-
Dalingshan Industrial Guangdong

what is a dry cooler & what are the differences between dry coolers vs. chiller systems
Dry Cooler vs. Chiller: What’s the Difference and Which is Best for Your Cooling Needs?
This article explores the critical differences between dry coolers and chillers, two essential components in various industrial koeling systems. We delve into how each system operates, their advantages, disadvantages, and ideal applications. By understanding these distinctions, you can make an informed decision about which cooling solution best suits your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency for your operations. Whether you’re in the plastics and rubber industry, machining, food and beverage, or any other sector requiring precise temperature control, this guide provides valuable insights into selecting the right koeling technology. This article is worth reading because it provides a clear and detailed comparison of dry coolers and chillers, helping readers determine the most efficient and cost-effective cooling solution for their specific industrial applications.
Inhoudsopgave
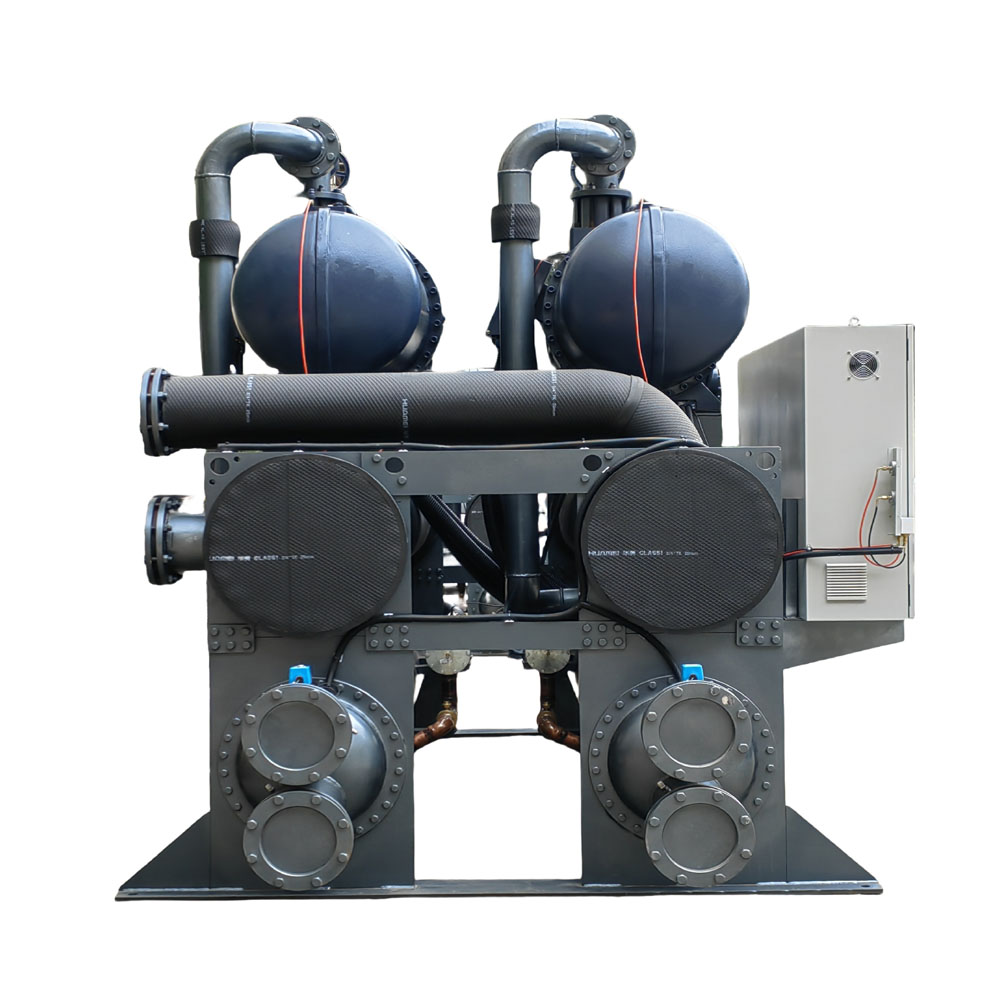
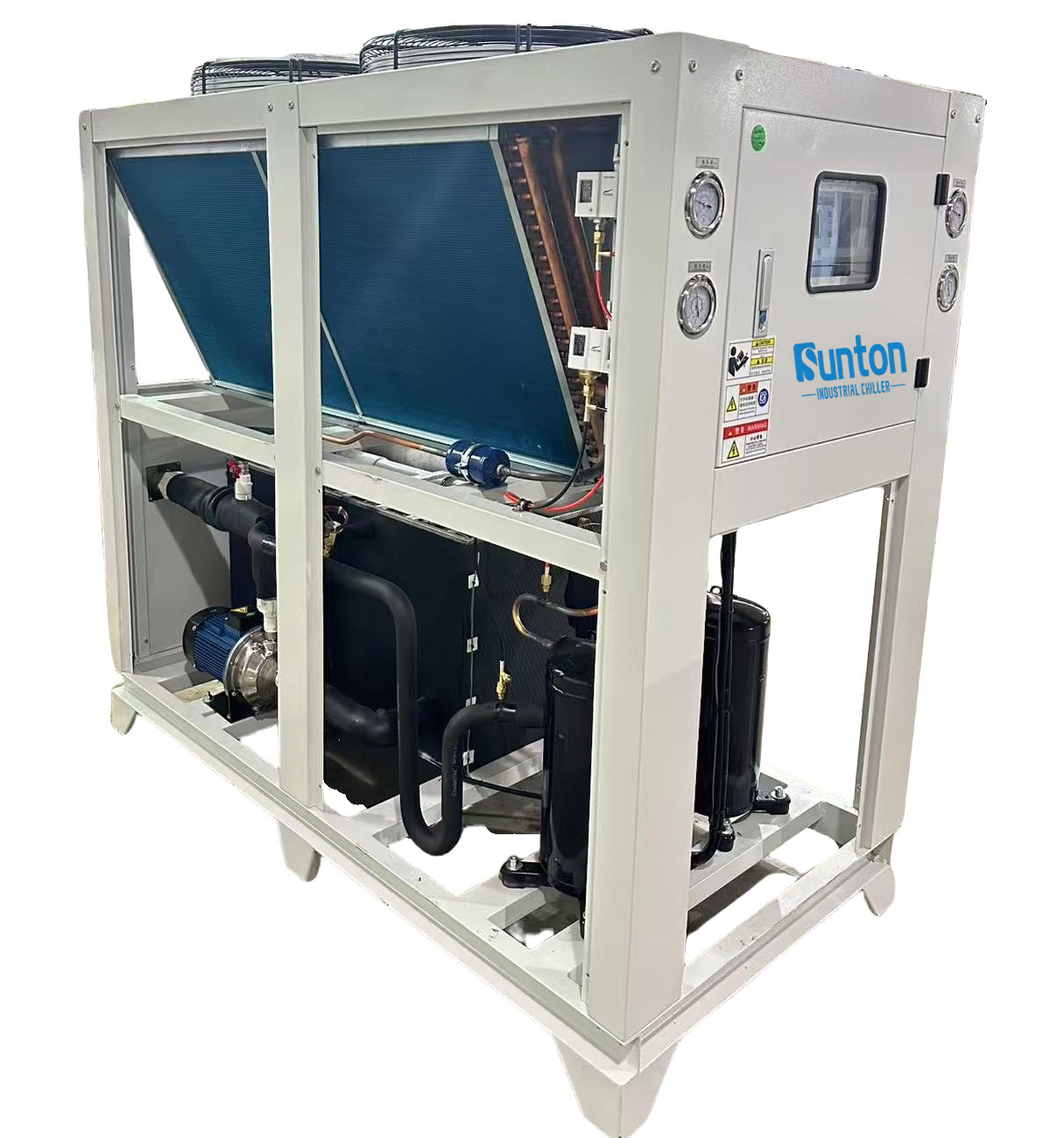
What is a Dry Cooler?
