-
Dalingshan Industriel Guangdong

Tour de refroidissement et refroidisseur – comment fonctionnent ensemble les tours de refroidissement et les refroidisseurs
Tour de refroidissement et refroidisseur : comment refroidir vos processus industriels
Cet article explique comment tours de refroidissement et refroidisseurs travailler ensemble pour fournir refroidissement efficace pour les processus industriels, de la fabrication de plastiques aux centres de données. Nous explorerons les mécanismes de chaque système, leurs avantages et pourquoi la compréhension de leur synergie est essentielle pour optimiser vos opérations et réduire les coûts. Que vous travailliez dans l'industrie agroalimentaire ou que vous dirigiez un laboratoire, ce guide vous éclairera sur l'importance de ces refroidissement technologies et pourquoi faire les bons choix peut avoir un impact significatif sur vos résultats.
Table des matières
1. Qu’est-ce qu’une tour de refroidissement et comment fonctionne-t-elle ?
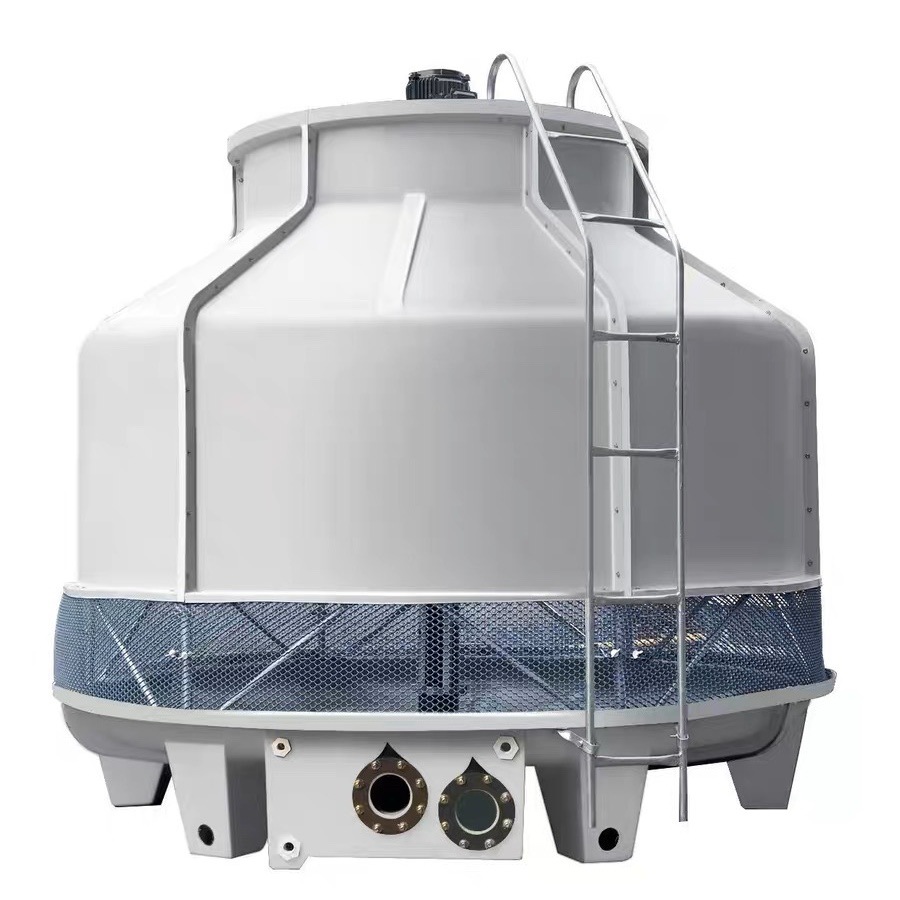
En tant qu'industriel refroidisseur d'eau usine de fabrication, nous comprenons le rôle critique tours de refroidissement jouer dans diverses industries. tour de refroidissement est essentiellement un dispositif de rejet de chaleur. élimine la chaleur provenant de l’eau utilisée dans les procédés industriels. Tours de refroidissement sont généralement utilisés lorsque de grandes quantités de refroidissement sont nécessaires, comme dans les centrales électriques, le traitement chimique et les systèmes CVC à grande échelle. Ils fonctionnent en apportant eau et l'air en contact. eau est pulvérisé dans le tour tandis que l'air est forcé ou aspiré à travers lui. Cette interaction provoque une partie de la eau s'évaporer, efficacement refroidissement le reste eau.
