-
Dalingshan Industrial Guangdong

penukar panas vs. pendingin – mana yang lebih sesuai dengan kebutuhan Anda
Penukar Panas vs Pendingin: Mana yang Sesuai dengan Kebutuhan Anda?
Artikel ini membahas perbedaan penting antara penukar panas dan pendingin, dua komponen penting dalam berbagai aplikasi industri dan komersial. Memahami fungsi dan kemampuan masing-masing sistem sangat penting untuk mengoptimalkan sistem pendingin dan memastikan operasi yang efisien. Baik Anda berkecimpung di Industri Plastik dan Karet, Permesinan, Makanan dan Minuman, Kimia dan Farmasi, Elektronik, Laser, Percetakan, Medis, Laboratorium dan Lembaga Penelitian, atau Pusat Data, panduan ini akan memberikan wawasan berharga dalam memilih solusi yang tepat untuk kebutuhan spesifik Anda. Di akhir bacaan ini, Anda akan memiliki pemahaman yang jelas tentang cara kerja setiap sistem, aplikasinya, dan mengapa membuat keputusan yang tepat sangat penting bagi bisnis Anda. proses industri.
Daftar Isi
Apa itu Penukar Panas dan Bagaimana Cara Kerjanya?
A penukar panas adalah perangkat yang dirancang untuk memindahkan panas antara dua atau lebih cairan, biasanya cairan atau gas, tanpa mencampurnya. Penukar panas digunakan untuk memanaskan atau Dingin cairan dengan mentransfer panas dari satu cairan ke cairan lain. Salah satu jenis yang umum adalah penukar panas pelat, yang menggunakan serangkaian pelat tipis dan paralel untuk menciptakan area permukaan yang besar untuk perpindahan panasTipe lainnya adalah penukar kalor cangkang dan tabung, yang terdiri dari sekumpulan tabung yang terkurung dalam suatu cangkang.
