-
Dalingshan Industrieel Guangdong

does hydroponic water temp affect growth?
Best Temperature for Hydroponics: Mastering Water Temperature for Optimal Nutrient Solution and Plant Growth
This article will guide you through the critical importance of maintaining the ideal water temperature in your hydroponic system. You will learn how the solution temperature directly impacts nutrient uptake and overall plant growth. By understanding these principles, you can optimize your hydroponics setup for healthier plants and more abundant harvests. This is a must-read for anyone serious about maximizing their hydroponic gardening, whether you’re a beginner or an experienced grower.
Inhoudsopgave
1. What is the Ideal Water Temperature for Hydroponics?
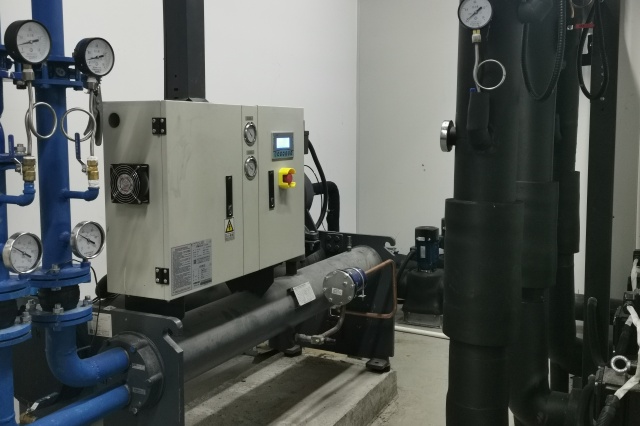
As a manufacturer of industrial water chillers, I often get asked about the ideal water temperature for hydroponics. Generally, the best temperature for most hydroponic systems is between 65°F and 80°F (18°C – 27°C). This temperature range allows for optimal nutrient absorption and healthy plant growth. It’s important to note that the ideal water temperature may vary slightly depending on the specific crop you are growing. For example, some leafy greens prefer slightly cooler temperatures, while fruiting plants like tomatoes may thrive in slightly warmer water.
Maintaining this ideal temperature range is crucial for several reasons. First, water temperature directly affects the amount of dissolved oxygen in the nutrient solution. Warmer water holds less oxygen than cool water, and plants require adequate oxygen for healthy root development and nutrient uptake. Secondly, the solution temperature influences the rate of nutrient absorption. When the water temperature is within the optimal range, plants can efficiently absorb the nutrients they need for healthy growth. My experience has shown that growers who pay close attention to water temperature consistently achieve better results, our products in the Plastics and Rubber Industry can help you achieve better results.
2. How Does Water Temperature Affect Plant Growth in Hydroponics?
Water temperature plays a pivotal role in plant growth within hydroponic systems. As an expert in this field, I’ve seen firsthand how fluctuations in water temperature can significantly impact the health and productivity of hydroponic crops. When the water temperature is too high, it can lead to several issues. First, as mentioned earlier, warmer water holds less dissolved oxygen. This can cause oxygen deprivation in the root zone, leading to stress, reduced nutrient uptake, and even root rot. High water temperatures can also promote the growth of harmful pathogens, such as Pythium, which can devastate a hydroponic crop.
Conversely, when the water temperature is too low, it can also negatively affect plant growth. Cold water can shock the plant roots, slowing down their metabolism and reducing their ability to absorb nutrients and water. This can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced yields. In severe cases, prolonged exposure to cold water temperatures can even kill hydroponic plants. That’s why it’s so important to maintain the water temperature within the optimal range for your specific crop. Through proper temperature control, we’ve helped numerous clients in the Machining Industry optimize their hydroponic systems.
3. Why is Maintaining Nutrient Solution Temperature Crucial in Hydroponics?
Maintaining the proper nutrient solution temperature is essential for a successful hydroponic operation. The temperature of the nutrient solution directly impacts the solubility and availability of nutrients to the plants. When the solution temperature is within the ideal range, the nutrients remain dissolved and readily available for uptake by the plant roots. However, if the temperature fluctuates too much, certain nutrients may precipitate out of the solution, making them unavailable to the plants.