Le principe de base derrière tours de refroidissement est refroidissement par évaporation. Comme eau s'évapore, il absorbe la chaleur de l'environnement eau, abaissant ainsi sa température. eau refroidie est ensuite collecté à la bas de la tour et recyclé dans le processus industriel. L'air chaud et humide est libéré de la sommet de la tour. Je l'explique souvent à mes clients de cette façon : imaginez la sensation que vous ressentez lorsque vous sortez d'une piscine par un jour venteux - ce froid que vous ressentez est refroidissement par évaporation en action. Tours de refroidissement exploiter ce processus naturel à l'échelle industrielle pour fournir des services fiables et refroidissement efficace.
2. Qu’est-ce qu’un refroidisseur et en quoi diffère-t-il d’une tour de refroidissement ?
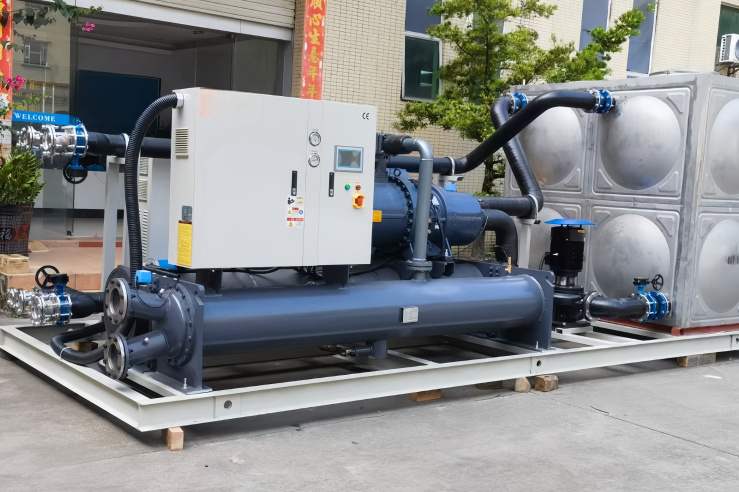
Refroidisseurs sont un autre élément crucial de l'industrie systèmes de refroidissement. Contrairement à tours de refroidissement que eau fraîche par évaporation, refroidisseurs utiliser un cycle de réfrigération pour cool un fluide, généralement eau ou un eau/glycol mélange. Ceci eau glacée est ensuite diffusé à enlever la chaleur provenant d'équipements ou de processus. Il existe deux principaux types de refroidisseurs: refroidi par air et refroidi par eau. Refroidisseurs à air utiliser l'air ambiant pour enlever la chaleur du réfrigérant, tandis que refroidisseurs à eau utiliser eau d'un tour de refroidissement ou une autre source.
La principale différence entre un refroidisseur et un tour de refroidissement est leur fonction. tour de refroidissement rejette la chaleur dans l'atmosphère, tandis qu'un refroidisseur activement refroidit un fluide à une température spécifique. Refroidisseurs sont généralement moins efficace que les tours de refroidissement en termes de consommation d'énergie, mais ils offrent un contrôle précis de la température. Par exemple, dans l'industrie du plastique, refroidisseurs sont essentiels pour refroidissement moules et produits extrudés pour maintenir la qualité du produit et la vitesse de production. Dans l'industrie médicale, refroidisseurs sont utilisés pour refroidir les machines d'IRM.
3. Comment les tours de refroidissement et les refroidisseurs fonctionnent-ils ensemble dans un environnement industriel ?