Fungsi utama dari sebuah penukar panas adalah untuk memfasilitasi efisiensi pertukaran panas antara cairan. Misalnya, di pembangkit listrik, penukar panas mungkin bisa digunakan untuk memindahkan panas dari uap panas yang dihasilkan oleh boiler ke sistem air, memanaskan air sebelum memasuki boiler. Hal ini meningkatkan efisiensi proses pembangkitan listrik. Efektivitas penukar panas tergantung pada faktor-faktor seperti luas permukaan yang tersedia untuk perpindahan panas, laju aliran fluida, dan perbedaan suhu di antara keduanya. Saya harus menekankan bahwa sebagai salah satu industri berkualitas tinggi produsen pendingin dalam industri. Pengalaman saya menunjukkan bahwa penukar panas umumnya digunakan dalam berbagai aplikasi, termasuk sistem HVAC, pendinginan, dan pembangkit listrik.
Apa itu Chiller dan Apa Bedanya dengan Penukar Panas?
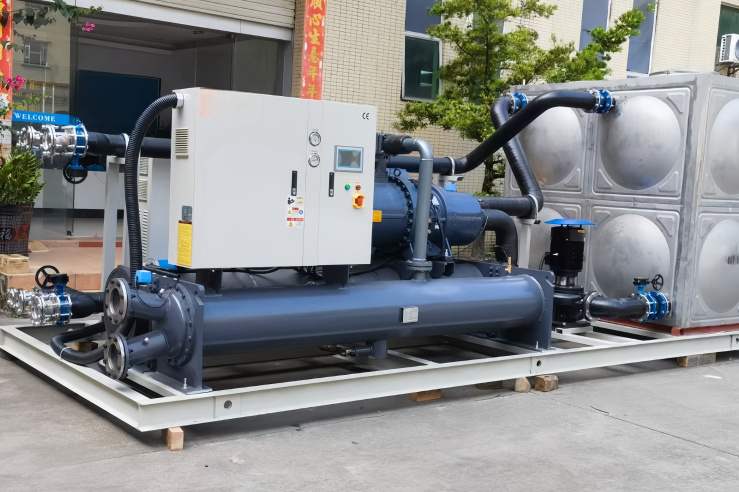
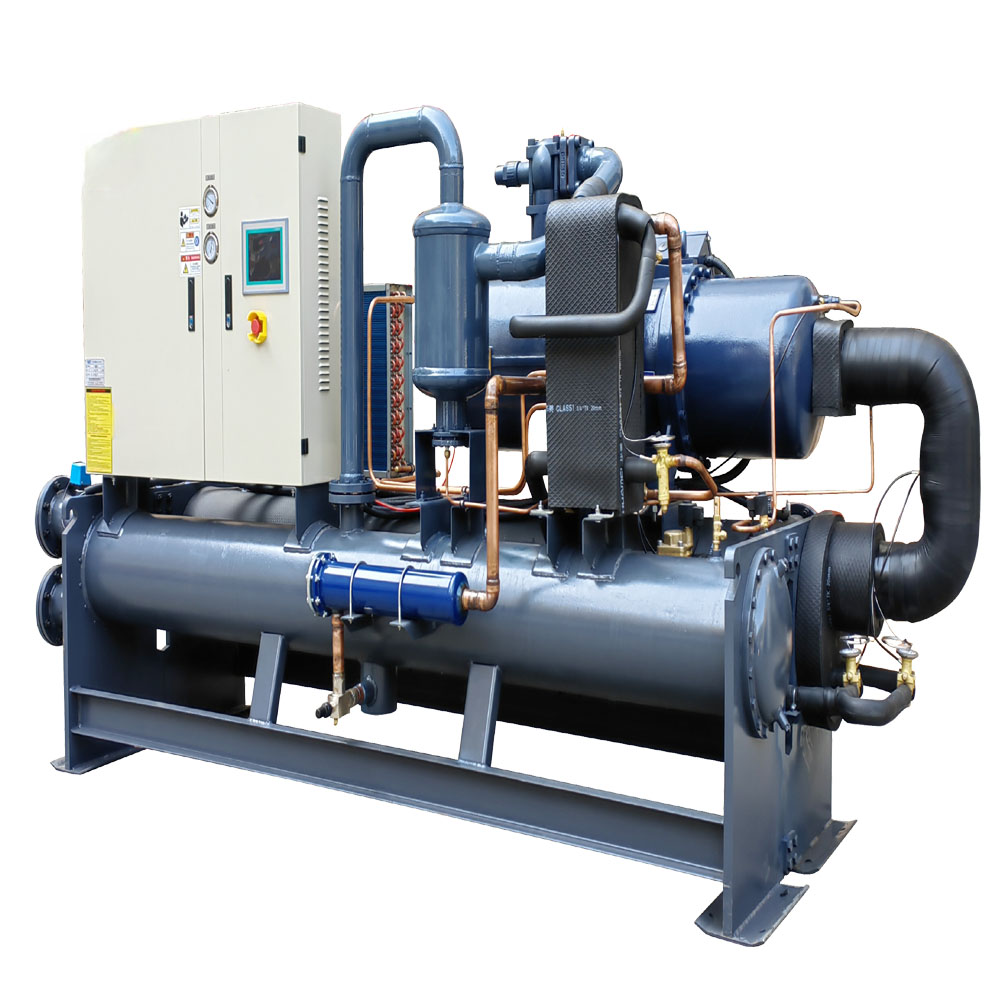
A pendingin adalah perangkat yang menghilangkan panas dari cairan melalui kompresi uap atau penyerapan pendinginan siklus. Cairan yang didinginkan ini kemudian dapat digunakan untuk Dingin peralatan atau aliran proses lainnya. Tidak seperti penukar panas, A pendingin dapat mencapai suhu yang jauh lebih rendah dan mampu secara aktif mendinginkan cairan di bawah suhu lingkungan. Itu perbedaan utama antara suatu penukar panas dan sebuah pendingin apakah itu penukar panas hanya mentransfer panas melalui berbagai cairan sedangkan sebuah pendingin secara aktif menghilangkan panas menggunakan unit pendingin.