A dry cooler is a type of koeling device that uses ambient air to cool a fluid. It is often called a fluid cooler or an air-cooled heat exchanger. Dry coolers are commonly used in various industrial applications where heat needs to be dissipated efficiently. For instance, as an industrial water chiller manufacturing plant, we often recommend dry coolers for businesses in the plastics and rubber industry and the food and beverage industry due to their reliability and energy efficiency.
Dry coolers operate by passing the process fluid through a series of tubes within a heat exchanger. Fans force ambient air across these tubes, facilitating heat transfer from the fluid to the air. This process reduces the temperature of the process fluid without the need for water or other koeling mediums, making it a “dry” koeling system. One significant advantage of dry coolers is their ability to operate efficiently in environments where water is scarce or its use is restricted. Dry coolers have fans that help move the air stream over the tubes, enhancing the koeling process.
A dry cooler uses ambient air to cool the fluid being cooled. The efficiency of a dry cooler depends largely on the ambient temperature. As such, they are most effective in cooler climates or during cooler parts of the day. Dry coolers are also sometimes used in conjunction with other koeling systems, such as koelmachines, to enhance overall system efficiency. For example, a dry cooler can be used for pre-cooling of the inlet air, reducing the load on the chiller and improving energy efficiency.
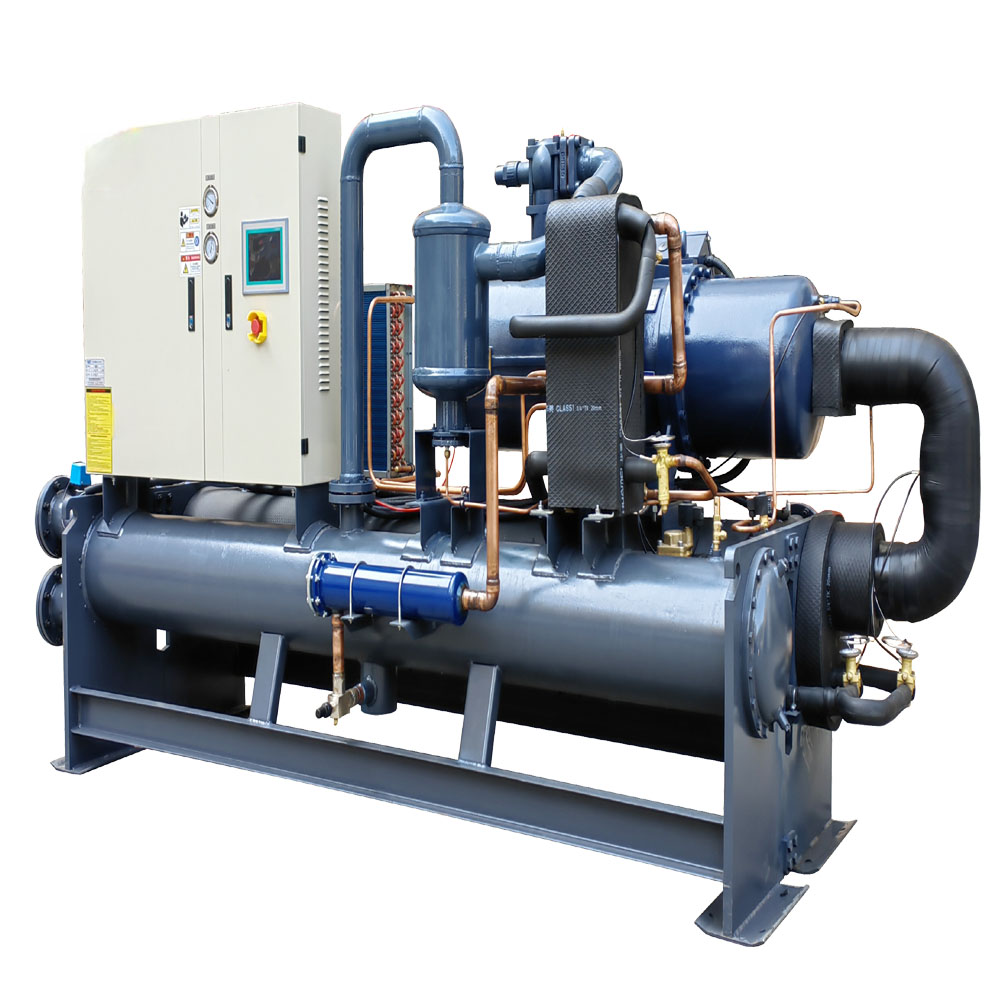
What is a Chiller?