Dans de nombreuses applications industrielles, tours de refroidissement et refroidisseurs travailler en tandem pour créer un environnement hautement refroidissement efficace système. Tours de refroidissement sont généralement utilisés en conjonction avec refroidisseurs à eau. Dans cette configuration, le refroidisseur refroidit le processus eau, et le chaleur absorbé par le refroidisseur est transféré à la eau du condenseur. Ce eau du condenseur c'est alors envoyé à la tour de refroidissement, où le chaleur est dissipée dans l'atmosphère par évaporation. eau refroidie de la tour de refroidissement est ensuite renvoyé à la condenseur du refroidisseur, complétant le cycle.
En utilisant refroidisseurs et tours de refroidissement ensemble permet une plus grande efficacité du refroidissement par rapport à l'utilisation de l'un ou l'autre système seul. Par exemple, il est possible de combiner un refroidisseur plus petit avec un tour de refroidissement plus petite pour atteindre le même objectif refroidissement capacité en tant que plus grande refroidisseur fonctionnant de manière indépendante. Cela peut conduire à des économies d'énergie importantes et à des coûts d'exploitation réduits. Je conseille souvent aux clients de considérer leur avenir à long terme besoins de refroidissement lors de la conception de leur systèmes de refroidissementUn système bien intégré peut offrir des avantages substantiels tout au long de sa durée de vie.
4. Quels sont les différents types de tours de refroidissement ?
Tours de refroidissement sont disponibles dans différents modèles, chacun avec ses propres avantages et inconvénients. Le principal types de tours de refroidissement sont tirage naturel et projet mécanique. Tours de refroidissement à tirage naturel s'appuient sur la convection naturelle de l'air pour cool le eauIl s'agit généralement de structures hautes et hyperboliques qui créent un effet de cheminée, attirant l'air à travers la tour. Tours de refroidissement à tirage mécanique, d'autre part, utiliser des ventilateurs pour forcer ou induire air couler à travers le tour.
Tours de refroidissement à tirage mécanique sont en outre divisés en forcés brouillon et induit brouillon types. Forcé tours de refroidissement à tirage avoir des fans en bas de la tour cette poussée air vers le haut, tandis qu'induit tours de refroidissement à tirage avoir des fans au sommet qui tirent air à travers le tour. Choisir le bon type de tour de refroidissement dépend de facteurs tels que la quantité de refroidissement requis, l'espace disponible et le budget. Par exemple, tours de refroidissement à tirage naturel sont plus économes en énergie mais nécessitent une plus grande empreinte au sol et sont plus coûteuses à construire.
5. Quels sont les différents types de refroidisseurs ?
Refroidisseurs sont classés principalement selon la méthode qu'ils utilisent pour dissiper chaleur: refroidi par air ou refroidi par eau. Refroidisseurs à air utiliser des ventilateurs pour souffler l'air ambiant air à travers un serpentin de condenseur, élimination de la chaleur du réfrigérant. Ils sont plus simples à installer et à entretenir que refroidisseurs à eau mais sont généralement moins efficace, surtout dans les climats chauds. Je recommande souvent refroidisseurs à air pour des applications plus petites ou lorsque eau la disponibilité est limitée. Refroidisseurs à eau utiliser eau à enlever la chaleur du réfrigérant. Ils nécessitent une connexion à un tour de refroidissement ou une autre source de eau fraîche. Refroidisseurs à eau sont plus efficace que refroidisseurs à air et sont souvent préférés pour des applications plus importantes ou lorsque le contrôle précis de la température est essentiel.

Au sein de ces deux catégories principales, il existe également différentes types de refroidisseurs en fonction de la technologie du compresseur utilisé, comme à spirale, à vis et centrifuge refroidisseurs. Chaque type a ses propres avantages en termes d'efficacité, de capacité et de coût. Par exemple, refroidisseurs à spirale sont connus pour leur fiabilité et leur fonctionnement silencieux, tandis que les vis refroidisseurs offrent un rendement élevé dans des conditions de pleine charge. J'encourage toujours les clients à examiner attentivement les exigences spécifiques de leur application lors choisir un refroidisseur.
