-
Dalingshan Industrial Guangdong
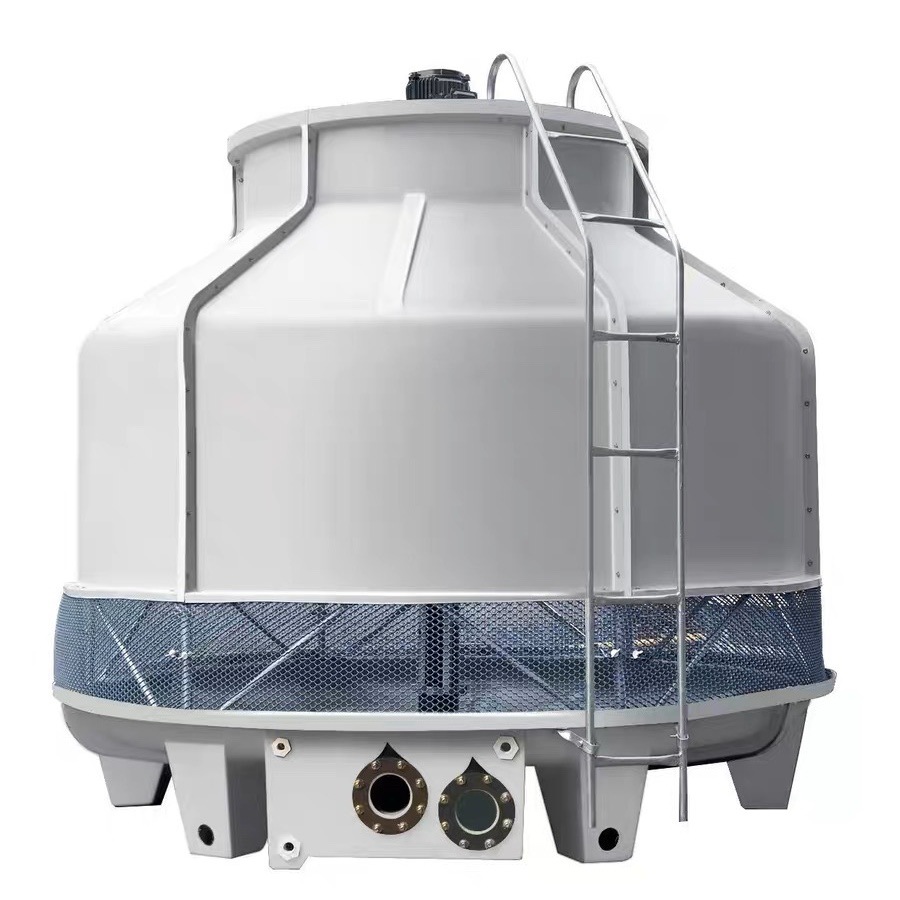

menara pendingin vs. kondensor evaporatif – jenis kondensor evaporatif
Memahami Kondensor Evaporatif dan Menara Pendingin: Panduan Lengkap untuk Aplikasi Industri
Artikel ini memberikan wawasan mendalam tentang dunia kondensor evaporatif dan menara pendingin, menjelaskan perbedaan, fungsi, dan aplikasinya. Baik Anda berkecimpung dalam industri plastik, mengelola pusat data, atau mengawasi pabrik pengolahan makanan, memahami sistem pendingin ini sangat penting untuk operasi yang efisien dan hemat biaya. Kami akan membahas cara kerja sistem ini, kelebihannya, dan mengapa memilih sistem yang tepat dapat berdampak signifikan pada proses industri Anda. Sebagai pabrik pembuat pendingin air industri, kami memahami seluk-beluk sistem ini dan siap memandu Anda dalam pemilihan dan penerapannya, menjadikan artikel ini wajib dibaca bagi siapa pun yang terlibat dalam solusi pendinginan industri.
