-
Dalingshan Industrial Guangdong
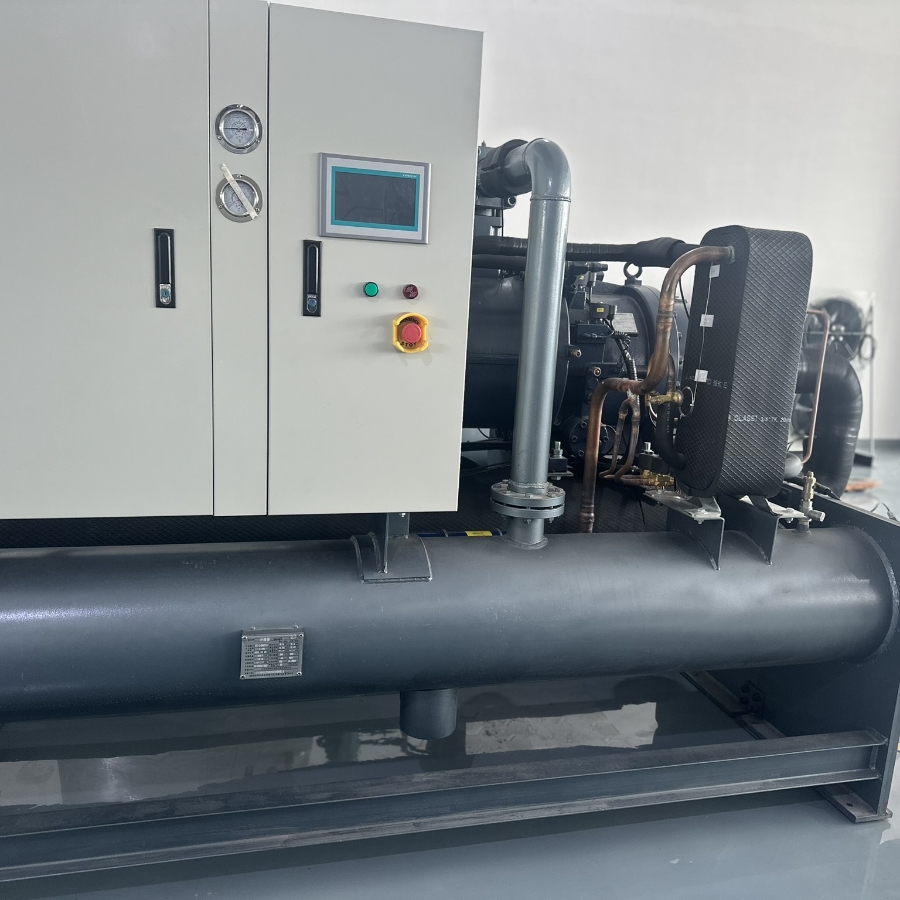

industrial anodizing chillers
Manufactures and Installs the Best Cooling industrial anodizing chillers: Understanding Anodizing and Plating Chillers
Are you involved in anodizing, plating, or other metal finishing processes? If so, you know how crucial precise temperature control is to achieving high-quality results. This article dives into the world of industrial chillers, specifically focusing on anodizing and Plating chillers are essential for maintaining the proper temperature during the plating process, with a capacity of an anodizing chiller ranging from 1 ton to 40 tons. We’ll explore what they are, why you need them, different types available, and how to choose the perfect one for your metal finishing needs. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out, understanding the role of chillers in your operation is essential for efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Let’s get cool and dive right in! We are a leading manufacturer and will help guide you through selecting the perfect We also have a diverse line of cooling equipment, including industrial process cooling equipment for optimal performance. solutions for your metal finishing operation, ensuring quality and efficiency.