In my experience, stable nutrient solution temperature is particularly important in recirculating hydroponic systems, such as the NFT hydroponic system. In these systems, the nutrient solution is continuously circulated past the plant roots, making it more susceptible to temperature changes. By carefully monitoring and controlling the solution temperature, you can ensure that your plants have consistent access to the nutrients they need for optimal growth. Proper temperature management of the nutrient water is one of the keys to maximizing yields in any hydroponic setup. The Food and Beverage Industry has successfully implemented our water chillers to enhance their hydroponic operations.
4. What Happens When Hydroponic Water Temperature is Too High or Too Low?
As mentioned earlier, extreme water temperatures can have detrimental effects on hydroponic plants. When the water temperature is too high, above 80°F (27°C), several problems can occur. The most immediate issue is the reduced oxygen content in the water. As water temperature increases, its ability to hold dissolved oxygen decreases. This can lead to oxygen deficiency in the root zone, stressing the plants and making them more susceptible to diseases like root rot. High temperatures also accelerate the evaporation of water from the hydroponic system, which can lead to increased salt concentration in the nutrient solution, potentially damaging the plants.
On the other hand, when the water temperature is too low, below 65°F (18°C), plant growth can be significantly slowed. Colder water reduces the metabolic rate of the plant roots, making it difficult for them to absorb nutrients and water. This can result in stunted growth, nutrient deficiencies, and reduced yields. Additionally, low temperatures can make plants more susceptible to certain diseases and pests. Maintaining a consistent water temperature within the optimal range is crucial for avoiding these issues and ensuring healthy plant growth. Based on our experience, the Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industry greatly benefits from precise temperature control in their hydroponic setups.
