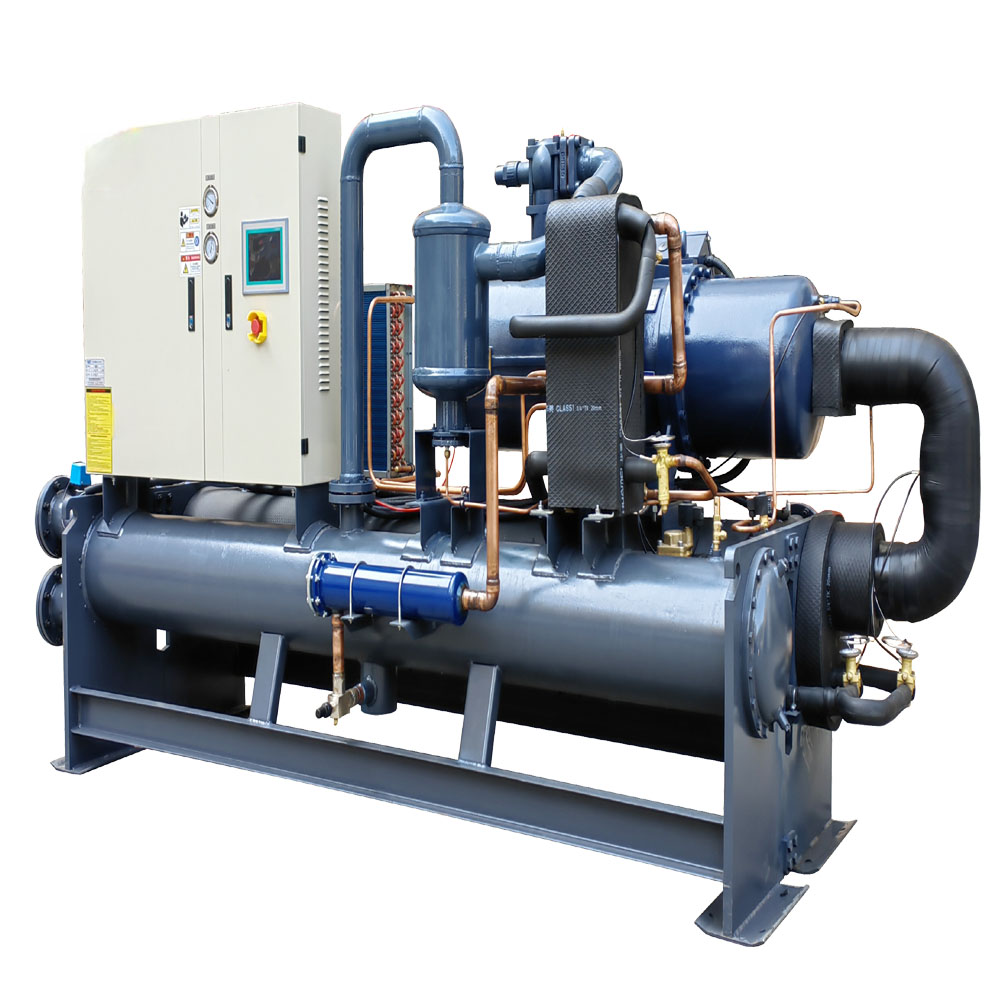
A packaged air-cooled chiller is a type of industrial cooling system that removes heat from a liquid via a vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycle. Unlike water-cooled chillers, which require a separate cooling tower and water supply, air-cooled chillers use ambient air to cool the refrigerant in the condenser. Packaged air-cooled chillers include all the necessary components, such as the compressor, condenser, evaporator, pump, and controls, integrated into a single unit.
Air-cooled chillers work by circulating a refrigerant through a closed-loop system. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the process fluid in the evaporator, causing it to evaporate. The vaporized refrigerant then enters the compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature. Next, the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant flows to the condenser, where ambient air is blown across the condenser coils, causing the refrigerant to condense back into a liquid, releasing the absorbed heat into the atmosphere. Finally, the liquid refrigerant passes through an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature, and returns to the evaporator to repeat the cycle.
