-
Dalingshan Industrial Guangdong
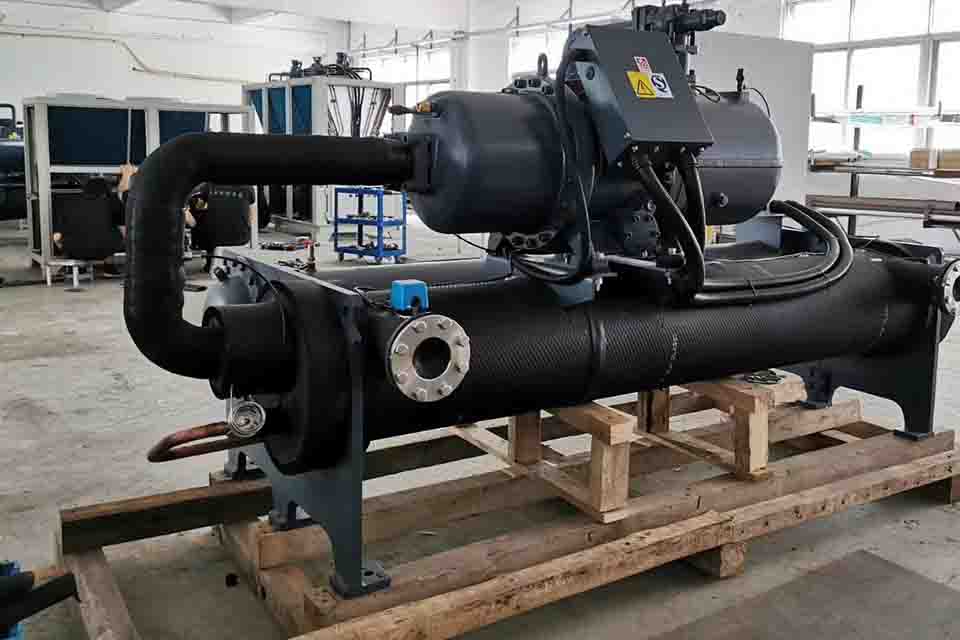

What are the 3 Types of Water-Cooled Condensers Used in Industrial Refrigeration?
Water-Cooled Condensers Used in Industrial Refrigeration
Water-cooled condenser types for industrial refrigeration: working, benefits, and uses.
Daftar Isi
What is a Water-Cooled Condenser and How Does It Work?
A kondensor berpendingin air adalah komponen penting dalam banyak hal pendinginan systems, particularly in industrial settings. Unlike kondensor berpendingin udara that use ambient air to cool the refrigerant, water-cooled condensers use water sebagai pendinginan medium. This jenis kondensor adalah sangat efisien because water has a higher capacity to absorb heat than air. In a water-cooled system, hot uap refrigeran dari kompresor memasuki kondensor, where it comes into contact with tubes or plates cooled by water flowing through the system. The perpindahan panas process causes the refrigeran untuk mengembun dari sebuah menguap back into a liquid.
Condenser work involves removing panas dari refrigeran, allowing it to change state. This is essential for the siklus pendinginan to continue. The water-cooled condenser unit is typically connected to a menara pendingin atau sumber lain air pendingin that helps dissipate the heat from the condenser. This setup makes pendingin berpendingin air particularly effective in environments where air cooling is insufficient or where precise temperature control is necessary. Our water-cooled condensers fitur sebuah highly efficient water-cooled design that ensures optimal performance. We understand that every facility has unique needs, and we’re committed to helping you find the perfect kondensor berpendingin air solusi.
What are the Three Primary Types of Water-Cooled Condensers?
Ada tiga jenis utama kondensor digunakan dalam berpendingin air systems: cangkang dan tabung, pelat yang dibrazing, and coaxial tube-in-tube. Each jenis kondensor offers unique benefits and is suited to different applications. Shell and tube condensers are known for their robustness and ease of maintenance, making them a popular choice in large industrial setups. A brazed plate heat exchanger provides a compact and efficient solution, ideal for applications with space constraints. Coaxial tube-in-tube kondensor, while less common in large-scale operations, are appreciated for their simplicity and effectiveness in smaller systems.