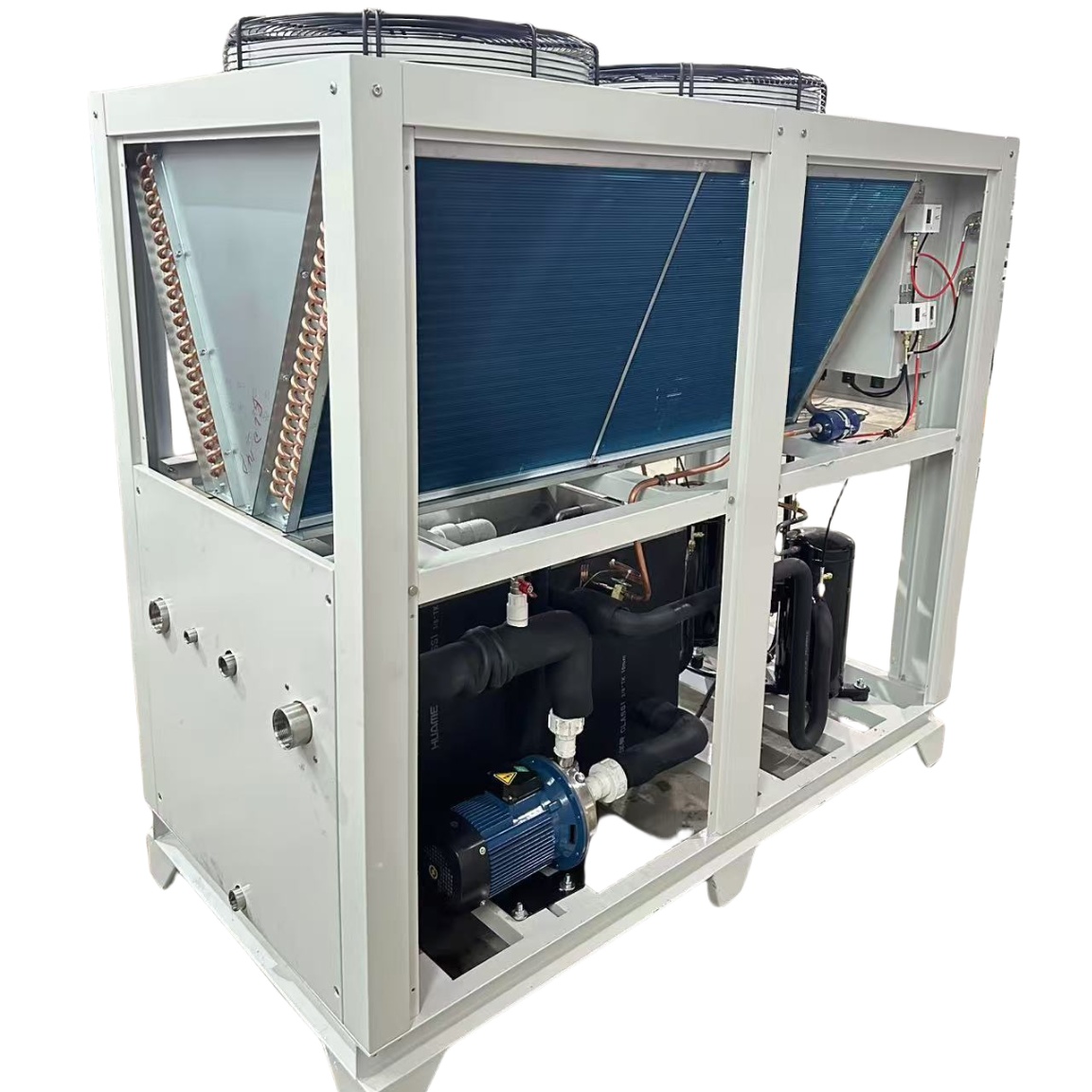
5. How Can a Water Chiller or Heater Help Regulate Hydroponic Water Temperature?
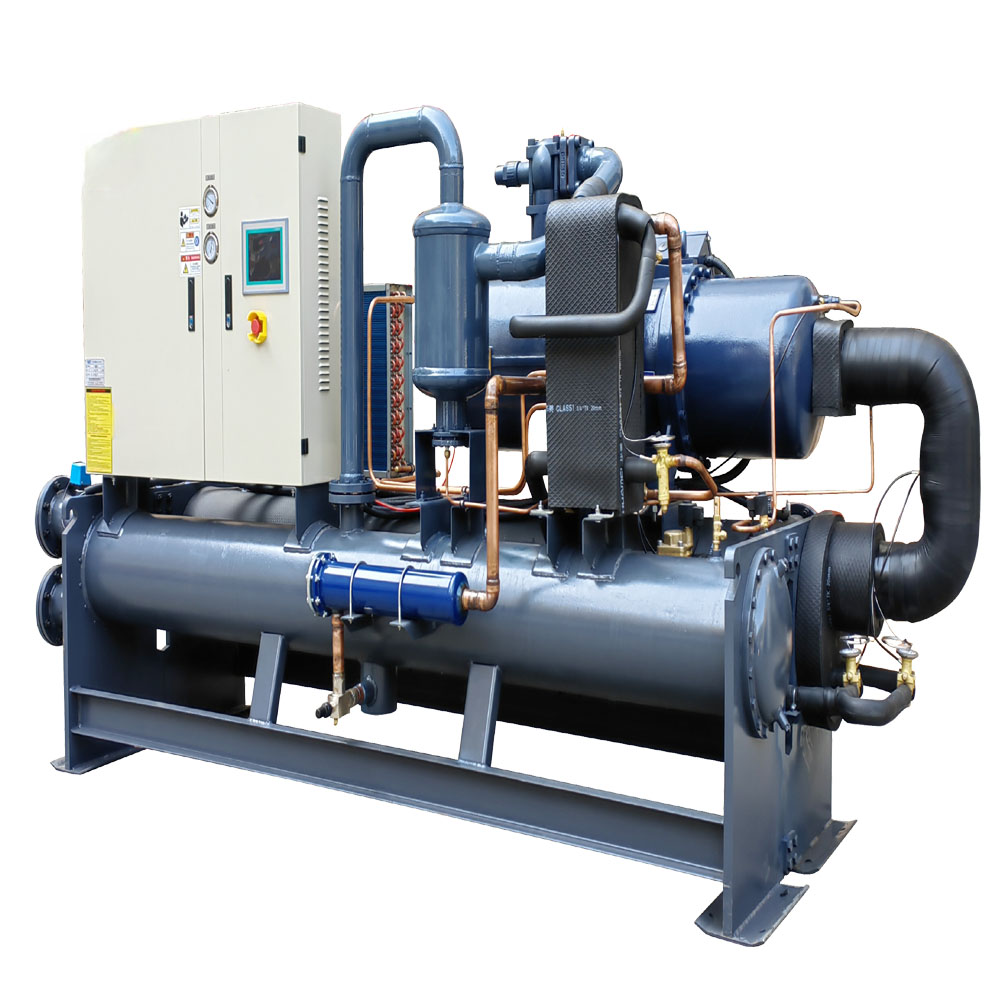
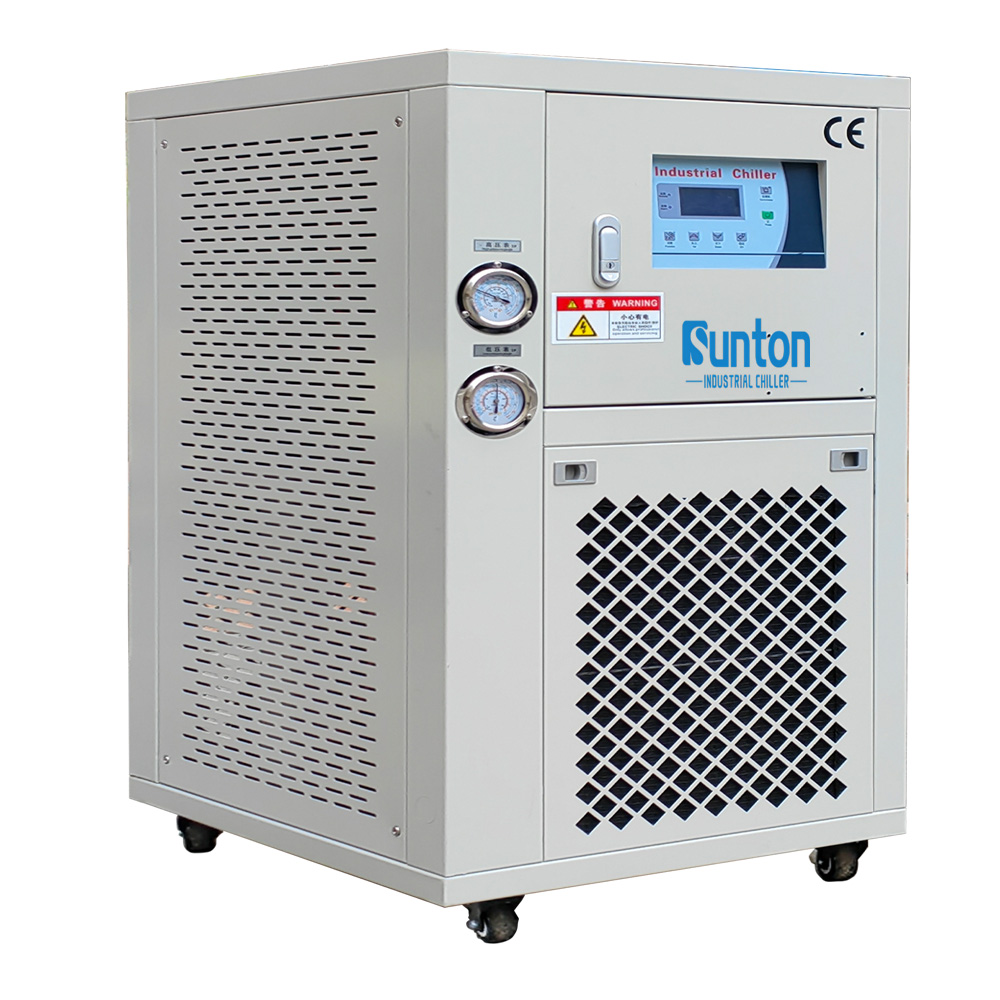
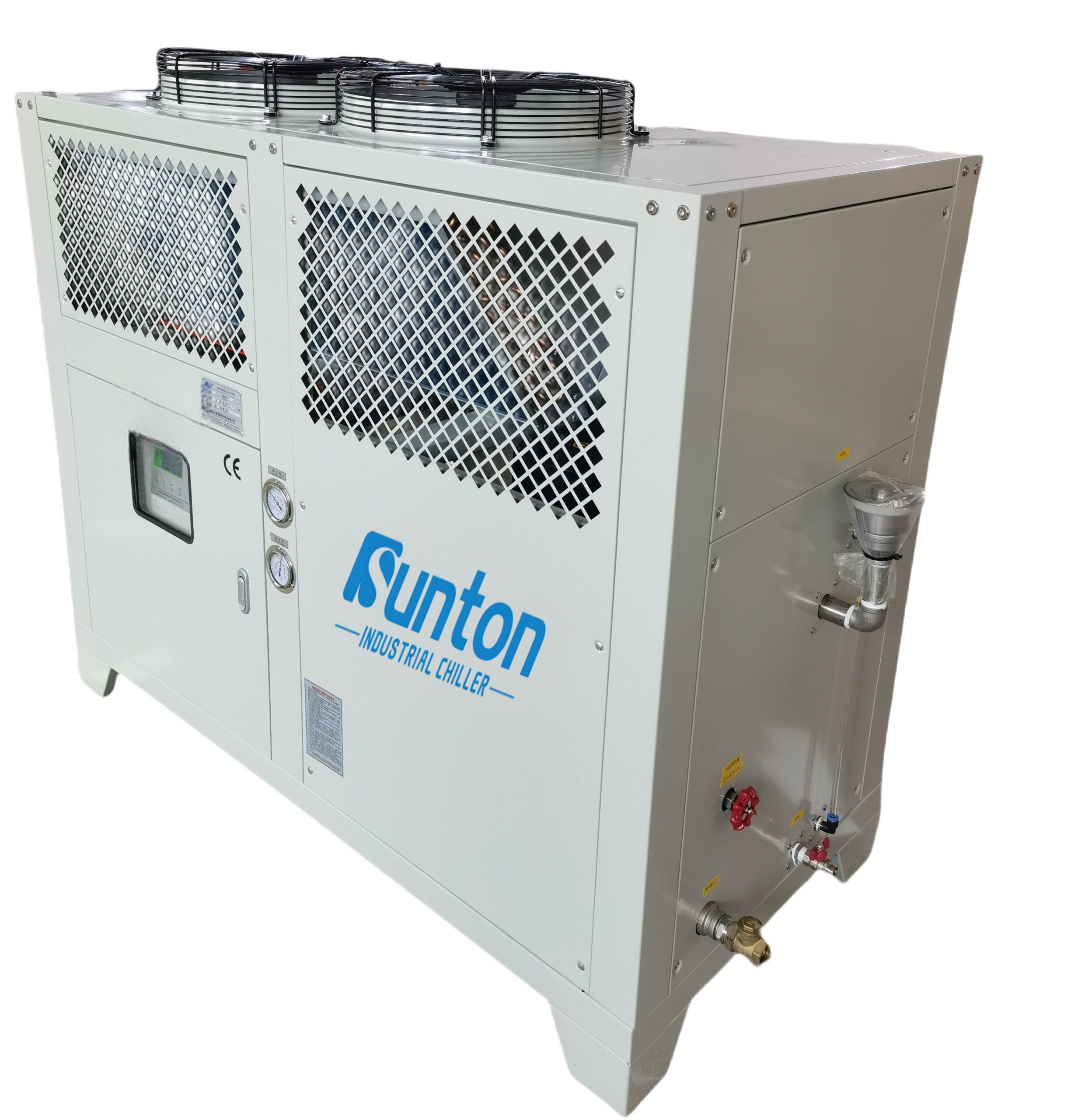
Controlling water temperature in a hydroponic system can be challenging, especially in environments with fluctuating air temperatures. This is where waterkoelers en heaters come into play. A water chiller is a device that cools the water in the hydroponic reservoir to the desired temperature. This is particularly useful in hot climates or during the summer months when water temperatures tend to rise. By using a water chiller, you can maintain a consistent, cool water temperature, ensuring optimal oxygen levels and nutrient uptake for your plants.
Conversely, a heater is used to warm the water in the hydroponic reservoir during colder months or in cooler climates. By maintaining a stable, warm water temperature, a heater prevents the water from becoming too cold and shocking the plant roots. This ensures that the plants can continue to absorb nutrients efficiently and maintain healthy growth even when the ambient temperature drops. In my experience, using a combination of a water chiller and a heater is the most effective way to maintain optimal water temperature throughout the year. Our products have proven essential for businesses in the Electronics Industry, where temperature control is critical.