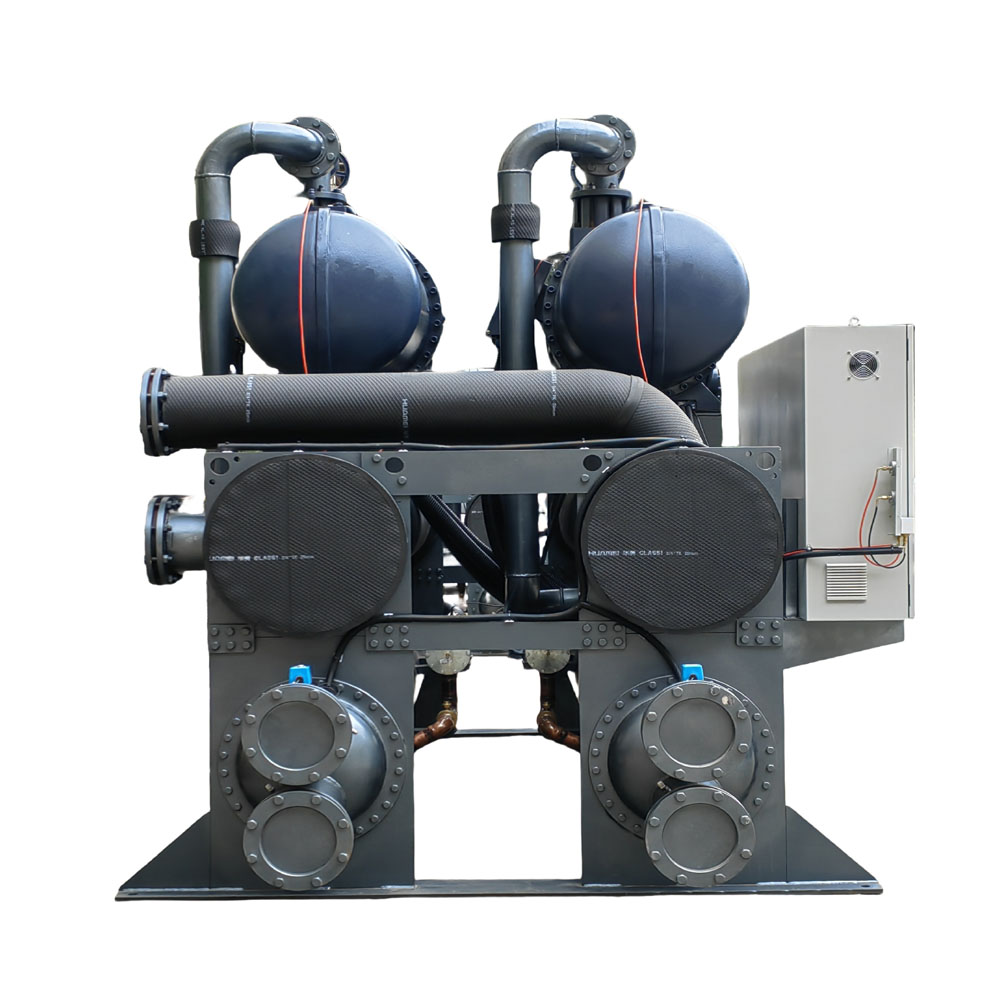
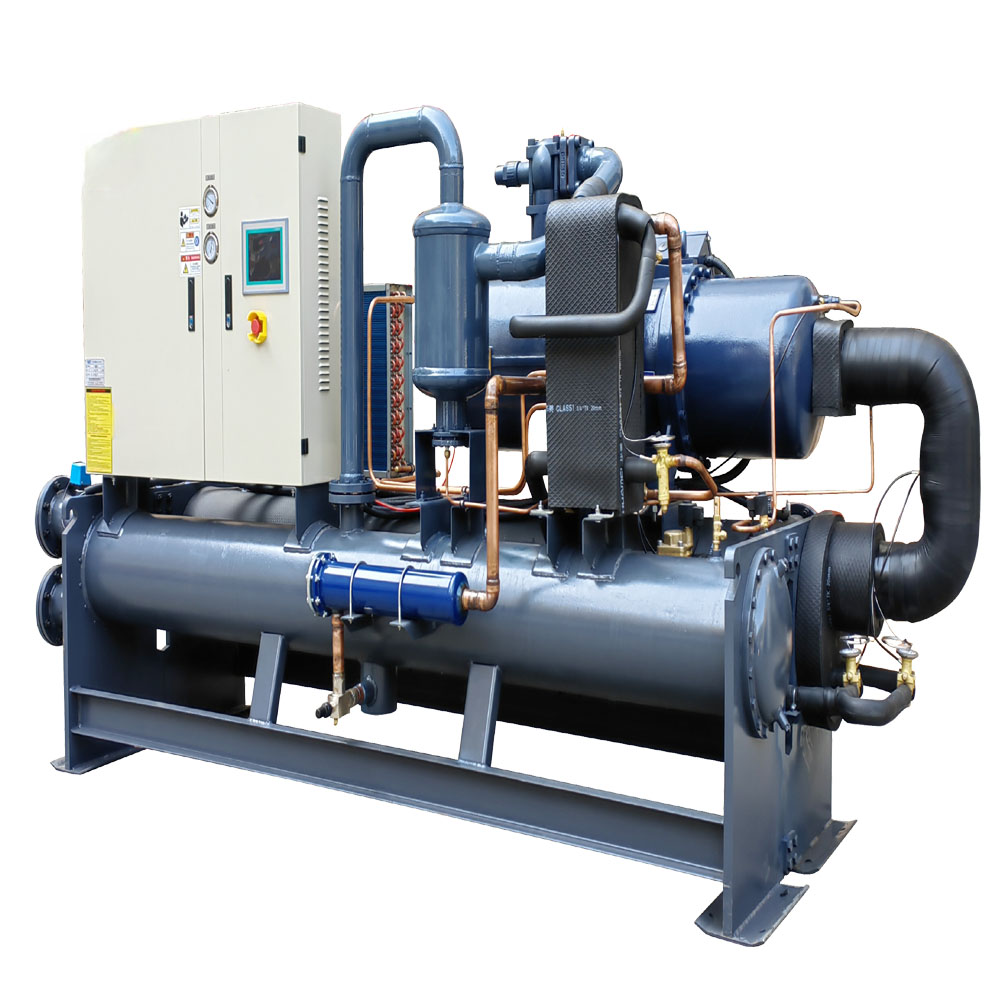
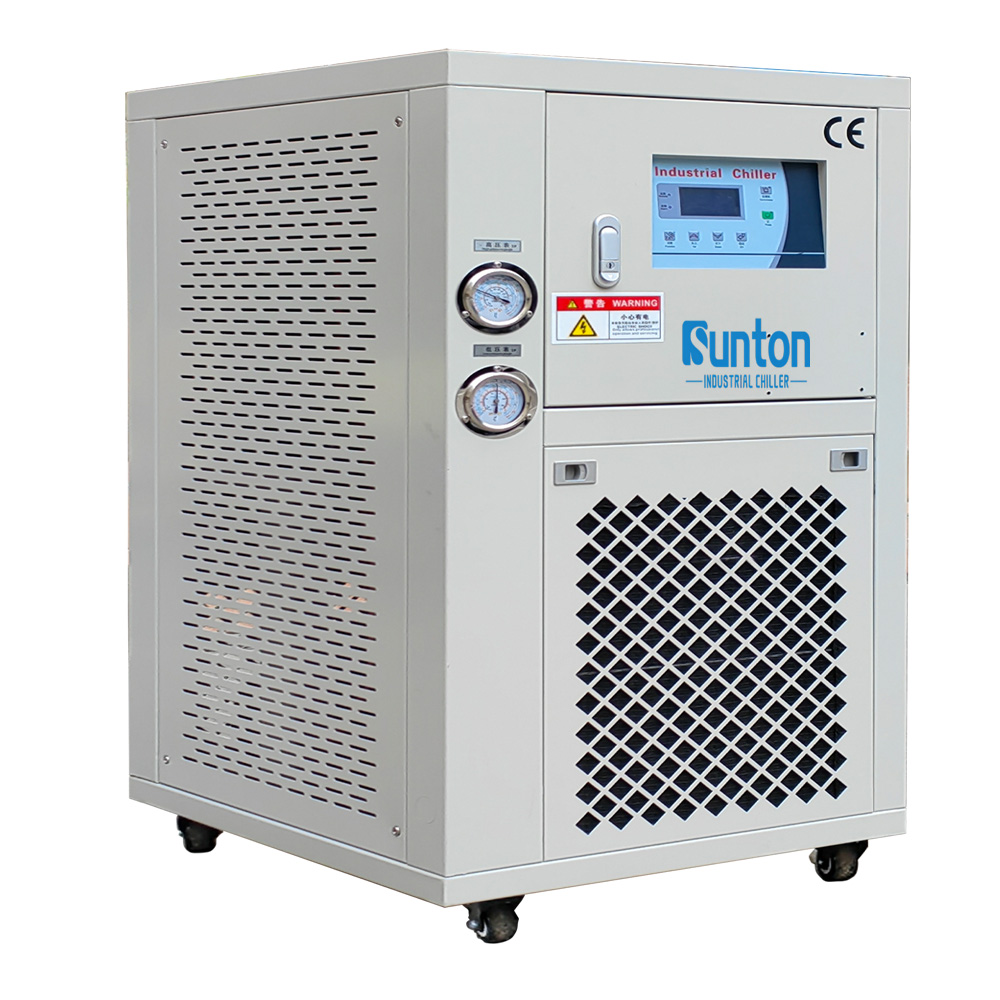
An industrial chiller is a refrigeration system that removes heat from a process liquid or industrial equipment. In the context of metal finishing, this process liquid is often the solution used in the anodizing or plating tank. These chillers are crucial because anodizing and plating processes generate a significant amount of heat due to the electric current involved. This heat, if not controlled, can negatively impact the quality of the coating, leading to defects, inconsistencies, and even damage to the equipment. A chiller works by circulating a refrigerant through a closed-loop system. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the process liquid in the evaporator, cooling it down. Then, the refrigerant carries the heat to the condenser, where it is released to the environment. This cycle repeats, maintaining the desired temperature of the process liquid for consistent and high-quality metal finishing.
What is the anodizing process, and why does it need a chiller?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that increases the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface of metals, most commonly aluminum. This enhanced oxide layer provides increased corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and better adhesion for paints and other Different applications of anodizing chillers can significantly improve the efficiency of the cooling process. Types of coatings can be applied using chillers that effectively manage heat from anodizing processes. The