Daftar Isi
1. Apa itu Kondensor Evaporatif dan Bagaimana Cara Kerjanya?
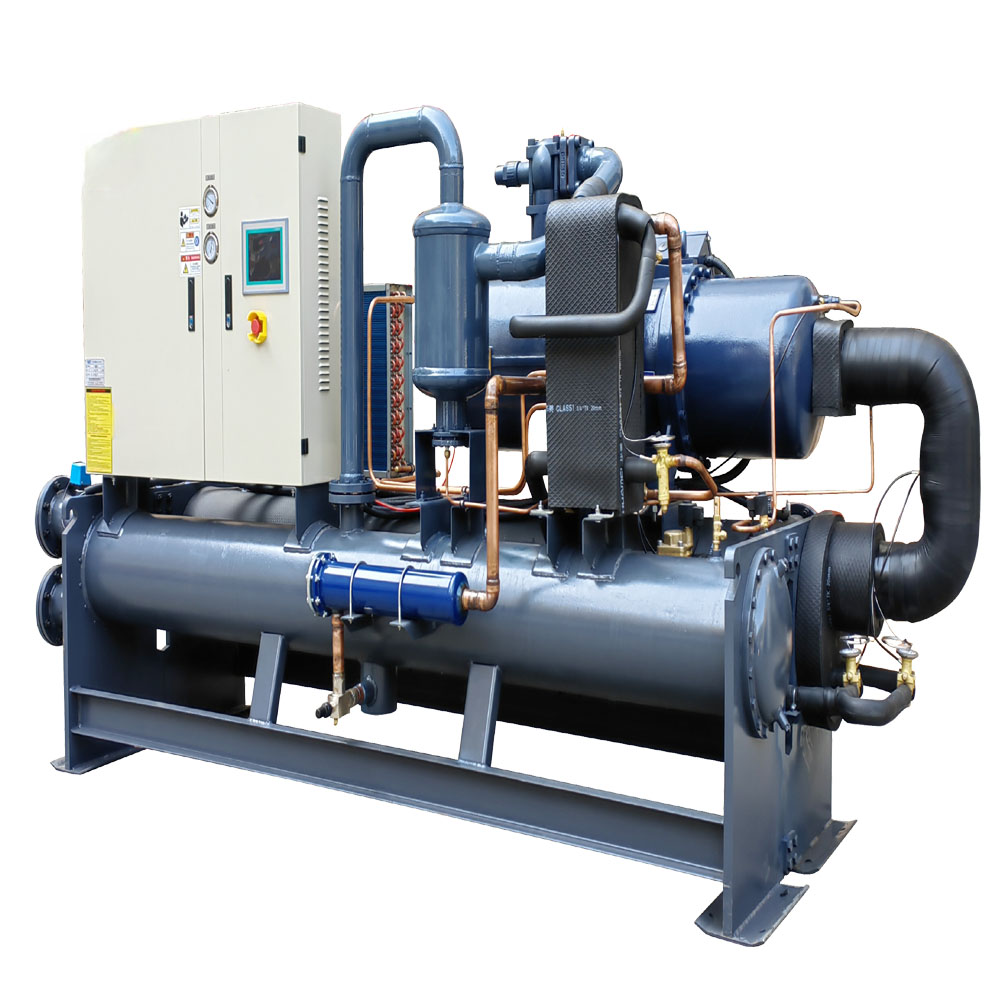
Kondensor evaporatif adalah perangkat yang digunakan untuk membuang panas berlebih dari sistem pendingin saat panas tersebut tidak dapat digunakan untuk keperluan lain. Perangkat ini menggabungkan fungsi kondensor berpendingin air dan menara pendingin menjadi satu unit. Jenis kondensor ini biasanya digunakan dalam sistem pendingin besar dan sistem pendingin udara yang membutuhkan pembuangan panas yang sangat penting. Tujuan utama kondensor evaporatif adalah untuk mendinginkan refrigeran dengan menggunakan proses penguapan.