6. Quels facteurs devez-vous prendre en compte lors du choix entre un refroidisseur et une tour de refroidissement ?
Décider d'utiliser ou non un refroidisseur, un tour de refroidissement, ou les deux dépendent de plusieurs facteurs. L'un des facteurs clés à prendre en compte est le quantité de refroidissement requis. Tours de refroidissement sont généralement plus efficaces pour les projets à grande échelle refroidissement, alors que refroidisseurs sont mieux adaptés aux applications nécessitant un contrôle précis de la température. Un autre facteur est la disponibilité et le coût des eau. Tours de refroidissement utiliser de l'eau pour évaporation refroidissement, ils peuvent donc ne pas être adaptés aux emplacements avec une capacité limitée eau ressources. Refroidisseurs à air peut être une alternative dans de tels cas.
Le climat ambiant joue également un rôle. Tours de refroidissement sont plus efficaces dans les zones à faible humidité, où refroidissement par évaporation est plus efficace. Refroidisseurs à air sont moins efficace dans les climats chauds. Si vous voulez utiliser des refroidisseurs et des tours de refroidissement ensemble, considérons la efficacité des tours de refroidissement. Plus le efficacité des tours de refroidissement, plus le refroidisseur vous pouvez utiliser, ce qui entraîne des coûts d'exploitation inférieurs. Il est également important de se rappeler que tours de refroidissement doit toujours être dimensionné de manière appropriée pour le refroidisseur ils sont jumelés avec.
7. Comment le débit d’eau affecte-t-il l’efficacité des tours de refroidissement et des refroidisseurs ?
Débit d'eau est un facteur critique dans la performance des deux tours de refroidissement et refroidisseurs. Dans tours de refroidissement, le taux de débit d'eau affecte le temps de contact entre eau et air, ce qui à son tour influence le taux d'évaporation et refroidissement. Un optimal débit d'eau le taux assure un maximum refroidissement efficacité. De même, dans refroidisseurs à eau, le débit d'eau le taux à travers le condenseur affecte la chaleur taux de transfert entre le réfrigérant et le eau. Un niveau inférieur débit d'eau le taux peut conduire à une réduction refroidisseur capacité et efficacité.
Maintenir le bon débit d'eau Le taux de rafraîchissement est essentiel à la fois pour l'efficacité énergétique et la longévité des équipements. J'ai vu des cas où le taux de rafraîchissement était insuffisant. débit d'eau conduit à une défaillance prématurée de l'équipement et à des réparations coûteuses. La surveillance et l'entretien réguliers des pompes, des tuyaux et des vannes sont essentiels pour garantir un fonctionnement correct débit d'eauEn règle générale, je conseille toujours aux clients de suivre les recommandations du fabricant pour débit d'eau tarifs et d'installer des débitmètres pour un suivi précis.
8. Quel rôle joue le refroidissement par évaporation dans les tours de refroidissement ?
Refroidissement par évaporation est le principe fondamental du fonctionnement de tours de refroidissement. Comme eau s'évapore, il absorbe chaleur du reste eau, provoquant une baisse de sa température. Le taux d'évaporation, et donc la refroidissement L'effet dépend de plusieurs facteurs, notamment la température de l'air, l'humidité et eau superficie. Tours de refroidissement sont conçus pour maximiser refroidissement par évaporation en créant une grande surface pour eau–air contact. Ceci est généralement réalisé en pulvérisant le eau sur un matériau de remplissage qui le brise en petites gouttelettes, augmentant la surface exposée à la air.
L'efficacité de refroidissement par évaporation est influencé par l'humidité relative de l'air air. Dans les climats secs, refroidissement par évaporation est très efficace car eau s'évapore plus facilement. Dans les climats humides, le air est déjà saturé d'humidité, donc l'évaporation est plus lente et la refroidissement l'effet est réduit. Par exemple, un tour de refroidissement en Arizona sera probablement plus efficace qu'en Floride en raison de l'humidité plus faible en Arizona.