A chiller is a koeling device that uses a refrigeration cycle to remove heat from a liquid. Unlike a dry cooler, a chiller unit typically uses a refrigerant to absorb and transfer heat, achieving lower temperatures than what can be reached with ambient air. Chillers are widely used in industries that require precise temperature control, such as the chemical and pharmaceutical, and medical industries. This is an essential device for these industries.
Chillers can be either air cooled or water-cooled, depending on how the condenser dissipates heat. Air cooled chillers use ambient air to cool the refrigerant, while water-cooled koelmachines use water. In my experience as an industrial water chiller manufacturer, we often design custom chiller solutions for clients in the electronics and laser industries, where precise and reliable koeling is critical. Chillers provide consistent koeling performance regardless of the ambient air temperature, making them ideal for applications requiring stable temperatures.
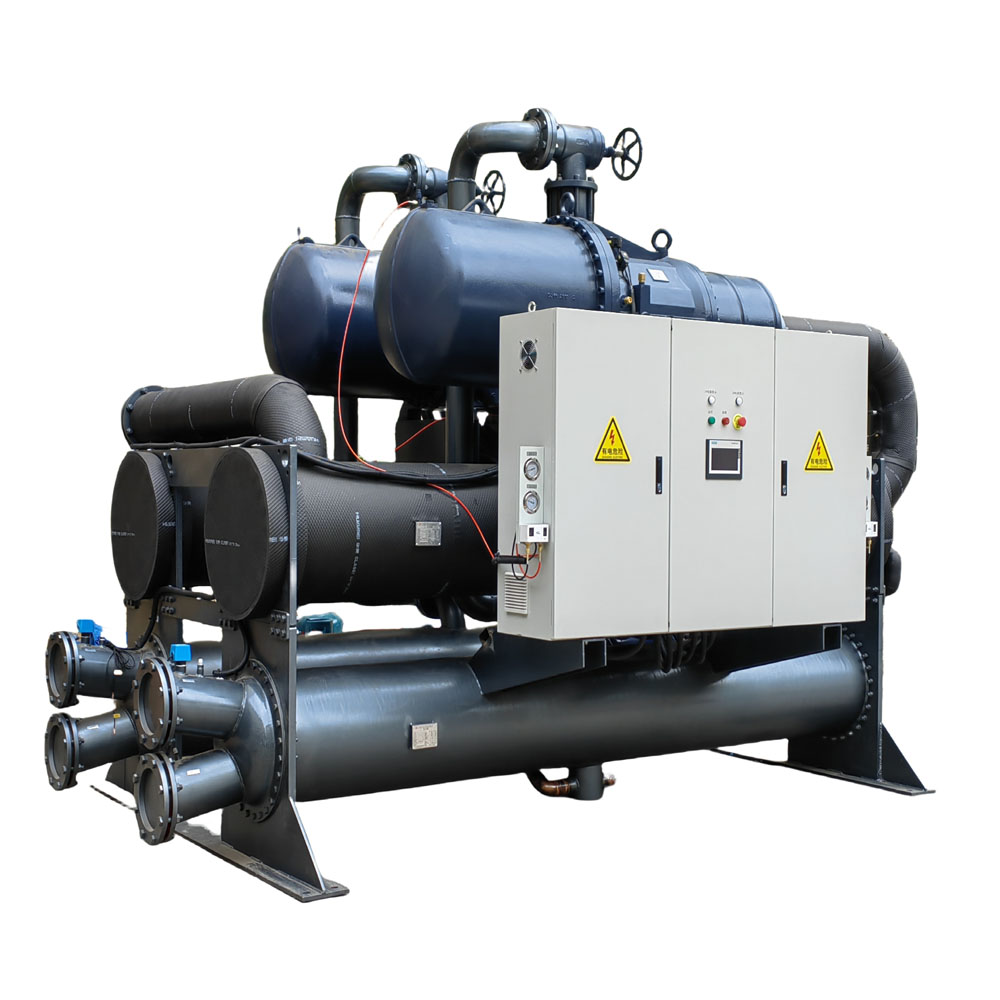

Chillers are particularly useful in applications where the required koeling temperature is below what can be achieved with a dry cooler. For instance, in laboratories and research institutions, koelmachines are used to maintain specific low temperatures needed for experiments and sample storage. Additionally, data centers often rely on koelmachines for liquid cooling to manage the substantial heat generated by servers and other equipment. If you need a chiller for your industrial needs, consider visiting our Water Cooled Screw Water Chiller page for more information.
What is the Main Difference Between a Dry Cooler and a Chiller?
The main difference between a dry cooler and a chiller lies in their koeling mechanisms and the temperatures they can achieve. A dry cooler uses ambient air to cool a fluid, while a chiller uses a refrigeration cycle to achieve lower temperatures. In essence, a dry cooler is a koeling device that utilizes air to regulate process temperature, whereas a chiller employs a refrigerant to cool a liquid.
Dry coolers are simpler in design and generally require less maintenance than koelmachines. They are also more energy-efficient when the ambient temperature is significantly lower than the desired process fluid temperature. However, the koeling capacity of a dry cooler is limited by the ambient air temperature. This is the key temperature difference to consider. Chillers, on the other hand, can provide consistent koeling even when the ambient air temperature is high, making them suitable for a wider range of applications.