Pendingin menggunakan refrigeran yang mengalami perubahan fase untuk menyerap dan menghilangkan panas dari air dingin. Itu refrigeran kemudian melewati sebuah kompresor, yang meningkatkan tekanan dan suhunya. Panas ini refrigeran kemudian didinginkan di kondensor, sering kali menggunakan air atau udara, sebelum diekspansi dan dikembalikan ke evaporator untuk memulai siklus lagi. Pendingin berpendingin air menggunakan air untuk Dingin itu kondensor, ketika pendingin berpendingin udara menggunakan udara sekitar. Pilihan antara pendingin berpendingin air dan pendingin berpendingin udara tergantung pada faktor-faktor seperti ketersediaan air, persyaratan efisiensi energi, dan aplikasi spesifik. Misalnya, dalam proses pencetakan injeksi plastik, pendingin digunakan untuk dengan cepat Dingin bagian yang dicetak, mengurangi waktu siklus dan meningkatkan kualitas produk. Anda dapat memeriksa Pendingin Air Sekrup Berpendingin Air.
Apa Saja Jenis Penukar Panas yang Berbeda?
Ada beberapa jenis penukar panas, masing-masing dirancang untuk aplikasi dan kondisi pengoperasian tertentu. Beberapa jenis yang umum meliputi:
- Penukar Panas Pelat: Ini terdiri dari serangkaian pelat bergelombang tipis yang ditumpuk bersama-sama. Cairan mengalir di antara pelat, dan luas permukaan yang besar memfasilitasi efisiensi perpindahan panas. Penukar panas pelat Umumnya digunakan dalam pengolahan makanan, sistem HVAC, dan pengolahan kimia karena desainnya yang ringkas dan efisiensi termal yang tinggi.
- Penukar Panas Selongsong dan Tabung: Tabung ini terdiri dari sekumpulan tabung yang tertutup dalam cangkang silinder. Satu cairan mengalir melalui tabung, sementara cairan lainnya mengalir di sekitar tabung di dalam cangkang. Penukar panas cangkang dan tabung serbaguna dan dapat menangani tekanan dan suhu tinggi, membuatnya cocok untuk pembangkit listrik, proses petrokimia, dan aplikasi kelautan.
- Penukar Panas Berpendingin Udara: Ini menggunakan udara sekitar untuk Dingin cairan, biasanya berupa cairan atau gas. Umumnya digunakan dalam aplikasi yang airnya tidak tersedia atau yang memerlukan konservasi air. Contohnya termasuk sistem HVAC, proses industri, dan pembangkit listrik.
Setiap jenis penukar panas memiliki kelebihan dan keterbatasan. Misalnya, penukar panas pelat menawarkan efisiensi tinggi dan bentuk yang ringkas tetapi tidak cocok untuk aplikasi tekanan tinggi. Penukar panas cangkang dan tabung dapat menangani tekanan yang lebih tinggi dan lebih kuat tetapi biasanya lebih besar dan kurang efisien.

Apa Aplikasi Utama Pendingin di Berbagai Industri?
Pendingin memainkan peran penting dalam berbagai industri, menyediakan pendinginan untuk berbagai proses dan peralatan. Berikut ini beberapa aplikasi utamanya:
- Industri Plastik dan Karet: Pendingin penting untuk mendinginkan cetakan dan peralatan dalam proses cetak injeksi, cetak tiup, dan ekstrusi. Mendinginkan komponen plastik dengan cepat membantu mengurangi waktu siklus, meningkatkan kualitas produk, dan meningkatkan laju produksi.
- Industri Makanan dan Minuman: Pendingin sudah terbiasa Dingin produk selama berbagai tahap pemrosesan dan penyimpanan. Misalnya, di pabrik bir, pendingin digunakan untuk menjaga suhu fermentasi yang tepat dan untuk Dingin bir setelah diseduh.
- Industri Kimia dan Farmasi: Pendingin sangat penting untuk menjaga suhu optimal dalam reaktor, kondensor, dan tangki penyimpanan. Kontrol suhu yang tepat sangat penting untuk memastikan kualitas produk dan keamanan proses.