| Component | Function |
| Compressor | Increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant vapor |
| Condenser | Cools the refrigerant vapor, causing it to condense into a liquid and releasing heat to the ambient air |
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat from the process fluid, causing the refrigerant to evaporate |
| Expansion Valve | Reduces the pressure and temperature of the liquid refrigerant before it enters the evaporator |
| Pump | Circulates the process fluid through the evaporator |
| Controls | Monitor and regulate the operation of the chiller to maintain the desired temperature and optimize performance |
2. What Are the Main Advantages of Using Air-Cooled Chillers?
Air-cooled chillers offer several advantages over traditional water-cooled systems, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. One of the main advantages is their simplicity and ease of installation. Since chillers do not require a cooling tower or a separate water system, they can be installed quickly and easily, reducing installation time and costs. Additionally, air-cooled systems require less maintenance than water-cooled systems, as they do not have the same issues with water quality, scaling, and corrosion.
Another significant advantage of air-cooled chillers is their ability to operate in areas with limited water resources. As they do not use water to cool the refrigerant, they are an excellent option for facilities located in water-scarce regions or those looking to reduce their water consumption for environmental or cost reasons. Furthermore, air-cooled chillers eliminate the need for water treatment chemicals, further reducing operating costs and environmental impact.
Here are some advantages of using air-cooled chillers:
- Easy installation, saving on time and labor costs.
- Lower maintenance requirements compared to water-cooled systems.
- Suitable for areas with limited water resources.
- No need for water treatment chemicals.
- Lower operating costs.
3. How Efficient Are Air-Cooled Chillers Compared to Water-Cooled Chillers?
Efficiency is a crucial factor to consider when selecting a chiller for industrial applications. Historically, water-cooled chillers were considered more energy-efficient than air-cooled chillers, particularly in hot climates. However, advancements in technology have significantly improved the efficiency of air-cooled chillers, making them a competitive option in many applications.
Air-cooled chillers are highly efficient in moderate climates and can achieve comparable or even higher energy efficiency than water-cooled chillers in certain conditions. The efficiency of an air-cooled chiller is influenced by factors such as the ambient temperature, the design of the condenser and evaporator, and the type of compressor used. Modern air-cooled chillers often feature energy-efficient components, such as variable-speed compressors and advanced controls, that optimize performance and minimize energy consumption.
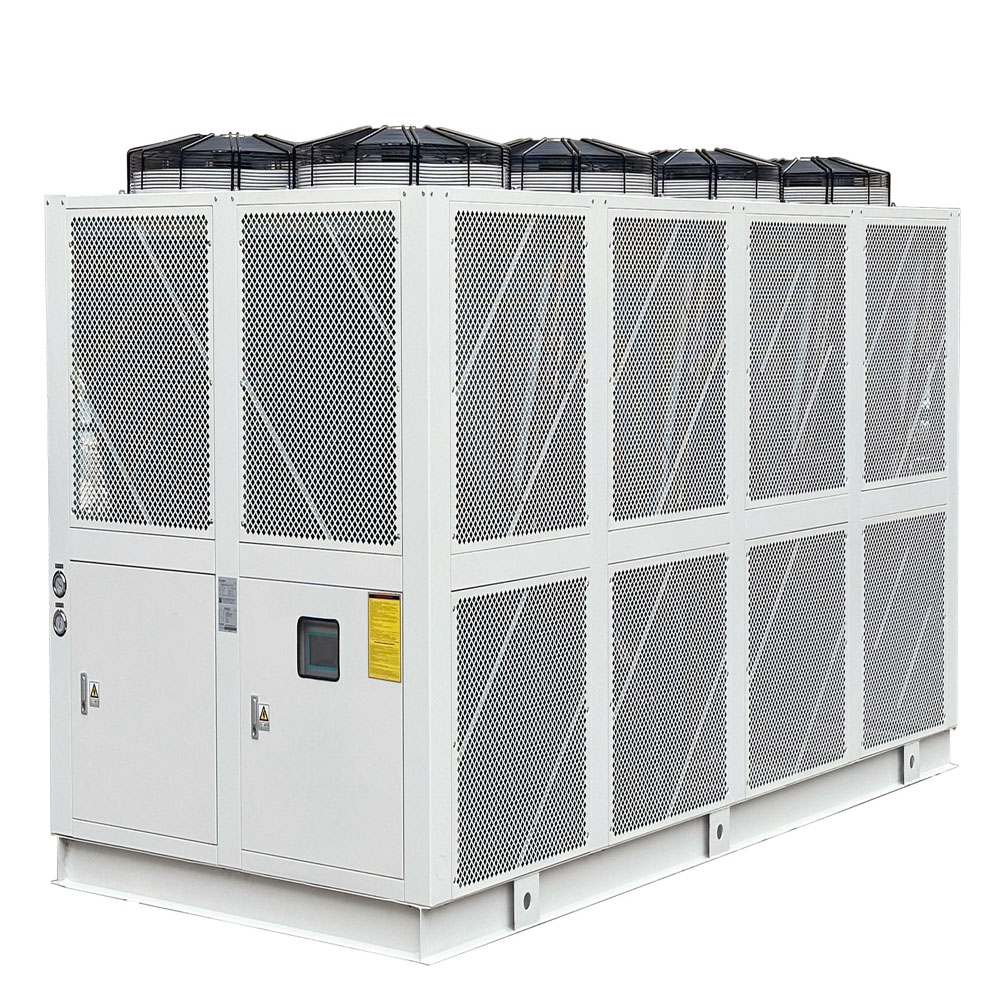