Dalam kondensor evaporatif, uap refrigeran panas mengalir melalui kumparan. Air disemprotkan ke kumparan, dan udara ditiupkan ke kumparan secara bersamaan. Saat air menguap, ia menyerap panas dari refrigeran, menyebabkannya mengembun dari uap kembali ke keadaan cair. Panas tersebut kemudian dilepaskan ke atmosfer. Proses pembuangan panas ini sangat efisien, menjadikan kondensor evaporatif pilihan yang sangat baik untuk aplikasi industri. Kondensor evaporatif bekerja dengan mengelola proses perpindahan panas secara efisien, memastikan bahwa sistem beroperasi pada suhu optimal. Menurut pengalaman saya, efisiensi sistem ini tak tertandingi, terutama dalam pengaturan industri.
2. Apa itu Menara Pendingin dan Mengapa Itu Penting?
Menara pendingin adalah penukar panas khusus yang dirancang untuk menghilangkan panas dari air yang digunakan dalam proses industri. Menara pendingin digunakan untuk mendinginkan air yang telah menyerap panas dari berbagai proses, seperti pembangkitan daya, sistem HVAC, dan manufaktur industri. Menara pendingin sangat penting untuk menjaga efisiensi dan keamanan operasi ini dengan mencegah panas berlebih. Menara pendingin mendinginkan air melalui campuran perpindahan panas dan massa, terutama menggunakan penguapan. Air disemprotkan ke bahan pengisi (material dengan luas permukaan tinggi), sementara udara ditarik menggunakan kipas, air panas didinginkan, terutama melalui penguapan sebagian air. Air yang didinginkan kemudian dikumpulkan dan digunakan kembali dalam sistem.
Menara pendingin memainkan peran penting dalam banyak industri. Misalnya, dalam industri plastik dan karet, menara pendingin sangat penting untuk mendinginkan mesin dan menjaga kualitas produk. Demikian pula, dalam industri makanan dan minuman, menara pendingin membantu mengawetkan barang yang mudah rusak dengan menjaga sistem pendinginan pada suhu optimal. Efektivitas menara pendingin berdampak langsung pada produktivitas dan efektivitas biaya operasi ini, mencegah panas berlebih, dan memastikan operasi berkelanjutan. Pengalaman saya di industri ini telah mengajarkan saya bahwa menara pendingin sangat diperlukan dalam menjaga efisiensi operasional.
3. Jenis Kondensor Evaporatif: Mana yang Tepat untuk Anda?
Terdapat dua jenis kondensor evaporatif: forced draft dan induced draft. Perbedaan utamanya terletak pada posisi dan pengoperasian kipas yang menggerakkan udara melintasi kumparan.
Kondensor evaporatif draft paksa memiliki kipas yang terletak di bagian bawah unit, yang mendorong udara melalui kumparan. Desain ini umumnya lebih kompak dan dapat menangani tekanan statis yang lebih tinggi. Namun, unit ini dapat lebih berisik dan mengonsumsi lebih banyak energi dibandingkan dengan unit draft terinduksi. Unit draft terinduksi sering digunakan dalam aplikasi di mana ruang terbatas. Ini adalah jenis kondensor utama yang digunakan dalam Pendingin HVAC sistem.
Kondensor evaporatif dengan draft terinduksi memiliki kipas yang terletak di bagian atas unit, yang menarik udara melalui kumparan. Desain ini biasanya menawarkan efisiensi energi yang lebih baik dan pengoperasian yang lebih senyap. Unit induced draft cocok untuk aplikasi yang lebih besar dan memberikan pembuangan panas yang lebih baik. Faktor yang perlu dipertimbangkan saat memilih antara kedua jenis ini meliputi ketersediaan ruang, persyaratan efisiensi energi, dan pembatasan kebisingan. Setiap jenis memiliki kelebihannya sendiri, dan pilihan terbaik bergantung pada kebutuhan spesifik aplikasi Anda.