6. What is the Role of Root Zone Temperature in Hydroponic Systems?
De root zone temperature is a critical factor in hydroponic systems, often overlooked but just as important as the water temperature. The root zone refers to the area surrounding the plant roots, including the growing medium and the nutrient solution. Maintaining an optimal root zone temperature is essential for healthy root development and nutrient uptake. In general, the ideal root zone temperature is similar to the ideal water temperature, typically between 65°F and 80°F (18°C – 27°C).
When the root zone temperature is within this range, the plant roots can efficiently absorb water and nutrients. The roots’ metabolic processes function optimally, allowing for healthy growth and development. However, if the root zone temperature deviates too much from the ideal range, problems can arise. For example, if the root zone is too warm, it can promote the growth of harmful pathogens and reduce oxygen levels, leading to root disease. Conversely, if the root zone is too cold, it can slow down root metabolism and hinder nutrient uptake. By monitoring and controlling the root zone temperature, you can create a healthy environment for your plant roots and promote vigorous growth.
7. How Do Different Types of Hydroponic Systems Influence Water Temperature Control?
The type of hydroponic system you use can significantly impact water temperature control. In general, hydroponic systems that use a larger volume of water, such as deep water culture (DWC) systems, are more stable in terms of water temperature. This is because a larger water volume takes longer to heat up or cool down, making it less susceptible to rapid temperature fluctuations. On the other hand, systems that use a smaller water volume, such as NFT hydroponic systems, can be more challenging to manage in terms of water temperature.
In an NFT system, a thin film of nutrient solution flows continuously over the plant roots. This small volume of water can heat up or cool down quickly, especially in response to changes in the ambient temperature. As a result, it’s crucial to monitor the water temperature closely in NFT systems and use waterkoelers or heaters as needed to maintain the optimal range. Similarly, in aeroponic systems, where the plant roots are suspended in the air and misted with nutrient solution, water temperature control can be challenging. The fine mist of water droplets can quickly change temperature, so it’s important to use a system that can maintain a consistent temperature of the nutrient solution.
8. What are the Best Practices for Monitoring and Adjusting Hydroponic Water Temperature?
Monitoring and adjusting hydroponic water temperature is a continuous process that requires attention to detail. The first step is to accurately measure the water temperature using a reliable thermometer. There are various types of thermometers available, including digital and analog models. It’s important to choose a thermometer that is specifically designed for use in liquids and can provide accurate readings within the relevant temperature range.
Once you have a thermometer, you should regularly measure the water temperature in your hydroponic reservoir. The frequency of measurement will depend on several factors, including the type of hydroponic system you are using, the ambient temperature, and the time of year. In general, it’s a good idea to measure the water temperature at least once a day, and more frequently during periods of extreme temperatures. In addition to measuring the water temperature, it’s also important to monitor the air temperature in the growing environment.
| Monitoring Practice | Frequency | Notes |
| Measure Water Temperature | Daily | Use a reliable thermometer; check more frequently during temperature extremes. |
| Monitor Air Temperature | Daily | Ensure the growing environment is within the acceptable range for your plants. |
| Check Nutrient Solution Levels | Daily | Low levels can lead to temperature fluctuations; refill as needed. |
| Inspect for Algae/Pathogen Growth | Weekly | High temperatures can promote growth; address any issues immediately. |
| Calibrate Equipment | Monthly | Ensure thermometers, chillers, and heaters are functioning accurately. |
| Review Historical Data | Monthly/Yearly | Analyze trends to anticipate and prevent issues related to seasonal temperature changes. |
| Inspect Insulation | Seasonally | Check reservoir and piping insulation to minimize temperature fluctuations, especially in extreme weather conditions. |
| Monitor Plant Health | Continuously | Observe plants for signs of temperature stress, such as wilting or discoloration, and adjust water temperature accordingly. |
9. Case Study: Optimizing Water Temperature for Hydroponic Lettuce
Hydroponic lettuce is a popular crop among hydroponic growers due to its fast growth and relatively simple requirements. However, maintaining the optimal water temperature is crucial for achieving high yields and quality produce. In one case study, a grower was experiencing issues with slow growth and tip burn in their hydroponic lettuce crop. Upon investigation, it was discovered that the water temperature in the hydroponic reservoir was consistently above 80°F (27°C), especially during the afternoon.