Dalam pengalaman saya sebagai salah satu pelaku industri berkualitas tinggi produsen pendinginSaya telah melihat bagaimana pendingin merupakan bagian penting dalam menjaga efisiensi dan keandalan proses industri. Misalnya, dalam industri medis, pendingin sudah terbiasa Dingin Mesin MRI dan peralatan diagnostik lainnya, memastikan operasinya akurat dan andal. Berikut adalah contoh Pendingin Industri Untuk Pelapisan Elektro.
| Industri | Aplikasi | Jenis Pendingin |
| Plastik dan Karet | Pendinginan Cetakan, Pendinginan Ekstrusi | Berpendingin Air |
| Makanan dan Minuman | Fermentasi, Pendinginan Produk | Pendingin Glikol |
| Kimia dan Farmasi | Pendinginan Reaktor, Pendinginan Kondensor | Berpendingin Air |
| Elektronik | Pembuatan Semikonduktor, Pendinginan PCB | Berpendingin Udara |
| Laser | Pemotongan Laser, Pengelasan Laser | Berpendingin Air |
| Pencetakan | Pendinginan Tinta, Pendinginan Rol | Berpendingin Udara/Glikol |
| Medis | Pendinginan MRI, Pendinginan Peralatan Laboratorium | Berpendingin Air |
| Laboratorium | Pendinginan Sampel, Pendinginan Peralatan | Berpendingin Udara/Portabel |
| Pusat Data | Pendinginan Server, Pendingin Udara | Berpendingin Air |
| Permesinan | Pendinginan Fluida Pemotongan, Pendinginan Perkakas Mesin | Berpendingin Udara/Portabel |
Bagaimana Penukar Panas dan Pendingin Bekerja Bersama dalam Sistem Pendinginan?
Dalam banyak aplikasi industri, penukar panas dan pendingin bekerja sama untuk memberikan efisiensi pendinginan. Itu pendingin mendinginkan cairan, biasanya air atau air-glikol campuran, untuk menghilangkan panas. Ini dingin cairan kemudian diedarkan melalui penukar panas, di mana ia menyerap panas dari suatu proses tertentu atau peralatan. Ini terintegrasi sistem pendingin chiller memastikan bahwa proses tetap dalam kisaran suhu yang diinginkan.
Misalnya, di pusat data, pendingin sudah terbiasa Dingin air yang kemudian dialirkan melalui penukar panas di rak server. penukar panas menyerap panas yang dihasilkan oleh server, mentransfernya ke air dinginAir yang sudah dihangatkan kemudian dikembalikan ke pendingin untuk didinginkan lagi. Siklus berkelanjutan ini mempertahankan suhu operasi optimal untuk server, mencegah panas berlebih, dan memastikan kinerja yang andal. Atau lihat cara kerja Pendingin Susu Sapi Perah.
Faktor Apa yang Perlu Dipertimbangkan Saat Memilih Antara Penukar Panas dan Pendingin?
Memilih antara penukar panas dan sebuah pendingin tergantung pada beberapa faktor, termasuk persyaratan pendinginan tertentu, kondisi pengoperasian, dan pertimbangan efisiensi energi. Berikut adalah beberapa faktor utama yang perlu dipertimbangkan:
- Persyaratan Suhu: Jika proses memerlukan pendinginan di bawah suhu lingkungan, A pendingin diperlukan. Penukar panas hanya dapat mendinginkan cairan hingga mendekati suhu lingkungan, ketika pendingin dapat mencapai suhu yang jauh lebih rendah dengan menggunakan pendinginan.
- Beban Panas: Jumlah panas yang perlu dihilangkan, dikenal sebagai panas beban, merupakan faktor krusial. Pendingin dirancang untuk menangani lebih tinggi panas beban dibandingkan dengan penukar panasMisalnya, tinggi panas-proses pembangkitan seperti pencetakan injeksi plastik atau pemotongan laser biasanya memerlukan pendingin.
- Efisiensi Energi: Konsumsi energi merupakan pertimbangan penting. Penukar panas umumnya lebih hemat energi dibandingkan pendingin karena mereka tidak memerlukan kompresor atau komponen lain yang membutuhkan banyak energi. Namun, pendingin diperlukan untuk aplikasi yang memerlukan suhu lebih rendah.
