-
Dalingshan Industrial Guangdong

the ultimate guide to chiller systems
The Ultimate Guide to Chiller Systems: How They Work and Why You Need Them
This article provides a comprehensive overview of Kältesysteme, explaining their operation, types, and applications across various industries. Whether you’re in the plastics, food and beverage, or data center industry, understanding Kältemaschinen is crucial for optimizing your operations and maintaining product quality. This guide is worth reading because it demystifies chiller technology, highlights the importance of choosing the right chiller for your needs, and outlines the benefits of efficient chiller maintenance, helping you make informed decisions and enhance your HVAC system’s performance.
Inhaltsübersicht
1. What is a Chiller and Why is it Important?
A chiller is a machine that removes heat from a liquid via a vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycle. This cooled liquid can then be circulated through a heat exchanger to cool equipment, or another process stream (such as air or process water). Chiller systems are essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in various industrial and commercial settings. They are integral to HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, providing efficient cooling solutions for large buildings, data centers, and industrial processes. As an industrial water chiller manufacturing plant, we understand the critical role Kältemaschinen play in industries such as:
- Plastics and Rubber Industry: Chillers are used to cool molds and equipment during the manufacturing process.
- Machining Industry: Precision Kühlung is vital for maintaining the accuracy of machining tools.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Chillers ensure consistent product quality by controlling temperatures during processing and storage.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industry: Precise temperature control is crucial for chemical reactions and drug manufacturing.
- Electronics Industry: Chillers cool down sensitive electronic components to prevent overheating.
Chiller systems provide consistent and reliable temperature control, which is crucial for maintaining product quality, equipment longevity, and operational efficiency. Without Kältemaschinen, many industrial processes would be impossible or significantly less efficient.
2. How Does a Chiller Work?