4. Bagaimana Proses Pendinginan Evaporatif Bekerja?
Pendinginan evaporatif adalah proses alami yang menggunakan penguapan air untuk mendinginkan udara. Dalam konteks kondensor evaporatif dan menara pendingin, proses ini dimanfaatkan untuk menghilangkan panas dari suatu sistem. Saat air menguap, ia menyerap sejumlah besar panas dari udara di sekitarnya, yang menyebabkan penurunan suhu. Inilah sebabnya mengapa pendinginan evaporatif merupakan metode yang efektif untuk pembuangan panas.
Baik pada kondensor evaporatif maupun menara pendingin, air disemprotkan ke penukar panas atau material pengisi, dan udara dialirkan melaluinya. Saat air menguap, ia mendinginkan air dan udara yang tersisa. Air yang didinginkan kemudian disirkulasikan kembali ke dalam sistem, sementara udara yang mengandung panas dikeluarkan ke atmosfer. Siklus berkelanjutan ini memastikan bahwa sistem pendingin beroperasi secara efisien, mempertahankan suhu yang diinginkan. Proses pendinginan evaporatif sederhana dan cerdik.
5. Menara Pendingin vs. Kondensor Evaporatif: Perbedaan Utama Dijelaskan
Meskipun menara pendingin dan kondensor evaporatif sama-sama memanfaatkan penguapan untuk mendinginkan, keduanya memiliki fungsi yang berbeda dalam sistem pendingin. Memahami perbedaan antara menara pendingin dan kondensor evaporatif sangat penting untuk memilih peralatan yang tepat untuk kebutuhan Anda.
Menara pendingin terutama digunakan untuk mendinginkan air, yang kemudian digunakan sebagai pendingin dalam berbagai proses industri. Air menyerap panas dari proses tersebut dan kemudian didinginkan di menara melalui penguapan. Di sisi lain, kondensor evaporatif digunakan untuk mendinginkan refrigeran secara langsung di dalam sistem pendingin udara atau refrigerasi. Kondensor ini menggabungkan fungsi kondensor dan menara pendingin, menjadikannya solusi yang lebih terintegrasi untuk pembuangan panas. Pilihan di antara keduanya bergantung pada apakah Anda perlu mendinginkan air atau mendinginkan refrigeran secara langsung.
Berikut tabel yang merangkum perbedaan utama:
| Fitur | Menara Pendingin | Kondensor Penguapan |
| Fungsi Utama | Mendinginkan air | Mendinginkan refrigeran |
| Integrasi | Unit terpisah | Menggabungkan fungsi kondensor dan menara pendingin |
| Aplikasi | Proses industri, HVAC | Sistem pendingin dan pendingin udara |
| Media Pemindah Panas | Air | Pendingin |
| Efisiensi Energi | Umumnya lebih rendah | Umumnya lebih tinggi |
| Pemeliharaan | Lebih mudah, biaya lebih rendah | Lebih rumit, berpotensi biaya lebih tinggi |
| Persyaratan Ruang | Jejak yang lebih besar | Jejak yang lebih kecil |
| Biaya Awal | Lebih rendah | Lebih tinggi |
| Biaya Operasional | Lebih tinggi karena pengolahan air dan pemompaan | Lebih rendah karena fungsi gabungan |
| Tingkat Kebisingan | Dapat bervariasi, biasanya sedang | Dapat bervariasi, biasanya sedang |
| Konsumsi Air | Lebih tinggi karena penguapan dan blowdown | Penggunaan air yang lebih rendah dan lebih efisien |
| Dampak Lingkungan | Sedang, tergantung pada pengolahan air | Penggunaan energi yang lebih rendah dan lebih efisien |
| Kompleksitas Sistem | Sistem yang lebih sederhana | Sistem yang lebih kompleks |
| Kapasitas Penolakan Panas | Variabel, tergantung pada ukuran dan desain | Tinggi, dioptimalkan untuk pendinginan refrigeran langsung |
Perbandingan ini akan membantu memperjelas peran dan manfaat masing-masing sistem.