Dalam pengalaman profesional saya, saya menemukan bahwa memahami hal-hal spesifik kebutuhan pendingin proses sangat penting untuk membuat keputusan yang tepat. Misalnya, laboratorium mungkin menggunakan penukar panas untuk tugas pendinginan sederhana tetapi membutuhkan pendingin untuk percobaan yang sensitif terhadap suhu.
Bagaimana Perbandingan Pendingin Berpendingin Udara dan Pendingin Berpendingin Air?
Pendingin secara garis besar dapat diklasifikasikan menjadi dua jenis: berpendingin udara dan berpendingin airSetiap jenis memiliki kelebihan dan kekurangannya masing-masing, sehingga cocok untuk kebutuhan anda dan aplikasi yang berbeda-beda.
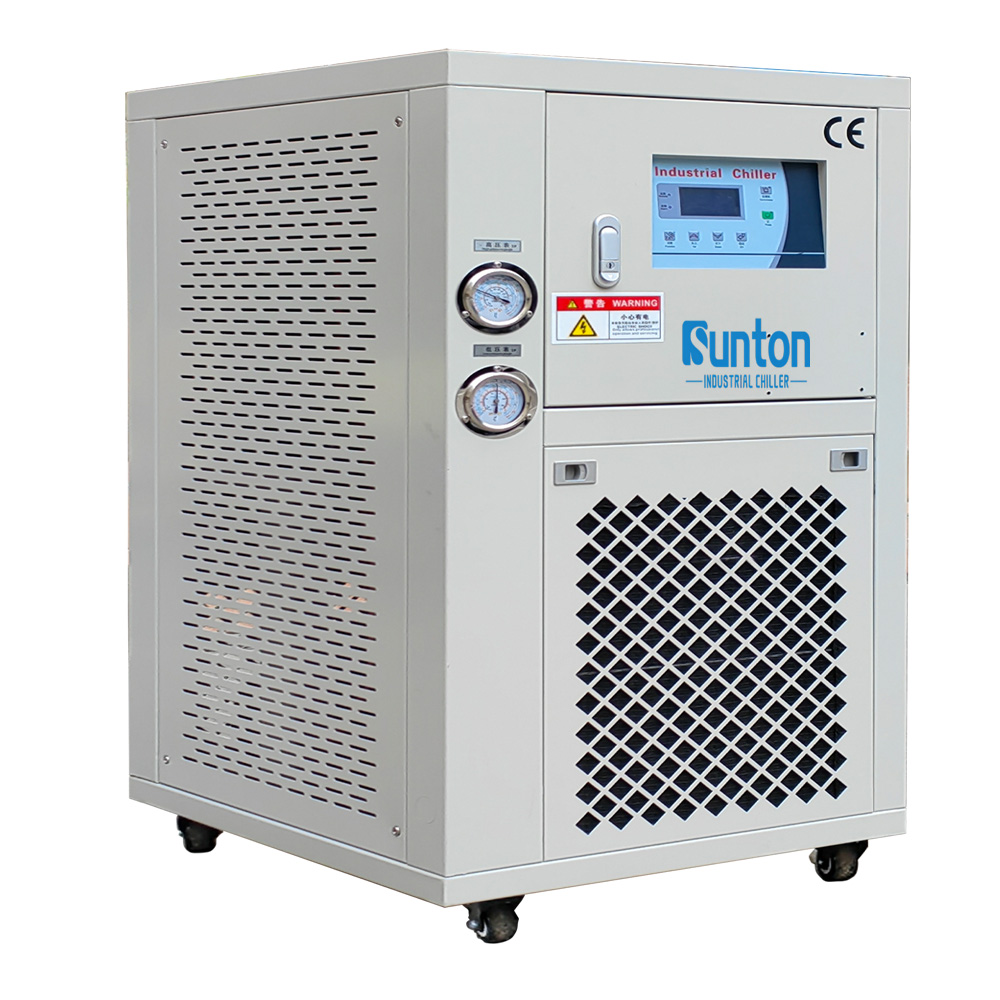
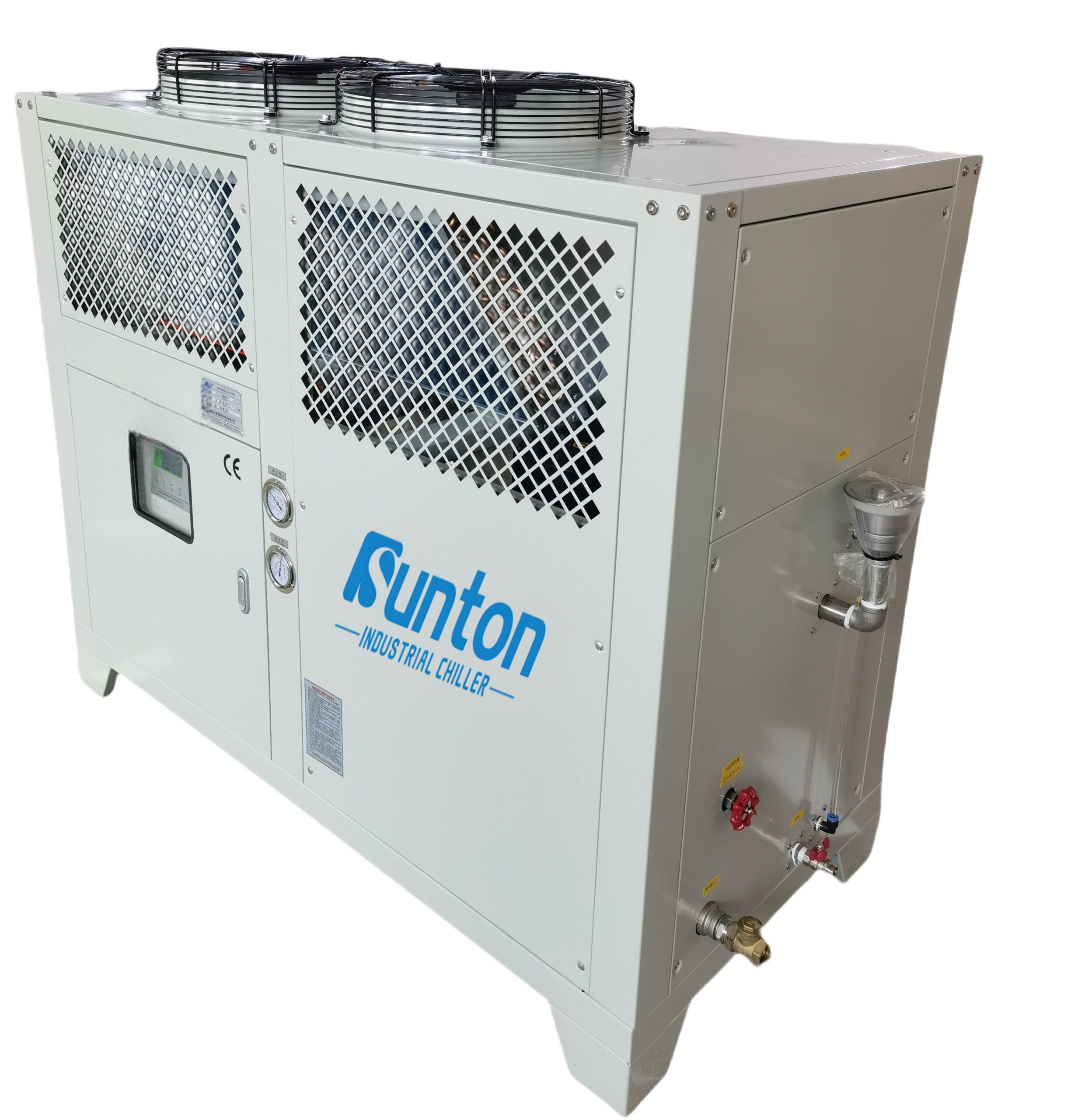
Pendingin berpendingin udara menggunakan udara sekitar untuk mendinginkan refrigeran di dalam kondensorBiasanya lebih mudah untuk dipasang dan dirawat daripada pendingin berpendingin air karena tidak memerlukan sumber air atau menara pendingin terpisah. Pendingin berpendingin udara Umumnya digunakan pada aplikasi yang lebih kecil atau di lokasi yang airnya langka atau mahal.