A chiller works by using a refrigeration cycle to remove heat from a liquid. The basic chiller operation involves a refrigerant that circulates through a closed-loop system. The process begins with the compressor, which compresses the refrigerant gas. This high-pressure gas then moves to the condenser, where it is cooled and changes phase to a high-pressure liquid, releasing heat in the process.
The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature. This low-pressure liquid enters the evaporator, where it absorbs heat from the water or other liquid being cooled, causing the refrigerant to evaporate back into a gas. The chilled water is then circulated to cool equipment or processes.
Die refrigerant gas returns to the compressor, and the cycle repeats. The principle of vapor compression or absorption is the backbone of this cycle, ensuring continuous heat transfer und Kühlung. There are two different types of condensers used in chillers: air-cooled and water-cooled, each offering different benefits depending on the application.
3. What are the Two Main Types of Chillers?
There are two main types of chillers: air-cooled chillers und wassergekühlte Kältemaschinen. Each type has its advantages and is suitable for different applications.
Air-Cooled Chillers:
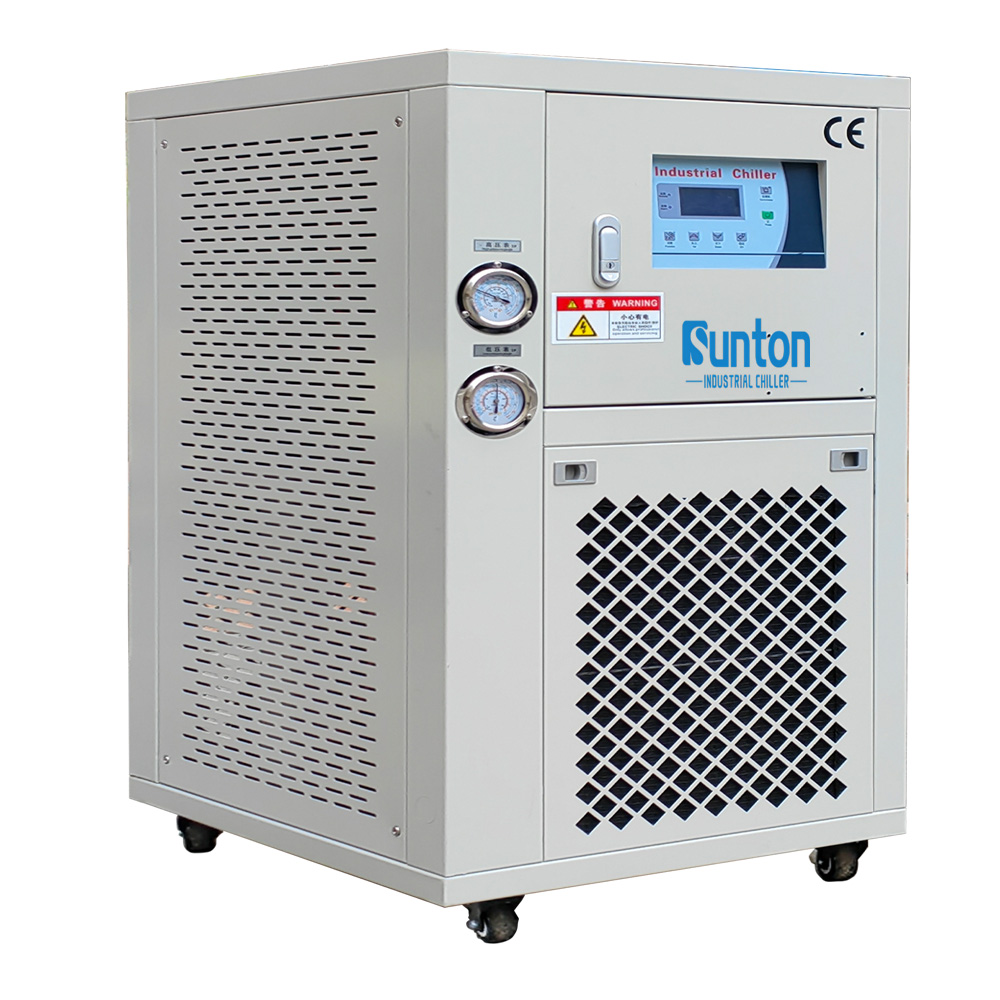