Memahami types of water-cooled systems available is crucial for selecting the right equipment. For example, the three types dari water-cooled condensers each cater to specific needs within industrial and commercial applications. Whether you need to cool machinery in a plastics factory or maintain precise temperatures in a laboratory, the right jenis kondensor can significantly impact efficiency and performance. Water-cooled condensers use water from an external source to provide optimal pendinginan, making them a reliable choice for many industries.
How Does a Shell and Tube Condenser Work in Industrial Settings?
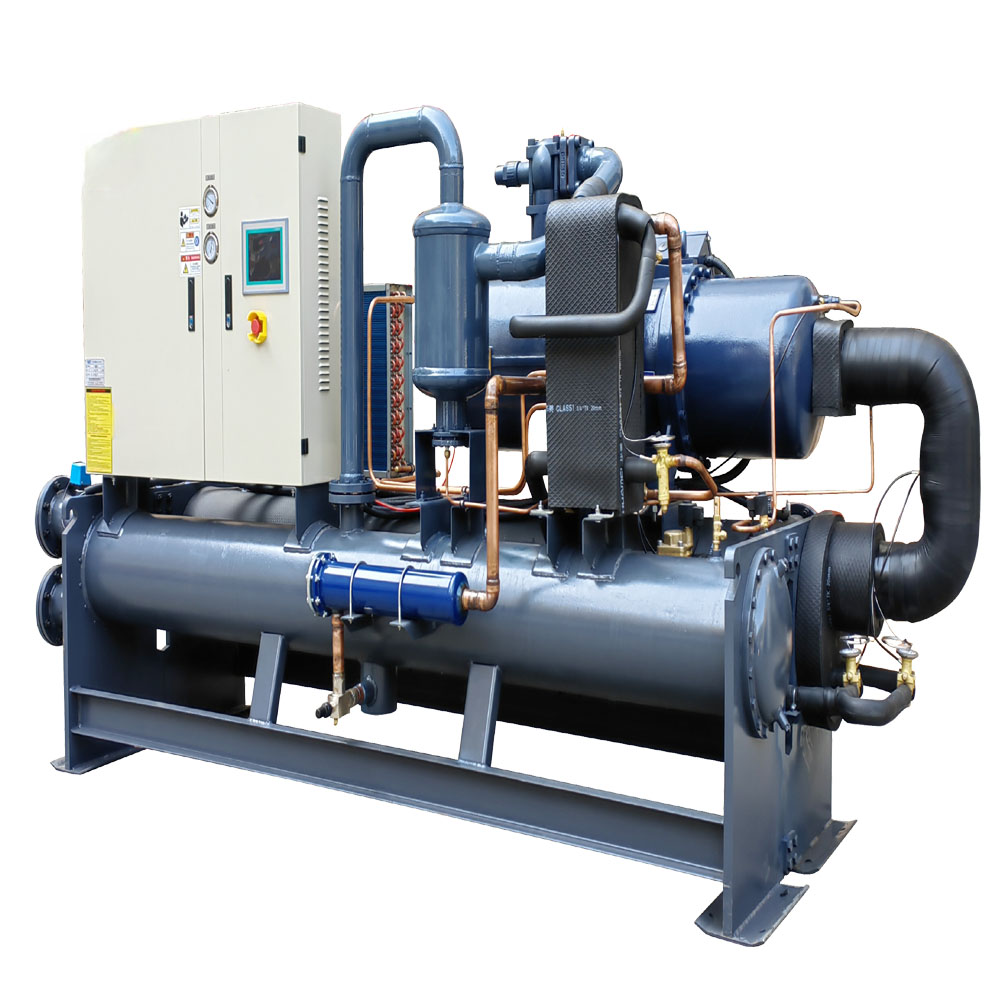
The shell and tube condenser is one of the most common types dari water-cooled condensers digunakan dalam pendingin industri. It consists of a cangkang silinder that houses a bundle of straight water tubes. Hot refrigerant vapor dari kompresor memasuki shell and flows around the outside of the tubes. Cooling water circulates through the water tubes, menyerap panas dari refrigeran. Ini perpindahan panas process causes the refrigeran untuk mengembun into a liquid.