To address this issue, the grower installed a water chiller to cool the nutrient solution. They set the chiller to maintain a water temperature of 68°F (20°C), which is within the ideal range for hydroponic lettuce. Within a few days of installing the chiller, the grower noticed a significant improvement in the growth rate and overall health of the lettuce plants. The tip burn issue was resolved, and the plants began producing larger, more vibrant leaves. This case study demonstrates the importance of maintaining optimal water temperature for hydroponic crops. By using a water chiller to cool the nutrient solution, the grower was able to create a more favorable growing environment and achieve better results. If you’re in the Medical Industry, consider how our chillers can benefit your operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the ideal water temperature for most hydroponic plants?
The ideal water temperature for most hydroponic plants is between 65°F and 80°F (18°C – 27°C). This temperature range allows for optimal nutrient absorption and healthy plant growth. However, it’s important to research the specific temperature requirements for the particular crop you are growing, as some plants may prefer slightly cooler or warmer temperatures.
2. How does water temperature affect nutrient uptake in hydroponics?
Water temperature significantly impacts nutrient uptake in hydroponics. When the water temperature is within the optimal range, the nutrients in the solution remain dissolved and readily available for the plant roots to absorb. However, if the water temperature is too high or too low, it can interfere with nutrient solubility and uptake, leading to nutrient deficiencies and reduced plant growth.
3. Can I use tap water in my hydroponic system?
While you can use tap water in your hydroponic system, it’s essential to test the water quality first. Tap water may contain chlorine, chloramine, and other chemicals that can harm hydroponic plants. It’s also important to check the pH and EC (electrical conductivity) of the tap water and adjust them as needed to meet the requirements of your hydroponic crop. Before adding water to your reservoir, make sure to adjust the temperature before adding.
4. How often should I change the nutrient solution in my hydroponic system?
The frequency of nutrient solution changes depends on several factors, including the type of hydroponic system, the size of the reservoir, the number of plants, and the growth stage of the plants. In general, it’s recommended to change the nutrient solution every 1-2 weeks. However, you may need to change it more frequently if you notice signs of nutrient deficiencies, algae growth, or other issues.
5. What are some signs that my hydroponic water temperature is not optimal?
There are several signs that your hydroponic water temperature may not be optimal. If the water temperature is too high, you may notice wilting, yellowing leaves, slow growth, or signs of root rot. If the water temperature is too low, you may see stunted growth, nutrient deficiencies, or leaf discoloration. It’s important to monitor your plants closely and take action to adjust the water temperature if you notice any of these signs.
6. What should I do if the water temperature in my hydroponic system is consistently too high or too low?
If the water temperature in your hydroponic system is consistently too high or too low, you may need to take steps to adjust it. For high water temperatures, you can use a water chiller to cool the nutrient solution. You can also try increasing the water volume in your reservoir, improving ventilation, or shading the reservoir from direct sunlight. For low water temperatures, you can use a heater to warm the nutrient solution. You can also try insulating the reservoir, moving the system to a warmer location, or using a larger water volume.
Conclusion
- Maintaining the ideal water temperature is crucial for success in hydroponics.
- The optimal water temperature range for most hydroponic plants is 65°F to 80°F (18°C to 27°C).
- Water temperature affects nutrient solubility, oxygen levels, and plant growth.
- Using waterkoelers en heaters can help regulate hydroponic water temperature.
- The type of hydroponic system can influence water temperature control.
- Regularly monitoring and adjusting water temperature is essential for healthy plant growth.
- Different crops may have specific water temperature requirements. For example, hydroponic lettuce often prefers slightly cooler temperatures.
- De root zone temperature is just as important as the water temperature.
- Extreme water temperatures can lead to various issues, including reduced yields, nutrient deficiencies, and root disease.
By understanding the importance of water temperature in hydroponics and implementing the best practices for monitoring and adjusting it, you can create an optimal growing environment for your plants and achieve greater success in your hydroponic endeavors. Remember that as an industrial waterkoelers manufacturer, I’ve seen firsthand how precise temperature control can make a significant difference in various industries, from plastics and rubber to food and beverage. Don’t hesitate to reach out if you need help optimizing your hydroponic system’s temperature control.