4. What Industries Benefit Most from Packaged Air-Cooled Chillers?
Packaged air-cooled chillers are used across a wide range of industries, providing reliable and efficient cooling for various processes and applications. Here are some of the industries that benefit most from these cooling systems:
- Plastics and Rubber Industry: Chillers are essential in the plastics and rubber industry for cooling molds, extruders, and other equipment used in injection molding, blow molding, extrusion, and calendaring processes. Air-cooled screw chillers provide precise temperature control, ensuring product quality and consistency.
- Machining Industry: In the machining industry, chillers are used to cool cutting fluids, spindles, and other components in CNC machines, lathes, and milling machines. Maintaining optimal temperatures helps to improve tool life, reduce thermal expansion, and enhance machining accuracy.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Chillers play a crucial role in the food and beverage industry for cooling processes such as brewing, fermentation, pasteurization, and refrigeration. Glycol chillers are commonly used in breweries and wineries to maintain precise temperatures during fermentation and storage.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industry: The chemical and pharmaceutical industries rely on chillers for temperature control in reactors, condensers, and other process equipment. Industrial chillers for electroplating offer precise temperature control and can handle corrosive and hazardous materials.
- Electronics Industry: Chillers are used in the electronics industry for cooling semiconductor manufacturing equipment, lasers, and other heat-sensitive components.
- Laser Industry: In the laser industry, chillers are essential for cooling laser systems, ensuring stable and reliable operation.
- Printing Industry: Chillers are used in the printing industry for cooling printing presses, rollers, and inks, maintaining print quality and preventing overheating.
- Medical Industry: The medical industry relies on chillers for cooling medical equipment such as MRI machines, CT scanners, and linear accelerators. Industrial chillers for textile industry offer the reliability and precision required for these critical applications.
- Laboratories and Research Institutions: Laboratories and research institutions use chillers for various applications, including sample cooling, temperature control in experiments, and equipment cooling.
- Data Centers: Data centers require efficient and reliable cooling to maintain optimal operating temperatures for servers and other IT equipment. Air-cooled screw central chillers provide high-capacity cooling for large data centers, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
5. Are Air-Cooled Chillers Suitable for All Climates?
Air-cooled chillers can operate effectively in a wide range of climates, but their performance is influenced by the ambient temperature. In moderate climates, air-cooled chillers are highly efficient and can provide reliable cooling throughout the year. However, in hot climates with high ambient temperatures, the efficiency of air-cooled chillers may be reduced, as the temperature difference between the refrigerant and the ambient air decreases.
To address this challenge, manufacturers have developed advanced air-cooled chillers that can operate efficiently even in high ambient conditions. These chillers often feature oversized condensers, high-efficiency fans, and advanced controls that optimize performance based on the ambient temperature. Additionally, some air-cooled chillers incorporate adiabatic cooling systems, which use water to pre-cool the ambient air before it reaches the condenser, further improving efficiency in hot climates. The use of cooling towers may also be considered.
6. How Do Air-Cooled Chillers Contribute to Cost Savings and Environmental Sustainability?
Air-cooled chillers offer significant cost savings and environmental benefits compared to traditional water-cooled systems. By eliminating the need for a cooling tower and reducing water consumption, air-cooled chillers can lower operating costs, particularly in areas with high water costs or limited water resources. Additionally, air-cooled chillers do not require water treatment chemicals, further reducing operating costs and minimizing the environmental impact associated with chemical use and disposal.