In this type of kondensor, yang water flows in the opposite direction to the refrigeran untuk memaksimalkan heat transfer rate. This counterflow arrangement ensures that the coldest water makes contact with the refrigeran that is about to exit the kondensor, enhancing efficiency. Shell and tube condensers are favored in industrial settings due to their ability to handle high pressures and their ease of cleaning. Maintenance often involves removing the end covers to access the water tubes for inspection and cleaning, helping to prevent korosi and maintain optimal performance. They are commonly used to cool large volumes of refrigeran in applications such as chemical processing and large-scale air conditioning systems.
Apa Keuntungan Menggunakan Penukar Panas Pelat Brazing sebagai Kondensor?
A brazed plate heat exchanger used as a kondensor offers a compact and sangat efisien solution for pendinginan di sebuah sistem pendingin. Ini jenis kondensor consists of a series of thin, corrugated plates that are brazed together to create a series of channels. Hot refrigerant dan air pendingin flow through alternating channels, facilitating rapid perpindahan panas. The large surface area provided by the plates, combined with the turbulent flow of the fluids, results in a very efficient perpindahan panas proses.
One of the primary advantages of brazed plate condensers is their compact size. They require significantly less space than kondensor cangkang dan tabung, making them ideal for applications where space is limited, such as in packaged pendingin berpendingin air or in retrofitting existing systems. Additionally, brazed plate heat exchangers are known for their high efficiency and ability to operate with smaller temperature differences between the refrigeran dan air pendingin. This can lead to lower konsumsi air and reduced operating costs. As a manufacturing plant specializing in industrial water chillers, we can incorporate brazed plate heat exchangers into systems designed for industries like plastics, food processing, and laboratories.
Why are Coaxial Tube-in-Tube Condensers Less Common in Large Industrial Applications?
Coaxial tube-in-tube kondensor, juga dikenal sebagai shell and coil condensers, are a simpler type of water-cooled condenser. They consist of one tube (the outer tube) with a smaller gulungan or tube inside it (the inner tube). Typically, air pendingin flows through the inner gulungan, ketika hot refrigerant vapor flows in the space between the inner and outer tube. Itu perpindahan panas occurs through the wall of the inner gulungan, menyebabkan refrigeran untuk mengembun.
While coaxial kondensor are efficient and compact, they are less common in large industrial applications for several reasons. One key limitation is their difficulty in cleaning and maintenance. Unlike kondensor cangkang dan tabung, coaxial kondensor cannot be easily disassembled for cleaning, which can be a significant drawback in applications where water quality is poor or where the refrigeran is prone to causing fouling. Additionally, the perpindahan panas capacity of coaxial kondensor is generally lower than that of cangkang dan tabung atau pelat yang dibrazing options, making them less suitable for high-capacity pendingin industri systems. However, they can still be a viable option for smaller, specialized applications where their simplicity and compact size are advantageous. We offer a range of kondensor berpendingin air solutions, including custom designs to fit specific industrial needs.
What Role Does Water Quality Play in the Efficiency of Water-Cooled Condensers?
Water quality is a critical factor in the performance and longevity of any kondensor berpendingin air. Impurities in the air pendingin, such as minerals, sediment, and biological growth, can lead to scaling, fouling, and korosi dalam kondensor. These issues can significantly reduce the perpindahan panas efficiency of the system and increase the risk of equipment failure. For example, hard water with high mineral content can cause scale buildup on the water tubes di sebuah shell and tube condenser or the plates in a brazed plate heat exchanger.
To mitigate these problems, it’s essential to use treated or filtered water in berpendingin air systems. Regular monitoring of water quality and implementing appropriate water treatment measures, such as chemical treatments or filtration, can help maintain optimal performance. In some cases, using a menara pendingin with a water treatment system can provide a continuous supply of clean air pendingin. Proper maintenance, including regular cleaning and inspection of the water side dari kondensor, is also crucial. Ensuring good water quality not only enhances the efficiency of the proses pendinginan but also extends the lifespan of the equipment, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
How to Choose the Right Water-Cooled Condenser for Your Industrial Needs?