These Kältemaschinen use ambient air to remove heat from the refrigerant. Fans blow air across the condenser coils, where the refrigerant condenses and releases heat. Air-cooled chillers are typically easier to install and maintain because they do not require a separate water source or cooling tower. They are ideal for applications where water availability is limited or where a simpler system is preferred. Here, the process water system does not directly interact with the ambient air, making it suitable for environments where maintaining water quality is critical.
Water-Cooled Chillers:
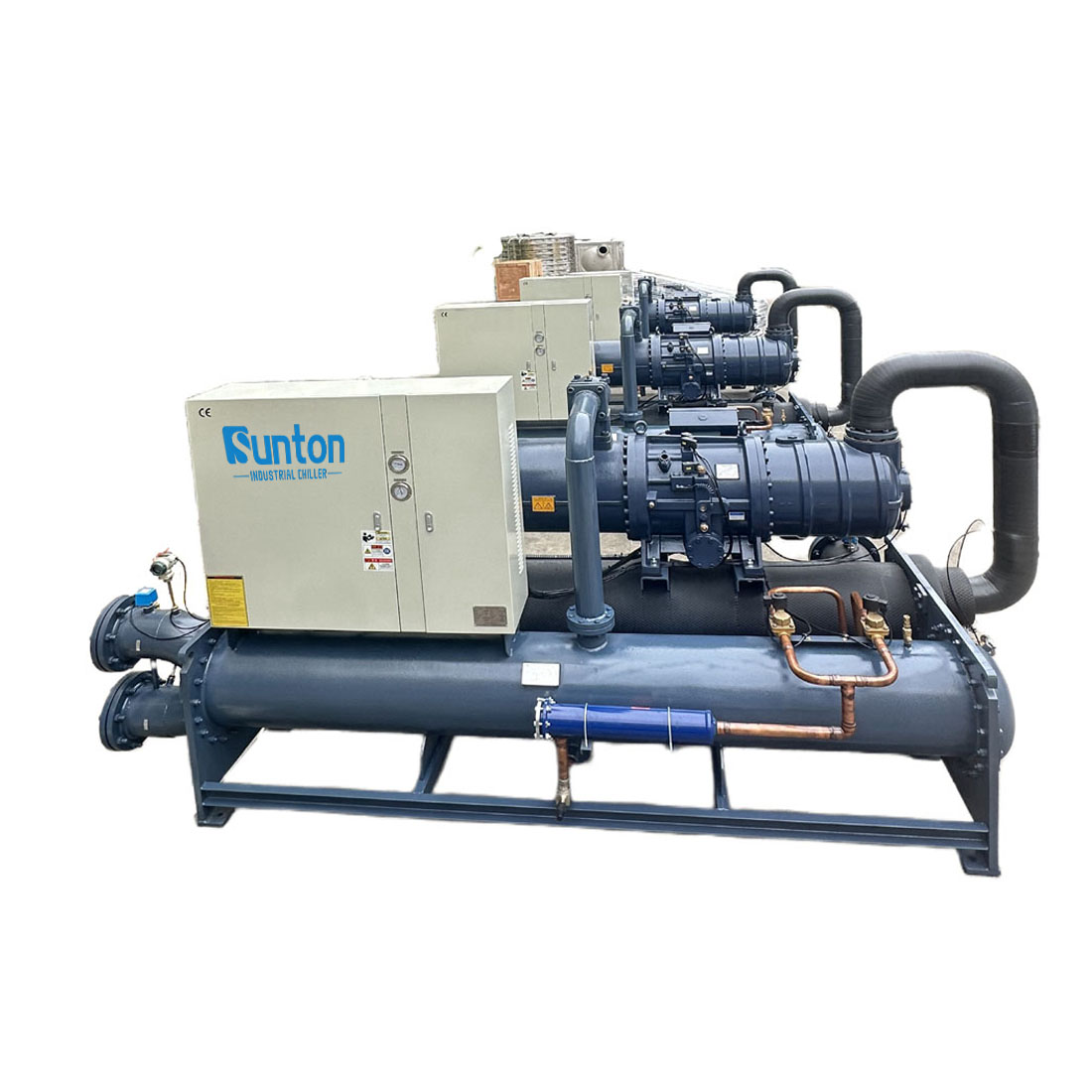
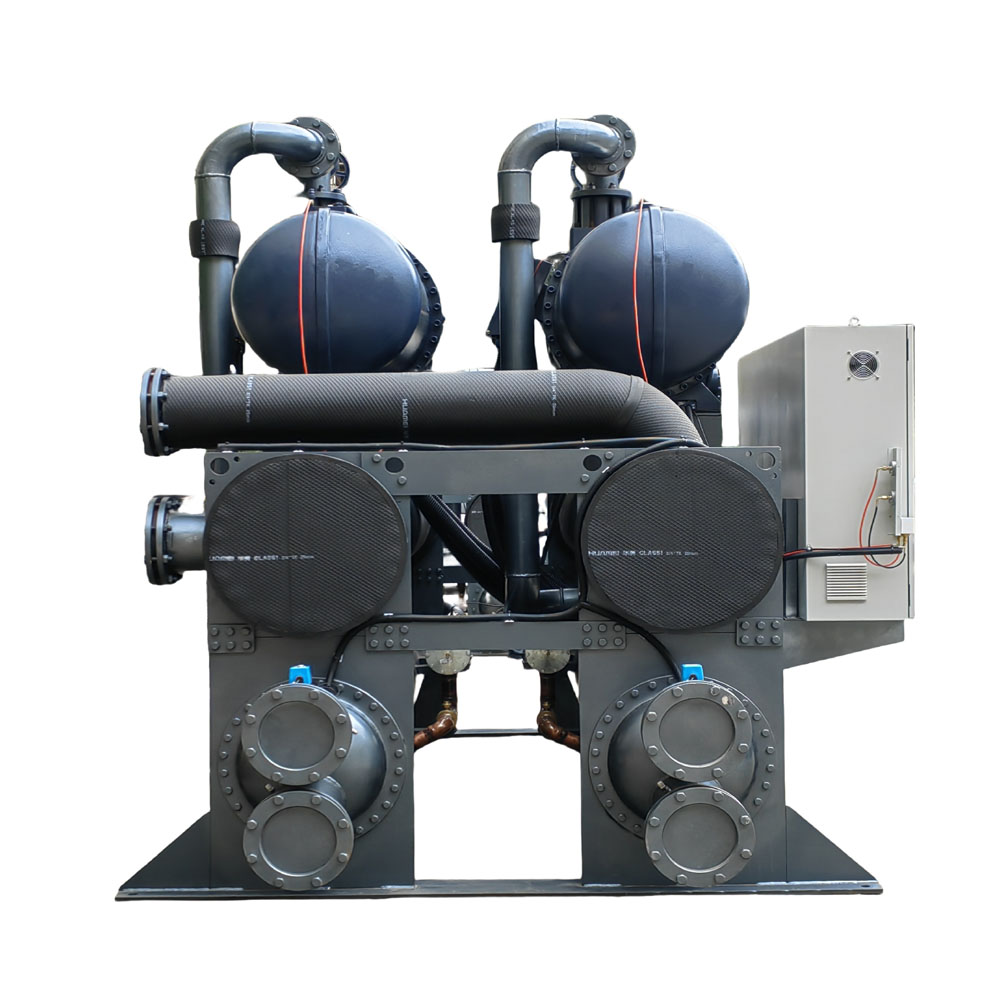
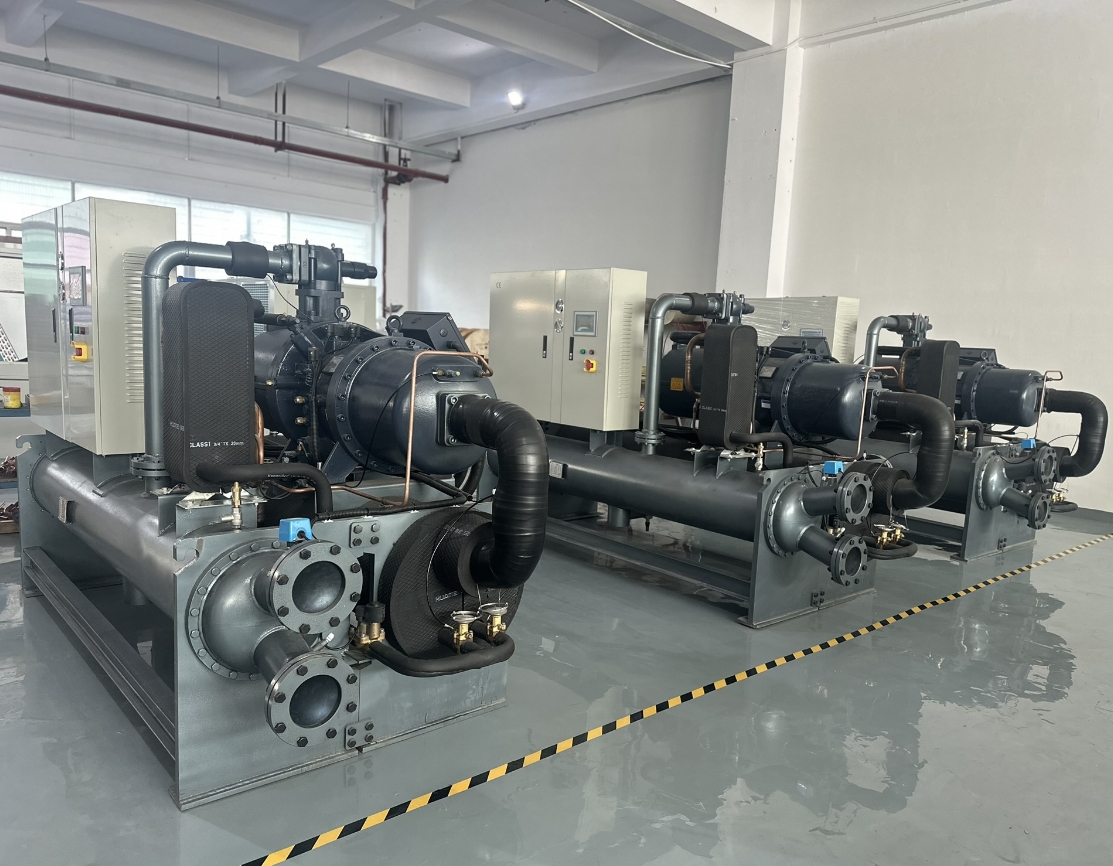
Water-cooled chillers use water from a cooling tower or another water source to cool the refrigerant. The warm water absorbs heat from the refrigerant in the condenser, and then the water is pumped to a cooling tower where the heat is dissipated. Water-cooled chillers are generally more energy-efficient than luftgekühlt models, especially in high-temperature environments. The Water Cooled Screw Water Chiller is an excellent example of an efficient water-cooled chiller used in industrial applications. They are often preferred for large-scale applications where energy efficiency and performance are critical.