9. Comment pouvez-vous optimiser votre système de refroidissement pour une efficacité maximale ?
Optimiser votre refroidissement système, qu'il s'agisse d'un refroidisseur, un tour de refroidissement, ou les deux, peuvent conduire à des économies d'énergie et de coûts importantes. Une stratégie clé consiste à garantir un dimensionnement approprié de l'équipement. Un équipement surdimensionné refroidisseur ou tour de refroidissement consommera plus d'énergie que nécessaire, tandis qu'une unité sous-dimensionnée peut ne pas fournir suffisamment d'énergie. refroidissement. Choisir le bon type de refroidisseur est également crucial. Par exemple, combiner une grande refroidisseur avec un tour de refroidissement peut être plus efficace que l'utilisation d'un refroidisseur à air seul dans de nombreuses applications.
Une autre stratégie d’optimisation consiste à intégrer les refroidisseur et tour de refroidissement contrôles. Cela permet aux deux systèmes de fonctionner ensemble de manière transparente, en ajustant leur fonctionnement en fonction de la refroidissement charge et les conditions ambiantes. Par exemple, lorsque le refroidissement la charge est faible, le refroidisseur peut réduire sa production, et la tour de refroidissement Les ventilateurs peuvent ralentir, ce qui permet d'économiser de l'énergie. Un entretien régulier est également essentiel pour des performances optimales. Cela comprend le nettoyage du tour de refroidissement remplir, vérifier eau qualité et assurer une charge de réfrigérant appropriée dans le refroidisseur. J'insiste toujours auprès de mes clients sur l'importance d'un plan de maintenance proactif. Il est beaucoup plus rentable de prévenir les problèmes que de les résoudre une fois qu'ils se sont produits.
10. Pourquoi un entretien régulier est-il essentiel pour les tours de refroidissement et les refroidisseurs ?
Un entretien régulier est essentiel pour garantir la fiabilité et l'efficacité à long terme de tours de refroidissement et refroidisseurs. Entretien des tours de refroidissement implique généralement le nettoyage du matériau de remplissage pour éliminer le tartre et les débris, l'inspection et le nettoyage du eau système de distribution et vérification du fonctionnement des ventilateurs et des moteurs. Entretien du refroidisseur comprend la vérification des niveaux de réfrigérant, l'inspection et le nettoyage des serpentins du condenseur et de l'évaporateur, ainsi que le test des contrôles de sécurité. Négliger l'entretien peut entraîner une réduction refroidissement capacité, augmentation de la consommation d'énergie et même défaillance de l'équipement. Par exemple, l'accumulation de tartre dans un tour de refroidissement peut réduire considérablement son refroidissement efficacité.
D'après mon expérience, un bien entretenu refroidissement Le système peut durer de nombreuses années, offrant une fiabilité et refroidissement efficace. À l’inverse, un système mal entretenu peut être une source constante de problèmes et de dépenses. tour de refroidissement accumulera de la saleté, des débris et d'autres contaminants au fil du temps. Un nettoyage et un traitement de l'eau réguliers peuvent éviter ces problèmes. tour de refroidissement ou refroidisseur entretien, je recommande toujours de suivre les directives du fabricant et de travailler avec des techniciens expérimentés.
FAQ
Quelle est la principale différence entre une tour de refroidissement et un refroidisseur ?
La principale différence est qu'un tour de refroidissement rejette chaleur à l'atmosphère à travers refroidissement par évaporation, tandis qu'un refroidisseur activement refroidit un fluide utilisant un cycle de réfrigération. Tours de refroidissement sont généralement plus efficaces pour les projets à grande échelle refroidissement, alors que refroidisseurs offrent un contrôle précis de la température.
Quand dois-je utiliser une tour de refroidissement plutôt qu’un refroidisseur à air ?