In my role, I often explain to clients that the choice between a dry cooler and a chiller depends on their specific koeling needs and operating conditions. For example, a dry cooler might be sufficient for a plastics manufacturing plant in a cooler climate, while a chiller might be necessary for a pharmaceutical company that requires precise temperature control year-round. Understanding the difference between dry coolers and chillers is crucial for making an informed decision.
Dry Cooler vs. Chiller: Pros and Cons
When comparing dry cooler vs chiller, it’s essential to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each system. Dry coolers are known for their simplicity, lower maintenance requirements, and energy efficiency in suitable conditions. They do not use water as a cooling medium, which can be a significant advantage in regions with water scarcity. A dry cooler uses air to regulate the temperature of the process fluid. Dry coolers are often used in industrial settings to provide koeling where water usage is a concern.
However, dry coolers are less effective in hot and dry climates and cannot achieve the low temperatures that koelmachines can. The koeling capacity of a dry cooler is directly tied to the ambient air temperature, making them less reliable in fluctuating or high-temperature environments. Dry coolers are also known as fluid coolers and are used to remove heat from a system by circulating air. The air is then expelled from the system, taking the heat with it.
Chillers, on the other hand, offer precise temperature control and consistent performance regardless of the ambient temperature. They are essential for industries where maintaining specific low temperatures is crucial, such as in the medical and laboratory sectors. Chillers can be a more complex cooling solution compared to dry coolers, but they provide more effective koeling. If you need a cooling solution that can handle demanding environments, consider exploring our Anti-Explosion Chillers.
How Do Dry Coolers Work in Data Centers?
In data centers, efficient koeling is crucial to maintain the performance and reliability of servers and other IT equipment. Dry coolers can play a significant role in managing heat in these environments, particularly in regions with moderate climates. They offer an energy-efficient alternative to traditional koeling methods by utilizing ambient air for koeling. Dry coolers can help reduce energy consumption and operational costs in data centers.