| Merkmal | Air-Cooled Chiller | Water-Cooled Chiller |
| Cooling Medium | Ambient Air | Water (from cooling tower or other source) |
| Installation | Simpler, no need for a separate water source | More complex, requires a cooling tower or water source |
| Maintenance | Easier, less complex | More complex, cooling tower maintenance needed |
| Energie-Effizienz | Generally lower, especially in high temperatures | Higher, especially in high-temperature environments |
| Anmeldung | Suitable where water is limited or simplicity is key | Preferred for large-scale, high-efficiency requirements |
4. What are the Main Components of a Chiller?
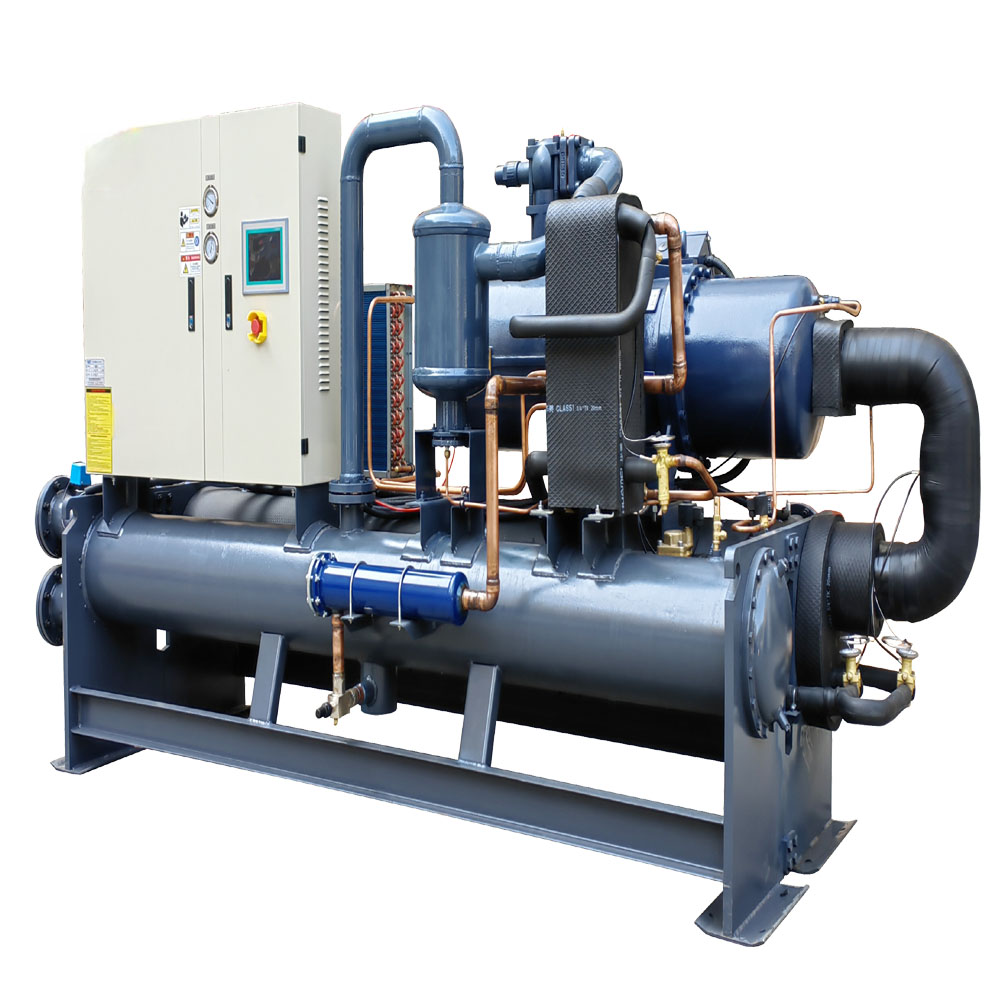
Understanding the components of a chiller is essential for grasping how these systems work. The four main components of a chiller are the compressor, condenser, expansion valveund evaporator.
- Compressor: The heart of the chiller, the compressor pressurizes the refrigerant gas, raising its temperature and pressure.
- Condenser: Die condenser cools the high-pressure refrigerant gas, causing it to condense into a liquid and release heat. In wassergekühlte Kältemaschinen, water is used to absorb this heat. In air-cooled chillers, air performs this function.
- Expansion Valve: This component reduces the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, allowing it to expand and cool down.
- Evaporator: Die evaporator is where the low-pressure liquid refrigerant absorbs heat from the water or process fluid, causing it to evaporate back into a gas. This process cools the water, which is then used for Kühlung applications.