Vous devriez envisager d'utiliser un tour de refroidissement quand vous avez besoin de grandes quantités de refroidissement et avoir accès à un service fiable eau source. Tours de refroidissement sont généralement plus économes en énergie que refroidisseurs à air, surtout dans les climats secs. Si eau la disponibilité est limitée ou le contrôle précis de la température n'est pas critique, un refroidisseur à air peut-être une meilleure option.
À quelle fréquence dois-je nettoyer ma tour de refroidissement ?
La fréquence de tour de refroidissement le nettoyage dépend de facteurs tels que eau la qualité, les conditions de fonctionnement et la type de tour de refroidissement vous utilisez. En règle générale, il est recommandé d'inspecter et de nettoyer votre tour de refroidissement au moins une fois par an. Cependant, dans certains cas, un nettoyage plus fréquent peut être nécessaire.
Puis-je utiliser une tour de refroidissement portable avec mon refroidisseur ?
Oui, vous pouvez utiliser un tour de refroidissement portable avec un refroidisseur, en particulier dans les situations où une tour de refroidissement n'est pas réalisable ou rentable. En combinant un refroidisseur à air avec un tour de refroidissement portable, assurez-vous que le tour de refroidissement est correctement dimensionné pour le refroidisseurs capacité. En utilisant un refroidisseur avec un tour de refroidissement portable peut améliorer l'efficacité et réduire les coûts d'exploitation par rapport à l'utilisation d'un refroidisseur à air seul.
Quels sont les avantages de l’utilisation d’un refroidisseur à eau avec une tour de refroidissement ?
En utilisant un refroidisseur à eau avec un tour de refroidissement offre plusieurs avantages, notamment une meilleure efficacité énergétique, des coûts d'exploitation inférieurs et un fonctionnement plus silencieux par rapport à refroidisseurs à air. Refroidisseurs à eau sont particulièrement bien adaptés aux applications de grande taille et où un contrôle précis de la température est nécessaire.
Existe-t-il une application pour les refroidisseurs anti-explosion ?
Oui, refroidisseurs anti-explosion sont utilisés dans des environnements dangereux où des gaz, des vapeurs ou des poussières inflammables peuvent être présents. Les industries telles que le pétrole et le gaz, le traitement chimique et les produits pharmaceutiques nécessitent souvent des équipements spécialisés refroidisseurs conçu pour empêcher les sources d'inflammation.
Principaux points à retenir
- Tours de refroidissement et refroidisseurs sont des composants essentiels de l'industrie systèmes de refroidissement.
- Tours de refroidissement rejeter chaleur à travers refroidissement par évaporation, alors que refroidisseurs activement cool un fluide utilisant la réfrigération.
- Tours de refroidissement et refroidisseurs peuvent travailler ensemble pour créer des refroidissement efficace solutions.
- Le choix entre un tour de refroidissement, un refroidisseur, ou les deux dépendent de facteurs tels que refroidissement charger, eau exigences en matière de disponibilité, de climat et de contrôle de la température.
- Un dimensionnement, une intégration et une maintenance appropriés sont essentiels pour optimiser les performances et l'efficacité de refroidissement systèmes.
- Différent types de tours de refroidissement et refroidisseurs sont disponibles, chacun avec ses propres avantages et inconvénients.
- Un entretien régulier est essentiel pour garantir la fiabilité et l'efficacité à long terme des deux tours de refroidissement et refroidisseurs.
- Comprendre les principes de refroidissement par évaporation et débit d'eau est la clé pour optimiser refroidissement performances du système.
- Intégration refroidisseur et tour de refroidissement les contrôles peuvent conduire à des économies d’énergie importantes.
J'espère que ce guide complet vous aura fourni des informations précieuses sur le monde de tours de refroidissement et refroidisseursEn tant qu'industriel refroidisseur d'eau usine de fabrication, nous nous engageons à aider nos clients à trouver la solution la plus efficace et la plus refroidissement efficace des solutions adaptées à leurs besoins spécifiques. Si vous avez d'autres questions ou si vous souhaitez discuter de vos refroidissement exigences plus en détail, n'hésitez pas à Contactez-nousNous sommes toujours là pour vous aider !