Pendingin berpendingin air Gunakan air untuk mendinginkan refrigeran di dalam kondensorMereka umumnya lebih hemat energi dibandingkan pendingin berpendingin udara, terutama pada aplikasi yang lebih besar. Namun, mereka memerlukan sumber air yang andal dan mungkin memerlukan menara pendingin atau cara lain untuk menolak panas dari air kondensor. Pendingin berpendingin air sering digunakan di fasilitas industri besar, pusat data, dan gedung komersial.
Mengapa Perawatan Penting untuk Penukar Panas dan Pendingin?
Perawatan rutin sangat penting untuk memastikan pengoperasian yang efisien dan andal dari keduanya penukar panas dan pendinginPemeliharaan yang tepat dapat membantu mencegah kerusakan, memperpanjang umur peralatan, dan mempertahankan kinerja yang optimal.
Untuk penukar panas, pemeliharaan biasanya melibatkan pembersihan perpindahan panas permukaan untuk menghilangkan kotoran atau kerak yang dapat mengurangi efisiensi. Ini mungkin melibatkan pembersihan mekanis, seperti menyikat atau mengikis, atau pembersihan kimia menggunakan bahan pembersih khusus. Memeriksa penukar panas untuk kebocoran atau kerusakan lainnya juga penting.
Untuk pendingin, pemeliharaan termasuk memeriksa refrigeran tingkat, memeriksa kompresor dan komponen lainnya untuk keausan atau kerusakan, dan membersihkan kondensor kumparan. Perawatan rutin dapat membantu mengidentifikasi dan mengatasi potensi masalah sebelum menyebabkan perbaikan mahal atau waktu henti.
Apa Kesalahpahaman Umum Tentang Penukar Panas dan Pendingin?
Ada beberapa kesalahpahaman umum tentang penukar panas dan pendingin yang dapat menyebabkan kebingungan dan keputusan yang salah. Berikut beberapa di antaranya:
- Penukar Panas Dapat Menggantikan Pendingin: Beberapa orang percaya bahwa penukar panas selalu dapat digunakan sebagai pengganti pendingin. Ketika penukar panas efektif untuk banyak aplikasi pendinginan, mereka tidak dapat mencapai suhu rendah yang pendingin bisa. Sebuah pendingin diperlukan untuk proses yang memerlukan pendinginan di bawah suhu lingkungan.
- Pendingin Mengkonsumsi Lebih Banyak Energi: Kesalahpahaman lainnya adalah bahwa pendingin selalu mengonsumsi lebih banyak energi daripada penukar panasMeskipun memang benar bahwa pendingin menggunakan kompresor dan komponen lain yang mengonsumsi energi, modern pendingin dirancang agar sangat hemat energi. Dalam banyak kasus, penghematan energi dari penggunaan pendingin untuk mencapai kendali suhu yang tepat dapat mengimbangi konsumsi energi yang lebih tinggi.
- Perawatan Tidak Diperlukan: Beberapa orang meremehkan pentingnya perawatan rutin untuk penukar panas dan pendinginPemeliharaan yang tepat sangat penting untuk memastikan pengoperasian sistem ini secara efisien dan andal. Mengabaikan pemeliharaan dapat menyebabkan penurunan efisiensi, peningkatan konsumsi energi, dan kerusakan yang merugikan.
Apa Tren Masa Depan dalam Teknologi Penukar Panas dan Pendingin?
Bidang penukar panas dan pendingin Teknologi terus berkembang, didorong oleh kebutuhan akan efisiensi, keberlanjutan, dan kinerja yang lebih baik. Berikut adalah beberapa tren utama:
- Bahan Canggih: Para peneliti sedang mengembangkan bahan baru untuk penukar panas dan pendingin tawaran itu ditingkatkan perpindahan panas properti, ketahanan terhadap korosi, dan daya tahan. Misalnya, paduan canggih dan material komposit dapat meningkatkan efisiensi dan masa pakai sistem ini.
- Kontrol Cerdas: Integrasi kontrol pintar dan otomatisasi menjadi semakin umum di penukar panas dan pendingin Sistem. Teknologi ini memungkinkan pemantauan waktu nyata, pemeliharaan prediktif, dan kinerja yang dioptimalkan berdasarkan berbagai kondisi pengoperasian.