Dry coolers work in data centers by using fans to draw ambient air across a heat exchanger containing the cooled fluid. This process transfers heat from the fluid to the air, which is then expelled from the system. Dry coolers are particularly effective in data centers during cooler months or in regions with low dry bulb temperatures. They can be used as a standalone cooling solution or in conjunction with other cooling technologies to enhance overall efficiency.
One of the primary advantages of using dry coolers in data centers is their ability to reduce reliance on mechanical refrigeration, which consumes significant amounts of energy. By leveraging free cooling when ambient air conditions permit, data centers can lower their energy consumption and environmental impact. Dry coolers are also relatively simple to install and maintain, making them an attractive option for data center operators. They utilize ambient air to cool the process fluid, which is circulated through the system.
What Are the Different Cooling Technologies Available?
Several cooling technologies are available for industrial applications, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The main types of cooling systems include dry coolers, koelmachines, koeltorens, and hybrid systems that combine multiple technologies. Understanding the differences between these systems is essential for selecting the most appropriate cooling solution for your needs. As someone deeply involved in the industrial koeling sector, I’ve seen firsthand how the right choice can impact operational efficiency and cost savings.
Dry coolers use ambient air to cool a fluid, making them energy-efficient in suitable conditions but less effective in high-temperature environments. A dry cooler is a type of heat exchanger that uses air as the koeling medium. The air stream passes over the heat exchanger, removing heat from the fluid. They are commonly used in the printing and chemical industries, and we have seen an increasing demand for these systems due to their low environmental impact.
Chillers use a refrigeration cycle to achieve lower temperatures and provide precise temperature control. They can be either air-cooled or water-cooled, depending on the method used to dissipate heat from the condenser. Chillers are essential in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and laboratories, where maintaining specific low temperatures is critical. Our expertise in manufacturing industrial water koelmachines allows us to offer tailored solutions that meet the unique requirements of these sectors. A typical chiller unit requires a cooling medium channeled through the system to remove heat.
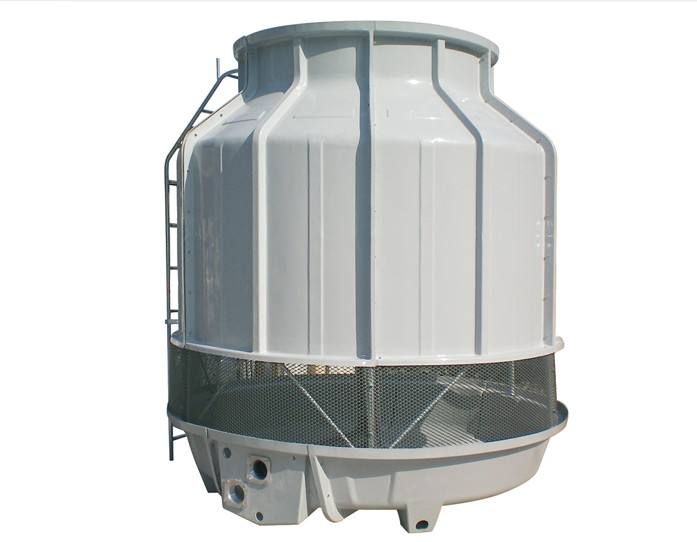
Cooling towers use evaporative koeling to remove heat from water, which is then used to cool equipment or processes. They are highly effective in hot and humid climates but require a continuous water supply and can be prone to issues such as scaling and biological growth. Wet cooling towers are a common example of this technology. A cooling tower relies on the latent heat of vaporization to cool the water.
What Are the Advantages of Dry Coolers?
Dry coolers offer several advantages that make them an attractive option for various industrial koeling applications. One of the primary advantages of dry coolers is their energy efficiency. By using ambient air to cool the process fluid, dry coolers can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to mechanical refrigeration systems. This makes them particularly appealing for businesses looking to lower their operational costs and environmental footprint. The cooler is a koeling device that uses air to regulate the temperature.