Die Water Cooled Scroll Water Chiller is an example of a chiller that utilizes a scroll compressor, known for its reliability and efficiency. These systems include sophisticated controls to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
5. How Do Chillers Enhance Energy Efficiency?
Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration in the design and operation of Kältesysteme. Efficient Kältemaschinen can significantly reduce operating costs and environmental impact. Several factors contribute to chiller operational efficiency, including the type of compressor, the condenser design, and the use of advanced control systems.
Water-cooled chillers are often more energy-efficient than luftgekühlt models because water is a more effective heat transfer medium than air. The use of water from a cooling tower allows for more efficient heat dissipation, especially in hot climates. Additionally, modern Kältemaschinen are designed with features such as variable-speed drives and intelligent controls that optimize performance based on real-time Kühlung demands.
Our manufacturing plant produces high-quality Kältemaschinen that incorporate the latest energy-saving technologies. For example, the Air Cooled Screw Chiller features advanced compressor technology and precise temperature control, resulting in significant energy savings for our customers.
6. Why is Chiller Maintenance Crucial?
Regelmäßig chiller maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of your chiller system. Proper maintenance can prevent unexpected breakdowns, reduce energy consumption, and extend the lifespan of your equipment. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning: Regularly cleaning the condenser und evaporator coils to remove dirt and debris that can reduce efficiency.
- Checking Refrigerant Levels: Ensuring that the refrigerant charge is correct and there are no leaks in the system.
- Inspecting Electrical Connections: Checking for loose or damaged connections that can cause malfunctions.
- Monitoring Water Quality: For wassergekühlte Kältemaschinen, maintaining the water quality in the cooling tower to prevent scaling and corrosion.
Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced performance, increased energy costs, and costly repairs. For instance, a buildup of scale in the condenser can significantly reduce heat transfer efficiency, forcing the chiller to work harder and consume more energy.
7. What are the Different Applications of Industrial Chillers?
Industrielle Kältemaschinen are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Their primary function is to provide precise temperature control for processes and equipment. Here are some examples:
- Plastics and Rubber Industry: Chillers cool molds and machinery used in injection molding, blow molding, and extrusion processes. This ensures the quality and consistency of plastic and rubber products. Industrial Chillers For Textile Industry is designed to meet the specific cooling needs of textile manufacturing.
- Machining Industry: Chillers provide Kühlung for cutting fluids and machine tools, maintaining precision and extending tool life.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Chillers are used for process Kühlung in brewing, winemaking, dairy processing, and food storage. For example, Dairy Milk Chillers ensure that milk is cooled quickly and efficiently to maintain freshness.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industry: Temperature control is critical in chemical reactions, crystallization processes, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Chillers maintain the required temperatures for these sensitive processes.
- Electronics Industry: Chillers cool down electronic components and systems, preventing overheating and ensuring reliable performance.
- Data Centers: Large data centers generate significant amounts of heat. Chillers are essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing equipment failure.
8. How Do You Choose the Right Chiller for Your Needs?
Selecting the right chiller for your application is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. Several factors should be considered when choosing a chiller:
- Kühlleistung: Determine the Kühlung load required for your application. This will depend on the amount of heat that needs to be removed and the desired temperature.
- Type of Chiller: Decide between an luftgekühlt or water-cooled chiller based on factors such as water availability, ambient temperature, and installation requirements.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for Kältemaschinen with high energy efficiency ratings to reduce operating costs. Consider features such as variable-speed drives and intelligent controls.
- Maintenance Requirements: Evaluate the maintenance needs of the chiller. Air-cooled chillers generally require less maintenance than wassergekühlt models.
- Application-Specific Needs: Consider any unique requirements of your application. For example, if you need precise temperature control, look for Kältemaschinen with advanced control systems.
Our team of experts can help you choose the right chiller for your needs. We offer a wide range of Kältemaschinen, including the Air Cooled Scroll Water Chiller, designed to meet the specific requirements of various industries.
9. What are the Latest Advancements in Chiller Technology?
Chiller technology has evolved significantly in recent years, with a focus on improving energy efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing performance. Some of the latest advancements include:
- Variable-Speed Drives: These drives adjust the speed of the compressor based on the Kühlung demand, resulting in significant energy savings.