6. Apa Aplikasi Utama Menara Pendingin dan Kondensor Evaporatif?
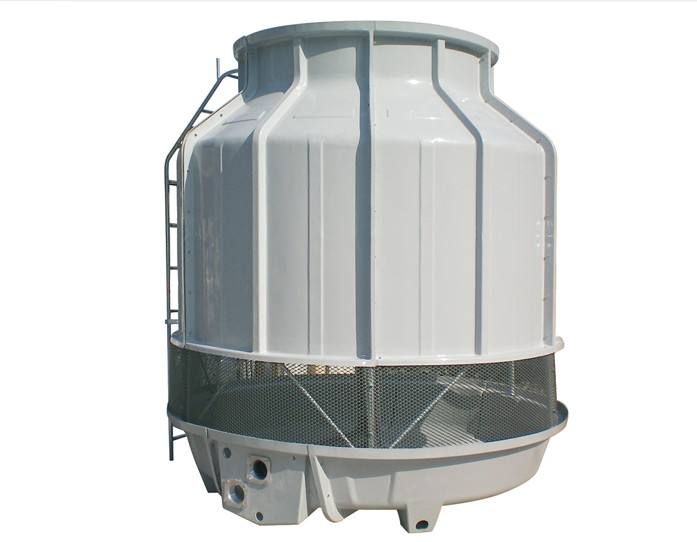

Menara pendingin dan kondensor evaporatif digunakan dalam berbagai industri. Menara pendingin umumnya ditemukan di pembangkit listrik, pabrik pengolahan kimia, dan sistem HVAC besar. Menara pendingin sangat penting untuk mendinginkan air yang digunakan dalam berbagai proses industri, memastikan bahwa peralatan beroperasi dalam batas suhu yang aman.
Kondensor evaporatif biasanya digunakan dalam sistem pendingin dan pendingin udara besar. Kondensor ini sangat berguna dalam aplikasi seperti sistem pendingin untuk penyimpanan dingin, pemrosesan makanan, dan bangunan komersial besar. Kemampuannya untuk mendinginkan refrigeran secara efisien menjadikannya pilihan yang lebih disukai dalam pengaturan ini. Fleksibilitas sistem ini membuatnya sangat diperlukan dalam banyak konteks industri. Misalnya, Pendingin glikol sistem dapat memperoleh manfaat besar dari integrasi kondensor evaporatif.
Berikut ini adalah beberapa industri dan penggunaan spesifiknya:
- Industri Plastik dan Karet:Mendinginkan cetakan dan mesin.
- Industri Permesinan: Mendinginkan cairan dan peralatan pemotongan.
- Industri Makanan dan Minuman: Memelihara sistem pendinginan untuk barang-barang yang mudah rusak.
- Industri Kimia dan Farmasi: Mendinginkan reaktor dan peralatan proses lainnya.
- Industri Elektronik: Menghilangkan panas dari proses manufaktur.
- Industri Laser: Sistem laser pendingin.
- Industri Percetakan: Kontrol suhu dalam proses pencetakan.
- Industri Medis: Mendinginkan peralatan medis seperti mesin MRI.
- Laboratorium dan Lembaga Penelitian: Menjaga suhu tetap stabil untuk percobaan.
- Pusat Data: Mendinginkan server dan peralatan TI lainnya.
7. Bagaimana Memilih Antara Kondensor Evaporatif dan Menara Pendingin?
Memilih antara kondensor evaporatif dan menara pendingin bergantung pada beberapa faktor. Pertama, pertimbangkan pendingin utama sistem pendingin. Jika Anda perlu mendinginkan air yang akan digunakan sebagai pendingin, menara pendingin adalah pilihan yang tepat. Jika Anda perlu mendinginkan refrigeran secara langsung, kondensor evaporatif lebih cocok.