- Efisiensi Energi: Terdapat peningkatan fokus pada peningkatan efisiensi energi penukar panas dan pendinginIni termasuk pengembangan sistem yang lebih efisien kompresor, canggih zat pendingin dengan potensi pemanasan global yang lebih rendah, dan desain sistem inovatif yang meminimalkan konsumsi energi.
Sebagai salah satu perusahaan industri terkemuka produsen pendinginSaya sangat antusias dengan kemajuan ini dan potensinya untuk mengubah industri. Dengan terus mendapatkan informasi tentang tren ini, bisnis dapat membuat keputusan yang lebih baik saat memilih dan menerapkan pendinginan solusi.
Pertanyaan Umum
Apa fungsi utama penukar panas?
Fungsi utama dari sebuah penukar panas adalah untuk memindahkan panas antara dua atau lebih cairan tanpa mencampurnya, memfasilitasi efisiensi pertukaran panas untuk tujuan pemanasan atau pendinginan.
Apa yang membedakan pendingin dengan penukar panas?
A pendingin secara aktif mendinginkan cairan menggunakan pendinginan siklus, mencapai suhu di bawah suhu sekitar, sementara penukar panas transfer panas antara cairan tanpa pendinginan aktif.
Apa saja jenis utama penukar panas?
Jenis umum termasuk penukar panas pelat, penukar panas cangkang dan tabungdan penukar panas berpendingin udara, masing-masing dirancang untuk aplikasi dan kondisi operasi tertentu.
Di industri apa saja pendingin umum digunakan?
Pendingin digunakan dalam industri seperti plastik dan karet, makanan dan minuman, kimia dan farmasi, elektronik, laser, percetakan, medis, laboratorium, dan pusat data untuk berbagai kebutuhan pendinginan.
Faktor apa yang harus dipertimbangkan saat memilih antara penukar panas dan pendingin?
Faktor-faktor kunci meliputi persyaratan suhu, panas beban, efisiensi energi, dan kebutuhan aplikasi spesifik.
Mengapa perawatan rutin penting untuk penukar panas dan pendingin?
Pemeliharaan rutin memastikan pengoperasian yang efisien, mencegah kerusakan, memperpanjang umur peralatan, dan mempertahankan kinerja yang optimal.
Kesimpulan
- Penukar panas dan pendingin merupakan komponen penting dalam berbagai aplikasi industri dan komersial.
- Penukar panas transfer panas antara cairan, sementara pendingin secara aktif mendinginkan cairan menggunakan pendinginan.
- Pemilihan sistem yang tepat tergantung pada faktor-faktor seperti persyaratan suhu, panas beban, dan efisiensi energi.
- Keduanya berpendingin udara dan pendingin berpendingin air memiliki kelebihan dan kekurangan.
- Perawatan rutin sangat penting untuk pengoperasian yang efisien dan andal dari keduanya penukar panas dan pendingin.
- Memahami kesalahpahaman umum tentang sistem ini dapat membantu dalam pengambilan keputusan yang tepat.
- Tren masa depan di penukar panas dan pendingin teknologi tersebut meliputi material canggih, kontrol cerdas, dan peningkatan efisiensi energi.
Dengan memahami perbedaan antara penukar panas dan pendingin dan dengan mempertimbangkan kebutuhan spesifik aplikasi Anda, Anda dapat memilih sistem yang paling sesuai untuk memastikan efisiensi dan keandalan pendinginanSebagai perusahaan industri terkemuka produsen pendinginSaya berkomitmen untuk memberikan solusi berkualitas tinggi dan panduan ahli untuk membantu Anda mengoptimalkan pendinginan proses.
Jika Anda siap untuk meningkatkan proses industri Anda dengan solusi pendinginan mutakhir, jangan ragu untuk menghubungi kami. Mari kita bahas bagaimana pendingin dan penukar panas canggih kami dapat memenuhi kebutuhan spesifik Anda dan mendorong keberhasilan Anda. Hubungi kami hari ini untuk mempelajari lebih lanjut dan mengambil langkah pertama menuju pengoptimalan operasi Anda!