anodizing process involves immersing the aluminum part in an electrolyte solution, typically sulfuric acid, and passing an electric current through it. This current causes an oxidation reaction at the surface of the metal, building up the oxide layer.
The passage of electric current during the anodizing process generates significant heat. This heat, if uncontrolled, can lead to several problems. First, it can cause the anodizing vessel or tank to overheat, potentially damaging the tank itself or the surrounding equipment. Second, excessive heat can negatively impact the quality of the anodic coating. It can lead to uneven coating thickness, powdery or soft coatings, and reduced corrosion resistance. Maintaining a consistent and controlled temperature is therefore essential for achieving the desired quality and performance of the anodized parts. This is where an anodizing chiller comes in. The chiller removes the excess heat, ensuring the anodizing cooling process is stable and effective. This leads to a consistent, high-quality metal coating. A reliable cooling system keeps the temperature of the anodizing process within the optimal range, typically between 60°F and 80°F (15°C and 27°C), ensuring consistent and high-quality results. Our koelmachines Our chillers can handle everything from basic cooling to specialized applications of an anodizing chiller. koeling to specialized applications.
<br>
What Happens in the Plating Process, and Why is Temperature Control Crucial?
Plating, also known as electroplating, is a surface finishing process where a thin layer of metal is deposited onto a substrate material, typically another metal. This is done by immersing the substrate in a solution containing dissolved metal ions and passing an electric current through it. The current causes the metal ions to be reduced and deposited onto the substrate, forming a plating cooling layer. coating. Common plating metals include nickel, chrome, zinc, and precious metals like gold and silver. The plating process is widely used to enhance the corrosion resistance, wear resistance, appearance, and other properties of metal parts. From automotive parts to electronics, plating is a critical step in the manufacturing of countless products.
The plating process, like anodizing, generates heat due to the electric current flowing through the solution. This heat can affect the plating process in several ways. It can alter the plating rate, influencing the thickness and uniformity of the deposited layer. It can also affect the adhesion of the coating to the substrate and the overall quality of the coating. Precise temperature control is, therefore, essential for achieving the desired plating thickness, uniformity, and adhesion. A plating chiller The plating cooling system maintains the plating solution at the optimal temperature, ensuring a consistent and high-quality industrial process. metal plating process throughout the entire process. For instance, a consistent temperature provided by a reliable chiller is vital for success in the zinc plating process. Without proper temperature control, you risk uneven coatings, poor adhesion, and other defects. We are the leading manufacturer of industrial chillers, providing you with high-quality and reliable units.