Another significant advantage of dry coolers is their simplicity and low maintenance requirements. Unlike koelmachines, which have complex refrigeration systems, dry coolers have fewer moving parts and do not require refrigerants. This reduces the risk of breakdowns and minimizes the need for regular maintenance. From my experience, clients in the machining and plastics industries appreciate the reliability and ease of maintenance that dry coolers offer. Dry coolers have fans that help move the air across the heat exchanger.
Dry coolers are also environmentally friendly, as they do not use water for koeling. This makes them an ideal cooling solution for regions with water scarcity or where water usage is restricted. Additionally, dry coolers can be used in conjunction with other koeling systems, such as koelmachines, to enhance overall system efficiency. For example, a dry cooler can be used for free cooling during cooler months, reducing the load on the chiller and saving energy. If you are looking for an environmentally friendly cooling solution, check out our Glycol Chillers page.
When to Use a Dry Cooler vs. a Chiller?
Deciding when to use a dry cooler vs chiller depends on several factors, including the specific koeling requirements, ambient temperature conditions, and energy efficiency goals. Dry coolers are best suited for applications where the desired process fluid temperature is higher than the ambient air temperature. They are particularly effective in cooler climates or during cooler parts of the day. Dry coolers are often used in industries such as plastics, rubber, and machining, where moderate koeling is sufficient.
Chillers, on the other hand, are necessary when precise temperature control is required or when the desired koeling temperature is below what can be achieved with a dry cooler. They are essential in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and laboratories, where maintaining specific low temperatures is crucial. Chillers provide consistent koeling performance regardless of the ambient temperature, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. In the context of industrial applications, the difference between dry coolers and chillers often comes down to the specific temperature requirements and environmental conditions.
In my role as an industrial water chiller manufacturer, I often advise clients to consider a hybrid koeling system that combines the benefits of both dry coolers and chillers. For example, a dry cooler can be used for free cooling when ambient conditions permit, while a chiller can provide additional koeling when needed. This approach maximizes energy efficiency and ensures reliable koeling performance year-round. For more details on how to optimize your koeling system, visit our page on Air Cooled Screw Central Chillers.
How Does Evaporative Cooling Work?
Evaporative cooling is a koeling method that uses the evaporation of water to reduce air temperature. It is commonly used in koeltorens and some types of air conditioners. Evaporative cooling works by passing warm air over a wetted surface, causing the water to evaporate. As the water evaporates, it absorbs heat from the air, resulting in a lower air temperature. This process is highly effective in hot and dry climates, where the low humidity allows for significant evaporation and koeling.
In a cooling tower, water is sprayed or trickled over a fill material, creating a large surface area for evaporation. Fans draw ambient air through the tower, promoting the evaporation of water and the removal of heat from the remaining water. The cooled water is then circulated through a heat exchanger to cool equipment or processes. Cooling towers that use evaporative cooling can achieve significant koeling but require a continuous supply of water.
Evaporative cooling is an energy-efficient koeling method, particularly in dry climates. However, it is less effective in humid environments, where the air is already saturated with moisture, limiting the potential for evaporation. Additionally, evaporative cooling systems require regular maintenance to prevent issues such as scaling and biological growth. Cooling tower relies on the latent heat of vaporization to cool the water efficiently in hot and dry climates.
How to Choose the Right Cooling Solution?
Choosing the right cooling solution for your industrial application requires careful consideration of several factors. First, you need to determine your specific koeling needs, including the required temperature range, koeling capacity, and any special requirements such as precise temperature control or redundancy. Understanding these parameters will help you narrow down your options and select the most appropriate koeling technology. Different industries have varying koeling needs, and selecting the right system is crucial for efficiency.
Next, you should evaluate the ambient temperature conditions in your location. If you are in a region with a moderate climate and your koeling needs are not stringent, a dry cooler might be sufficient. However, if you are in a hot climate or require precise temperature control, a chiller might be necessary. Considering the ambient air temperature is crucial when choosing between a dry cooler and a chiller.