Memilih yang sesuai kondensor berpendingin air for your industrial application involves considering several factors. First, assess the heat load of your system to determine the required kondensor capacity. This will help you decide between different types of condensers used, seperti cangkang dan tabung, pelat yang dibrazing, or coaxial designs. Consider the available space for installation; if space is limited, a compact brazed plate heat exchanger might be preferable.
Water quality is another crucial consideration. If your water source is prone to causing scaling or fouling, a shell and tube condenser, which is easier to clean, might be a better choice. Evaluate the operating temperatures and pressures of your system to ensure the selected kondensor can handle these conditions. Additionally, consider the energy efficiency of different condenser types. Brazed plate condensers often offer higher efficiency, which can lead to lower operating costs. In choosing the best option for your needs, it is essential to consider factors such as cooling capacity, flow rate, and pressure requirements.
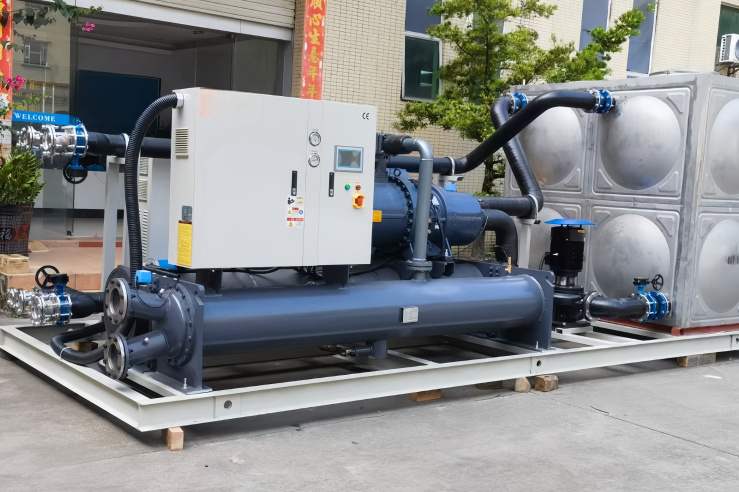
Here is an image of a Glycol Chiller:

What Maintenance is Required for Water-Cooled Condensers to Ensure Longevity?
Regular maintenance is essential to keep water-cooled condensers operating efficiently and to extend their lifespan. The specific maintenance tasks depend on the jenis kondensor but generally include cleaning, inspecting for leaks, and monitoring water quality. For kondensor cangkang dan tabung, maintenance often involves removing the end covers to access the water tubes for cleaning. This helps remove any scale or fouling that can reduce perpindahan panas efisiensi.
Brazed plate heat exchangers typically require less maintenance but should still be inspected regularly for signs of clogging or leakage. Chemical cleaning or backflushing may be necessary to maintain their performance. Monitoring the water quality and implementing appropriate water treatment measures are crucial for all types of water-cooled systems. Regular inspections should also include checking for korosi and ensuring that all connections are secure. By establishing a proactive maintenance schedule, you can prevent unexpected downtime, reduce repair costs, and ensure your kondensor berpendingin air continues to provide reliable pendinginan for your industrial processes.
Can Water-Cooled Condensers Be Used with a Cooling Tower?
Ya, water-cooled condensers are often used in conjunction with a menara pendingin in many industrial applications. A menara pendingin is a heat rejection device that removes waste heat from the condenser water and releases it into the atmosphere. In this setup, the water circulating melalui kondensor menyerap panas dari refrigeran and then flows to the menara pendinginDi dalam menara pendingin, the warm water is sprayed over a fill material, and outdoor air is drawn through the tower, causing some of the water to evaporate.
This evaporative proses pendinginan reduces the temperature of the remaining water, which is then returned to the kondensor to continue the cooling cycle. Using a menara pendingin dengan kondensor berpendingin air allows for continuous operation and helps maintain optimal pendinginan efficiency. It’s particularly beneficial in applications where large amounts of heat need to be dissipated, such as in chemical plants, power generation, and large air conditioning systems. This combination is highly effective in maintaining consistent temperatures and ensuring efficient operation of the sistem pendingin. Check HVAC Chiller Solutions page to learn more about HVAC applications.
What are the Environmental Impacts of Using Water-Cooled Condensers?