<br>
What are the Key Features to Consider in an Anodizing Chiller?
When selecting an anodizing chiller, several key features need to be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Firstly, the cooling capacity is crucial. It determines the chiller’s ability to remove heat from the anodizing solution and maintain the desired temperature. The cooling capacity is typically measured in tons or BTUs per hour and needs to be sized appropriately for the volume of the anodizing tank, the heat load generated by the process, and the desired operating temperature.
Secondly, the type of refrigerant used is important for environmental and efficiency reasons. Modern chillers often use environmentally friendly refrigerants with low global warming potential (GWP). The chiller’s control system is also a critical feature. It should allow for precise temperature control and monitoring, with alarms and safety features to prevent overheating and other issues. Finally, the chiller’s construction and materials should be durable and corrosion-resistant, especially considering the often-corrosive environment of anodizing operations. Look for watergekoeld options if you need higher efficiency and have access to a cooling water source. We also have a diverse line of cooling equipment that includes custom pump tank systems and systems that can be equipped with heaters. We specialize in cooling and anodizing chiller needs.
<br>
What are the Different Types of Anodizing Processes and How Do They Impact Chiller Selection?
There are various types of anodizing processes, each with its own specific requirements and operating parameters. The most common type is sulfuric acid anodizing, which is widely used for general-purpose applications. Other types include chromic acid anodizing, often used for aerospace applications due to its superior corrosion resistance, and hard coat anodizing (Type III), which produces a thicker and more wear-resistant coating. The specific type of anodizing being performed will impact the chiller selection process. For instance, chromic acid anodizing typically requires lower temperatures than sulfuric acid anodizing, and hard coat anodizing generates more heat due to the higher current densities involved. Different metal finishes require different approaches.
The choice of electrolyte solution also affects the chiller selection. Some electrolytes are more corrosive than others, requiring chillers with corrosion-resistant materials and components. Additionally, the operating temperature range varies depending on the type of anodizing and the desired coating properties. Understanding the specific requirements of the anodizing process is therefore crucial for selecting the right chiller that can provide the necessary koeling performance and withstand the operating environment. For specialized processes like titanium anodizing, you might need a custom-designed chiller. These products come with specific features designed for various applications of anodizing chillers. Also, we are a manufacturer and supplier in China and can supply the equipment for your metal finishing needs We also produce plating chillers in our facility.
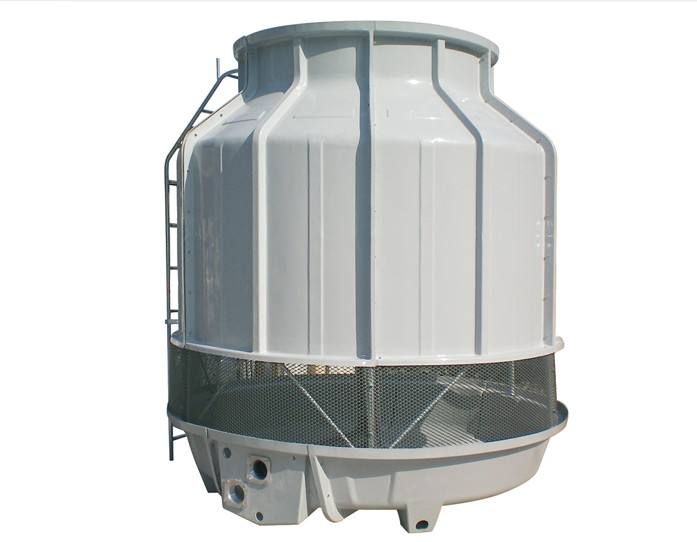
What are the advantages of water-cooled anodizing chillers?
Water-cooled anodizing chillers offer several advantages over air-cooled chillers in certain applications. Firstly, they typically have a higher cooling capacity and efficiency, making them suitable for larger anodizing tanks and higher heat loads. Secondly, watergekoelde koelmachines have a smaller footprint than air-cooled chillers of the same capacity, which can be an advantage in facilities with limited space. Thirdly, water-cooled chillers are highly effective for managing heat from anodizing processes in various manufacturing applications.