- Intelligent Controls: Advanced control systems monitor and optimize chiller performance in real time, ensuring efficient operation and precise temperature control.
- Low-GWP Refrigerants: Many new Kältemaschinen use refrigerants with low global warming potential (GWP), reducing their environmental impact.
- Magnetic Bearing Compressors: These compressors use magnetic bearings instead of traditional oil bearings, reducing friction and improving efficiency.
- Hybrid Systems: Some Kältemaschinen combine luftgekühlt und wassergekühlt technologies to optimize performance in different conditions.
These advancements have led to the development of highly efficient chillers that offer significant benefits to users. For example, the Anti-Explosion Chillers are designed to provide safe and reliable Kühlung in hazardous environments.
10. What is the Role of Chillers in Commercial HVAC Systems?
Chillers are a critical component of commercial HVAC systems, providing Kühlung for large buildings and facilities. HVAC chillers are typically used in conjunction with air handlers to circulate cool air throughout a building. The chilled water produced by the chiller is pumped through coils in the air handlers, where air is blown across the coils and cooled before being distributed to various parts of the building.
In large commercial buildings, Kältemaschinen are often part of a centralized HVAC system that provides Kühlung to multiple zones or floors. These systems are designed to provide efficient and reliable Kühlung while minimizing energy consumption. Modern HVAC chillers incorporate advanced features such as variable-speed drives, intelligent controls, and energy recovery systems to optimize performance and reduce operating costs. HVAC Chillers are specifically designed to meet the demanding cooling needs of commercial buildings.
FAQs
What is the difference between an air-cooled chiller and a water-cooled chiller?
Air-cooled chillers use ambient air to remove heat from the refrigerant, while wassergekühlte Kältemaschinen use water from a cooling tower or other water source. Water-cooled chillers are generally more energy-efficient, especially in high-temperature environments.
How often should a chiller be serviced?
A chiller should be serviced at least once a year to ensure optimal performance and prevent unexpected breakdowns. Regular maintenance tasks include cleaning coils, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting electrical connections.
What is the role of a compressor in a chiller?
Die compressor is the heart of the chiller. It pressurizes the refrigerant gas, raising its temperature and pressure, which is the first step in the refrigeration cycle.
Why is energy efficiency important in chillers?
Energy efficiency is important in Kältemaschinen because it can significantly reduce operating costs and environmental impact. Efficient Kältemaschinen use less energy to provide the same level of Kühlung, resulting in lower utility bills and reduced carbon emissions.
What type of industries use industrial chillers?
Industrielle Kältemaschinen are used in a wide range of industries, including plastics and rubber, machining, food and beverage, chemical and pharmaceutical, electronics, laser, printing, medical, laboratories, and data centers.
What is chilled water?
Chilled water is the water that has been cooled by a chiller and is used to absorb heat from a process or building. It is typically circulated through a closed-loop system, where it absorbs heat and is then returned to the chiller to be cooled again.
Conclusion
Here are the most important things to remember about Kältesysteme:
- Chillers are essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in various industrial and commercial settings.
- There are two main types of chillers: luftgekühlt und wassergekühlt, each with its advantages and suitable for different applications.
- The main components of a chiller are the compressor, condenser, expansion valveund evaporator.
- Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration in the design and operation of Kältesysteme.
- Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of your chiller system.
- Industrielle Kältemaschinen are used in a wide range of applications, including plastics and rubber, machining, food and beverage, chemical and pharmaceutical, electronics, laser, printing, medical, laboratories, and data centers.
- Choosing the right chiller for your needs requires careful consideration of factors such as Kühlung capacity, type of chiller, energy efficiency, maintenance requirements, and application-specific needs.
- The latest advancements in chiller technology include variable-speed drives, intelligent controls, low-GWP refrigerants, magnetic bearing compressors, and hybrid systems.
- Chillers play a critical role in commercial HVAC systems, providing Kühlung for large buildings and facilities.
By understanding the principles of chiller operation, the different types of chillers available, and the importance of energy efficiency and maintenance, you can make informed decisions that enhance your operations and contribute to a sustainable future. As a leading industrial water chiller manufacturing plant, we are committed to providing high-quality Kältemaschinen that meet the diverse needs of our customers. Our expertise and experience in the field ensure that we deliver reliable and efficient Kühlung solutions for a wide range of applications. Contact us today to learn more about how our Kältesysteme can benefit your business.