Air-cooled chillers can also contribute to energy savings, particularly when equipped with energy-efficient components such as variable-speed compressors and advanced controls. These features allow the chiller to adjust its capacity based on the cooling load, minimizing energy consumption during periods of low demand. Furthermore, air-cooled chillers can be integrated with other energy-saving technologies, such as free cooling systems, which utilize low ambient temperatures to provide cooling without running the compressor.
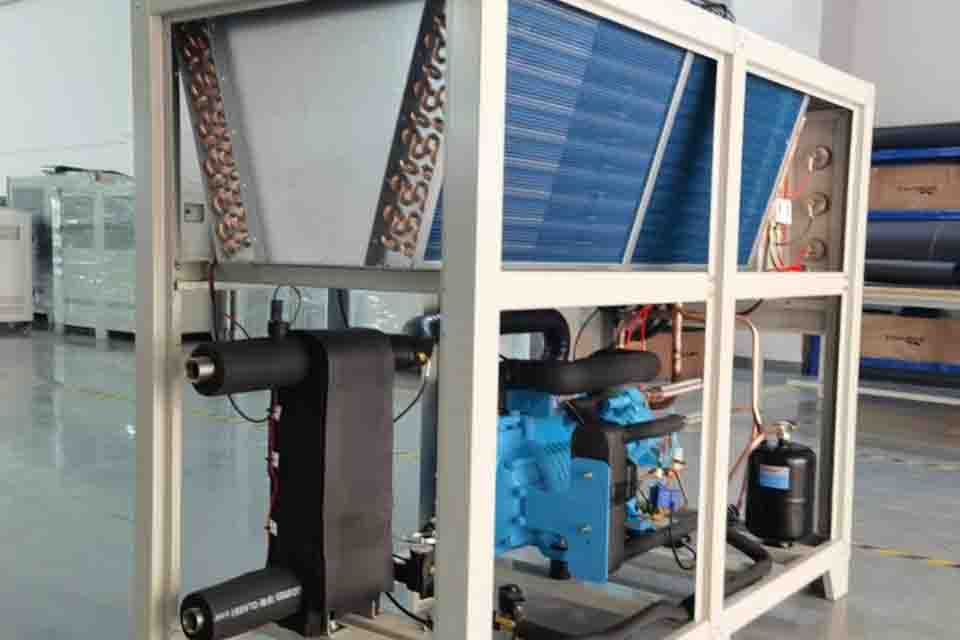
7. What are the Key Components of a Packaged Air-Cooled Chiller?
A packaged air-cooled chiller consists of several key components that work together to provide efficient and reliable cooling. The main components include:
- Compressor: The compressor is the heart of the refrigeration system, responsible for compressing the refrigerant vapor and increasing its pressure and temperature.
- Condenser: The condenser is a heat exchanger that cools the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant vapor, causing it to condense into a liquid. In air-cooled chillers, the condenser is cooled by ambient air blown across the condenser coils by fans.
- Evaporator: The evaporator is another heat exchanger that absorbs heat from the process fluid, causing the refrigerant to evaporate. The chilled water or process fluid is then circulated to the application to provide cooling.
- Expansion Valve: The expansion valve reduces the pressure and temperature of the liquid refrigerant before it enters the evaporator.
- Pump: The pump circulates the process fluid through the evaporator and to the application.
- Controls: The controls monitor and regulate the operation of the chiller, including the compressor, fans, pump, and expansion valve, to maintain the desired temperature and optimize performance.
8. How to Choose the Right Air-Cooled Chiller for Your Specific Needs?
Choosing the right air-cooled chiller for your specific needs requires careful consideration of several factors, including the cooling capacity, efficiency, operating conditions, and application requirements. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Cooling Capacity: The cooling capacity of the chiller should match the cooling load of the application. It is essential to accurately calculate the cooling load, taking into account factors such as the heat generated by the equipment or process, the desired temperature, and the flow rate of the process fluid.
- Efficiency: Consider the energy efficiency of the chiller, particularly if energy costs are a significant concern. Look for chillers with high efficiency ratings and energy-efficient components, such as variable-speed compressors and advanced controls.
- Operating Conditions: Evaluate the operating conditions, including the ambient temperature range and the availability of water resources. If operating in a hot climate, consider air-cooled chillers designed for high ambient conditions or those with adiabatic cooling systems.