Energy efficiency is another critical factor to consider. Dry coolers are generally more energy-efficient than koelmachines when ambient conditions permit. However, koelmachines can provide more consistent koeling performance, which might be necessary for certain applications. Evaluating the energy consumption of different koeling systems and selecting the most efficient option can help you reduce operational costs and minimize your environmental impact. A hybrid system, combining a dry cooler and a chiller, can offer the best of both worlds by maximizing energy efficiency and ensuring reliable koeling performance.
Finally, you should consider the maintenance requirements and overall lifecycle costs of different koeling systems. Dry coolers typically require less maintenance than koelmachines, but they might not be suitable for all applications. Evaluating the initial investment, operational costs, and maintenance expenses will help you make an informed decision. As an industrial water chiller manufacturer, we offer comprehensive support and maintenance services to ensure the long-term performance and reliability of your koeling system. For a reliable cooling solution, consider our Industrial Chillers For Concrete Batch Plant.
FAQs
What is a dry cooler and how does it work?
A dry cooler is a koeling device that uses ambient air to cool a fluid. It works by passing the process fluid through tubes within a heat exchanger, while fans force ambient air across the tubes, transferring heat from the fluid to the air. Dry coolers are efficient in cooler climates and are used in various industrial applications.
What is a chiller and how is it different from a dry cooler?
A chiller is a koeling device that uses a refrigeration cycle to remove heat from a liquid, achieving lower temperatures than a dry cooler. Unlike a dry cooler, a chiller uses a refrigerant to absorb and transfer heat. Chillers provide precise temperature control and are essential in industries requiring specific low temperatures.
When should I use a dry cooler instead of a chiller?
Use a dry cooler when the desired process fluid temperature is higher than the ambient air temperature and precise temperature control is not critical. Dry coolers are ideal for applications in cooler climates or during cooler parts of the day and are commonly used in industries like plastics, rubber, and machining.
What are the advantages of using a dry cooler?
The advantages of dry coolers include energy efficiency, simplicity, low maintenance requirements, and environmental friendliness. They do not use water for koeling, making them suitable for regions with water scarcity. Dry coolers are also cost-effective and easy to install.
How can I improve the energy efficiency of my cooling system?
Improve energy efficiency by using a dry cooler for free cooling when ambient conditions permit, combining dry coolers en koelmachines in a hybrid system, and selecting koeling equipment with high-efficiency ratings. Regular maintenance and monitoring can also enhance system performance and reduce energy consumption. Utilizing ambient air to cool a fluid can significantly reduce energy costs.
What industries commonly use dry coolers and chillers?
Dry coolers are commonly used in the plastics and rubber, machining, and printing industries. Chillers are essential in the food and beverage, chemical and pharmaceutical, medical, laboratories, and data centers. Choosing the right koeling system depends on the specific needs of each industry.
Conclusion
- Dry coolers use ambient air to cool a fluid, while koelmachines use a refrigeration cycle for lower temperatures.
- The main difference between a dry cooler and a chiller is their koeling mechanism and achievable temperatures.
- Dry coolers are energy-efficient and low-maintenance, ideal for moderate koeling needs in cooler climates.
- Chillers offer precise temperature control, necessary for industries requiring specific low temperatures.
- Evaporative cooling, used in koeltorens, is effective in hot, dry climates but requires a continuous water supply.
- Choosing the right cooling solution involves evaluating koeling needs, ambient temperature, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements.
- Hybrid systems combining dry coolers en koelmachines can maximize energy efficiency and ensure reliable performance.
- Dry coolers are environmentally friendly, as they do not rely on water for koeling.
- Understanding the specific requirements of your industry is crucial for selecting the most efficient and cost-effective koeling system.
- Proper maintenance and monitoring are essential for optimizing the performance and longevity of any koeling system.
For more information on our industrial koeling solutions, visit our homepage.