Faktor lain yang perlu dipertimbangkan adalah skala dan kompleksitas kebutuhan pendinginan Anda. Untuk proses industri berskala besar, menara pendingin sering kali lebih praktis karena kemampuannya menangani volume air yang besar. Untuk sistem pendinginan terpadu, kondensor evaporatif menawarkan efisiensi yang lebih tinggi dan ukuran yang lebih kecil. Selain itu, pertimbangkan faktor-faktor seperti efisiensi energi, persyaratan perawatan, dan biaya investasi awal.
| Pertimbangan | Menara Pendingin | Kondensor Penguapan |
| Pendingin | Air | Pendingin |
| Skala | Proses industri besar | Sistem pendingin terpadu |
| Efisiensi Energi | Lebih rendah | Lebih tinggi |
| Pemeliharaan | Lebih mudah, biaya lebih rendah | Lebih rumit, biaya lebih tinggi |
| Investasi Awal | Lebih rendah | Lebih tinggi |
| Persyaratan Ruang | Lebih besar | Lebih kecil |
| Kompleksitas Sistem | Lebih sederhana | Lebih kompleks |
| Aplikasi | Pendinginan umum air | Pendinginan langsung refrigeran |
| Biaya Operasional | Lebih tinggi karena pengolahan air | Lebih rendah karena fungsi gabungan |
| Dampak Lingkungan | Sedang, terkait dengan pengolahan air | Pemanfaatan energi yang lebih rendah dan efisien |
| Tingkat Kebisingan | Umumnya sedang | Umumnya sedang |
Membuat keputusan yang tepat memerlukan penilaian menyeluruh terhadap persyaratan dan kendala spesifik Anda.
8. Mengapa Kondensor Evaporatif dan Menara Pendingin Penting dalam Proses Industri?
Kondensor evaporatif dan menara pendingin sangat penting untuk menjaga efisiensi dan keamanan proses industri. Mereka memainkan peran penting dalam pembuangan panas, mencegah peralatan dari panas berlebih, dan memastikan operasi berkelanjutan. Tanpa sistem ini, banyak proses industri tidak akan dapat berfungsi secara efektif, yang menyebabkan berkurangnya produktivitas dan potensi bahaya keselamatan.
Dalam industri seperti pembangkit listrik dan pemrosesan kimia, menara pendingin sangat penting untuk menghilangkan panas berlebih yang dihasilkan selama operasi. Demikian pula, dalam industri makanan dan minuman, kondensor evaporatif membantu mempertahankan suhu rendah yang diperlukan untuk pendinginan dan pengawetan. Keandalan dan kinerja sistem pendingin ini secara langsung memengaruhi keberhasilan keseluruhan operasi ini. Inilah sebabnya mengapa berinvestasi dalam sistem berkualitas tinggi Pendingin Sentral Sekrup Berpendingin Air adalah keputusan yang dapat berdampak signifikan terhadap efisiensi operasional jangka panjang.
9. Efektivitas Biaya Kondensor Evaporatif dan Menara Pendingin
Baik kondensor evaporatif maupun menara pendingin menawarkan penghematan biaya yang signifikan dibandingkan dengan metode pendinginan alternatif. Pendinginan evaporatif pada dasarnya hemat energi, karena mengandalkan proses penguapan alami untuk menghilangkan panas. Hal ini menghasilkan konsumsi energi yang lebih rendah dan biaya pengoperasian yang lebih rendah.
Kondensor evaporatif, khususnya, menawarkan efisiensi yang lebih tinggi karena desainnya yang terintegrasi. Dengan menggabungkan fungsi kondensor dan menara pendingin, kondensor menghilangkan kebutuhan akan unit terpisah, sehingga mengurangi investasi awal dan biaya perawatan berkelanjutan. Menara pendingin, meskipun memerlukan lebih banyak perawatan karena pengolahan air dan pemompaan, tetap merupakan solusi hemat biaya untuk kebutuhan pendinginan skala besar.