- Application Requirements: Consider the specific requirements of the application, such as the desired temperature range, the type of process fluid, and any special considerations, such as the need for precise temperature control or the presence of corrosive or hazardous materials.
9. What are the Installation and Maintenance Requirements for Air-Cooled Chillers?
Air-cooled chillers are generally easier to install and maintain than water-cooled chillers. Since they do not require a cooling tower or a separate water system, the installation process is simpler and less time-consuming. Air-cooled chillers can be installed outdoors, on a rooftop, or in a mechanical room, providing flexibility in terms of location.
Maintenance requirements for air-cooled chillers are also typically lower than for water-cooled chillers. Regular maintenance tasks include cleaning the condenser coils, checking the refrigerant charge, inspecting the fans and motors, and monitoring the operation of the controls. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and to schedule regular inspections by qualified technicians.
10. Why Choose Our Industrial Water Chiller Manufacturing Plant for Your Cooling Needs?
As a leading industrial water chiller manufacturing plant, we are committed to providing high-quality, reliable, and energy-efficient cooling solutions for a wide range of industries. Our packaged air-cooled chillers are designed and manufactured to the highest standards, using premium components and advanced technologies to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
We offer a comprehensive range of air-cooled chillers, from small-capacity units for laboratory applications to large-capacity systems for industrial processes. Our chillers are available in various configurations, including scroll, screw, and centrifugal compressors, and can be customized to meet your specific needs. We also offer a range of options and accessories, such as adiabatic cooling systems, free cooling systems, and advanced controls, to further enhance performance and efficiency.
Our team of experienced engineers and technicians is dedicated to providing exceptional customer service and support. We work closely with our clients to understand their unique requirements and develop tailored solutions that meet their specific needs. We also offer comprehensive installation, maintenance, and repair services to ensure that your chiller operates at peak performance throughout its lifespan.
FAQs
1. What are the differences between air-cooled and water-cooled chillers?
The primary difference is how they cool the refrigerant. Air-cooled chillers use ambient air, while water-cooled chillers use a water source, typically from a cooling tower. This makes air-cooled chillers easier to install and maintain, while water-cooled chillers are generally more energy-efficient in hotter climates.
2. Can air-cooled chillers be used for air conditioning?
Yes, air-cooled chillers can be used for air conditioning systems, particularly in large commercial or industrial buildings. They can be connected to fan coil units or air handling units to distribute cooled air throughout the building.
3. What is the lifespan of an air-cooled chiller?
The lifespan of an air-cooled chiller depends on various factors, including the quality of the equipment, the operating conditions, and the maintenance practices. With proper maintenance, a well-built air-cooled chiller can last for 15-20 years or more.
4. What is a split system air-cooled chiller?
A split system air-cooled chiller separates the condensing unit (containing the compressor and condenser) from the evaporator unit. This allows for greater flexibility in installation, as the condensing unit can be located outdoors while the evaporator is placed indoors near the application.
5. How often should an air-cooled chiller be serviced?
It is recommended to have an air-cooled chiller serviced at least once a year by a qualified technician. Regular maintenance helps to ensure optimal performance, prevent breakdowns, and extend the lifespan of the equipment.
6. What refrigerant is used in air-cooled chillers?
The type of refrigerant used in air-cooled chillers varies depending on the manufacturer and the specific model. Common refrigerants include R-410A, R-407C, and R-134a. These refrigerants are chosen for their cooling properties, environmental impact, and compliance with regulations.
Key Takeaways
- Air-cooled chillers offer a simple, reliable, and cost-effective cooling solution for a wide range of industrial applications.
- They are easier to install and require less maintenance than water-cooled chillers.
- Air-cooled chillers are suitable for areas with limited water resources and can contribute to environmental sustainability.
- Advancements in technology have significantly improved the efficiency of air-cooled chillers, making them a competitive option in many applications.
- Choosing the right air-cooled chiller requires careful consideration of factors such as cooling capacity, efficiency, operating conditions, and application requirements.
- Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of air-cooled chillers.
- As an industrial water chiller manufacturing plant, we offer high-quality, reliable, and energy-efficient air-cooled chillers tailored to your specific needs.
For more information on our packaged air-cooled chillers and how they can benefit your business, please explore our website or give us a call today. We look forward to helping you find the perfect cooling solution for your needs.