Ketika water-cooled condensers offer high efficiency and are often preferred in industrial settings, they do have environmental implications that need to be considered. One primary concern is konsumsi air. berpendingin air systems, especially those using once-through pendinginan, can use significant amounts of water. However, systems that incorporate menara pendingin can reduce water usage by recirculating and cooling the water.
Another environmental aspect is the potential for thermal pollution. If air pendingin is discharged directly into a natural water body at a higher temperature, it can affect aquatic ecosystems. Proper management and treatment of discharge water are essential to mitigate this impact. Additionally, the energy consumption of berpendingin air systems, including the kompresor and pumps, contributes to their overall environmental footprint. However, the high efficiency of water-cooled condensers, khususnya pelat yang dibrazing designs, can lead to lower energy use compared to some berpendingin udara alternatives.
Pertanyaan Umum
What are the main advantages of water-cooled condensers over air-cooled condensers?
Kondensor berpendingin air offer higher efficiency, especially in high-temperature environments, because water is a more effective pendinginan medium than air. They provide more stable and precise temperature control, which is crucial for many industrial processes. Additionally, berpendingin air systems are generally quieter and can be installed indoors, offering more flexibility in system design.
How often should I clean my water-cooled condenser?
The frequency of cleaning depends on the jenis kondensor and the quality of your air pendingin. Shell and tube condensers may require cleaning every 6-12 months, while brazed plate heat exchangers might need less frequent cleaning. Regular monitoring of system performance and water quality can help determine the optimal cleaning schedule. Check Pendingin Anti-Ledakan page for specific needs.
Can I use any type of water in my water-cooled condenser?
It’s crucial to use treated or filtered water to prevent scaling, fouling, and korosi. Hard water or water with high levels of impurities can significantly reduce the efficiency and lifespan of your kondensor. Implementing a water treatment system, especially when using a menara pendingin, can help maintain optimal water quality.
What is the typical lifespan of a water-cooled condenser?
Dengan perawatan yang tepat, kondensor berpendingin air can last 15-20 years or even longer. The lifespan depends on factors such as the jenis kondensor, operating conditions, water quality, and the quality of maintenance. Regular inspections and timely repairs can help maximize the longevity of your equipment.
Are water-cooled condensers more energy-efficient than air-cooled condensers?
Secara umum, ya. Kondensor berpendingin air, especially those using brazed plate heat exchangers, are often more energy-efficient than berpendingin udara options. Water’s higher heat capacity allows for more efficient perpindahan panas, which can lead to lower energy consumption by the kompresor and overall system.
What industries benefit most from using water-cooled condensers?
Many industries that require precise temperature control and high pendinginan capacity benefit from water-cooled condensers. These include plastics and rubber manufacturing, chemical and pharmaceutical processing, food and beverage production, data centers, and large commercial buildings with centralized air conditioning systems. The Pendingin Susu Sapi Perah page provides information on specific uses in the dairy industry.
Kesimpulan
- Kondensor berpendingin air are crucial for efficient pendinginan in many industrial applications.
- Ada three primary types of water-cooled condensers: cangkang dan tabung, pelat yang dibrazing, and coaxial tube-in-tube.
- Shell and tube condensers are robust and easy to maintain, suitable for large industrial setups.
- Brazed plate heat exchangers offer compact and sangat efisien solusi.
- Water quality significantly impacts the performance and lifespan of water-cooled condensers.
- Regular maintenance, including cleaning and water treatment, is essential for optimal operation.
- Kondensor berpendingin air can be effectively used with menara pendingin for continuous pendinginan.
- Ketika berpendingin air systems have environmental considerations, their efficiency can lead to lower energy consumption compared to some alternatives.
- Memilih yang tepat kondensor berpendingin air involves considering factors like heat load, space availability, water quality, and operating conditions.
- Industries such as plastics, chemicals, food processing, and data centers greatly benefit from using water-cooled condensers.
By understanding these key points, industries can make informed decisions about implementing and maintaining kondensor berpendingin air systems, ensuring efficient and reliable pendinginan for their operations. If you’re ready to optimize your pendinginan system with a kondensor berpendingin air, contact us today to discuss your specific needs and explore our range of solutions! If you are working in textile industry check our Pendingin Industri Untuk Industri Tekstil page. Here you can find more info about Pendingin Industri Untuk Pertanian.