Berikut rincian faktor biaya:
| Faktor Biaya | Menara Pendingin | Kondensor Penguapan |
| Investasi Awal | Lebih rendah | Lebih tinggi |
| Konsumsi Energi | Lebih tinggi | Lebih rendah |
| Pemeliharaan | Lebih rendah, tetapi membutuhkan perawatan rutin | Komponen yang lebih tinggi dan lebih kompleks |
| Biaya Operasional | Lebih tinggi karena penggunaan air dan energi | Lebih rendah karena efisiensi lebih tinggi |
| Penggunaan Air | Lebih tinggi | Pengelolaan air yang lebih rendah dan lebih efisien |
| Biaya Penggantian | Lebih rendah | Lebih tinggi |
| Efisiensi Sistem | Nilai keseluruhan lebih rendah | Lebih tinggi secara keseluruhan |
| Tabungan Jangka Panjang | Sedang | Penting karena efisiensi energi |
Secara keseluruhan, kedua sistem memberikan manfaat biaya yang besar, menjadikannya investasi yang berharga untuk aplikasi industri.
10. Pertanyaan yang Sering Diajukan
1. Apa fungsi utama kondensor evaporatif?
Kondensor evaporatif terutama digunakan untuk mendinginkan refrigeran dalam sistem pendingin udara atau refrigerasi dengan menggunakan proses penguapan untuk menghilangkan panas.
2. Apa yang membedakan menara pendingin dengan kondensor evaporatif?
Menara pendingin dirancang untuk mendinginkan air yang digunakan sebagai pendingin dalam proses industri, sementara kondensor evaporatif mendinginkan refrigeran secara langsung di dalam sistem pendingin.
3. Apa saja jenis utama kondensor evaporatif?
Jenis utama kondensor evaporatif adalah aliran paksa dan aliran induksi, dibedakan berdasarkan lokasi dan pengoperasian kipas.
4. Mengapa pendinginan evaporatif dianggap hemat energi?
Pendinginan evaporatif hemat energi karena mengandalkan proses penguapan alami, yang membutuhkan lebih sedikit energi dibandingkan metode pendinginan lainnya.
5. Industri apa yang umum menggunakan menara pendingin?
Menara pendingin umumnya digunakan di pembangkit listrik, pabrik pengolahan kimia, dan sistem HVAC besar. Misalnya, mereka sering digunakan dengan Pendingin Industri Untuk Pabrik Batch Beton.
6. Apakah kondensor evaporatif cocok untuk semua jenis sistem pendinginan?
Kondensor evaporatif sangat cocok untuk sistem pendinginan dan pendingin udara berskala besar di mana pembuangan panas yang efisien sangat penting.
Ringkasan
- Kondensor evaporatif dan menara pendingin sangat penting untuk operasi industri yang efisien dan aman.
- Kondensor evaporatif mendinginkan refrigeran secara langsung menggunakan penguapan, sementara menara pendingin mendinginkan air yang digunakan sebagai pendingin.
- Jenis-jenis kondensor evaporatif meliputi draft paksa dan draft induksi, masing-masing punya kelebihannya sendiri.
- Pendinginan evaporatif adalah metode hemat energi yang mengandalkan proses penguapan alami.
- Memilih antara kondensor evaporatif dan menara pendingin bergantung pada kebutuhan pendinginan spesifik, skala operasi, dan pertimbangan biaya.
- Kedua sistem menawarkan penghematan biaya yang signifikan dibandingkan dengan metode pendinginan alternatif.
- Industri seperti pembangkit listrik, pengolahan kimia, makanan dan minuman, dan pusat data sangat bergantung pada sistem pendingin ini.
- Pemeliharaan yang tepat dan pemilihan sistem yang tepat sangat krusial untuk kinerja dan umur yang optimal.
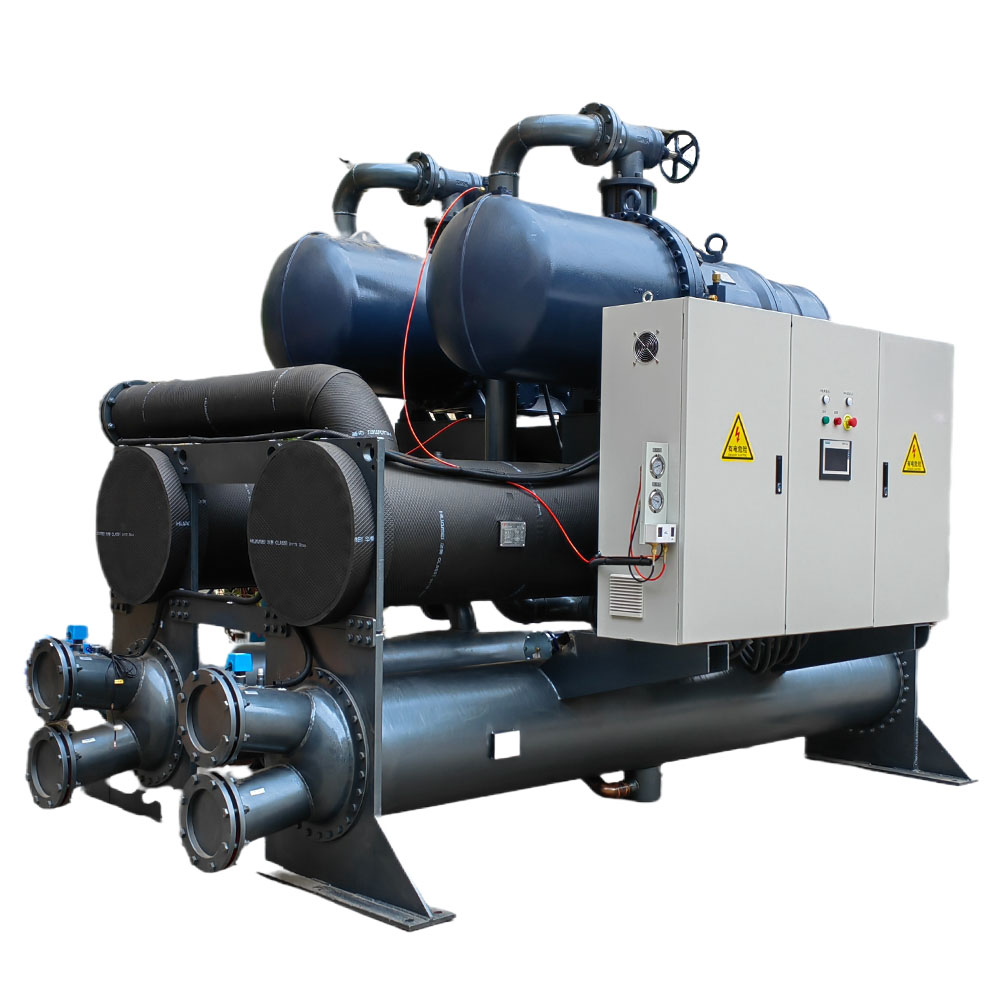

Memilih antara Pendingin Air Sekrup Berpendingin Air dan sistem berpendingin udara dapat berdampak signifikan pada efisiensi dan biaya operasional Anda. Memahami perbedaan ini sangatlah penting. Selain itu, Pendingin Sekrup Berpendingin Udara mungkin lebih cocok untuk lingkungan tertentu di mana penggunaan air menjadi perhatian. Penting untuk mempertimbangkan persyaratan khusus aplikasi Anda untuk membuat keputusan yang tepat.